ASTM D2625-94(2015)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Endurance (Wear) Life and Load-Carrying Capacity of Solid Film Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Method)
Standard Test Method for Endurance (Wear) Life and Load-Carrying Capacity of Solid Film Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Method)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method differentiates between bonded solid lubricants with respect to their wear life and load-carrying capacity. If the test conditions are changed, wear life may change and relative ratings of the bonded solid film lubricants may be different.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method (see Note 1) covers the determination of the endurance (wear) life and load-carrying capacity of dry solid film lubricants in sliding steel-on-steel applications.
Note 1: Reference may be made to Coordinating Research Council, Inc. (CRC) Report No. 419, “Development of Research Technique for Measuring Wear Life of Bonded Solid Lubricant Coatings for Airframes, Using the Falex Tester.” See also Military Specification MIL-L-8937 (ASG), Jan. 22, 1963, and Methods 3807 and 3812 of Federal Test Method 791a.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard except where equipment is supplied using inch-pound units and would then be regarded as standard. The metric equivalents of inch-pound units given in such cases in the body of the standard may be approximate.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2625 − 94 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Endurance (Wear) Life and Load-Carrying Capacity of Solid
1
Film Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2625; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope MIL-P-16232FPhosphate Coatings, Heavy, Manganese or
Zinc Base (for Ferrous Metals)
1.1 This test method (see Note 1) covers the determination
4
2.3 Other Standards:
of the endurance (wear) life and load-carrying capacity of dry
42USC7671aClean Air Act Amendments of 1990
solid film lubricants in sliding steel-on-steel applications.
Federal Test Method 791aMethods3807 and3812
NOTE 1—Reference may be made to Coordinating Research Council,
Inc. (CRC) Report No. 419, “Development of Research Technique for
3. Terminology
Measuring Wear Life of Bonded Solid Lubricant Coatings forAirframes,
3.1 Definitions:
Using the Falex Tester.” See also Military Specification MIL-L-8937
(ASG), Jan. 22, 1963, and Methods3807 and3812 of Federal Test
3.1.1 dry solid film lubricants—dry coatings consisting of
Method 791a.
lubricating powders in a solid matrix bonded to one or both
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the surfaces to be lubricated.
standardexceptwhereequipmentissuppliedusinginch-pound
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
units and would then be regarded as standard. The metric
3.2.1 direct load, n—theloadthatisappliedlinearly,bisect-
equivalentsofinch-poundunitsgiveninsuchcasesinthebody
ing the angle of the vee block corrected to either the 800lbf
of the standard may be approximate.
(3550N) gauge reference or the 3000lbf (13300N) gauge
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
reference.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 3.2.1.1 Discussion—This load is equivalent to the true load
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
times the cos 42°.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.2.2 endurance (wear) life—the length of test time before
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
failure under a constant loaded condition, in minutes, in which
the applied test lubricant performs its function.
2. Referenced Documents
3.2.3 gauge load, n—the value obtained from the gauge
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
while running the test after being corrected to the standard
B16/B16MSpecification for Free-Cutting Brass Rod, Bar
curve using the calibration procedure for the 4500 lbf
and Shapes for Use in Screw Machines
(20000N) reference gauge.
F22Test Method for Hydrophobic Surface Films by the
3.2.3.1 Discussion—Thegaugereadingisirrespectiveofthe
Water-Break Test
particulargaugeused,andcorrectionsaremadebycomparison
3
2.2 U.S. Military Specifications:
totheBrinellballimpressiondiametersonastandardreference
MIL-L-8937
copper test coupon with a Rockwell hardness range of HB37
5
to HB39. An electronic calibration instrument is available
1 which can be used in place of the copper coupon.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.L0.05 on Solid Lubricants.
4
CurrenteditionapprovedJuly1,2015.PublishedJuly2015.Originallyapproved AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D2625–94 (2010). DOI: 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
10.1520/D2625-94R15. www.access.gpo.gov.
2 5
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Trademark of and available from Falex Corp., 1020Airpark Dr., Sugar Grove,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM IL 60554. A new model of the Falex Pin and Vee Block Test Machine has been
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on available since 1983. Certain operating procedures are different for this new model.
the ASTM website. Consult instruction manual of machine for this information. If you are aware of
3
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http:// Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
1
dodssp.daps.dla.mil. responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Ha
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D2625 − 94 (Reapproved 2010) D2625 − 94 (Reapproved 2015)
Standard Test Method for
Endurance (Wear) Life and Load-Carrying Capacity of Solid
1
Film Lubricants (Falex Pin and Vee Method)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2625; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method (see Note 1) covers the determination of the endurance (wear) life and load-carrying capacity of dry solid
film lubricants in sliding steel-on-steel applications.
NOTE 1—Reference may be made to Coordinating Research Council, Inc. (CRC) Report No. 419, “Development of Research Technique for Measuring
Wear Life of Bonded Solid Lubricant Coatings for Airframes, Using the Falex Tester.” See also Military Specification MIL-L-8937 (ASG), Jan. 22, 1963,
and Methods 3807 and 3812 of Federal Test Method 791a.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard except where equipment is supplied using inch-pound units
and would then be regarded as standard. The metric equivalents of inch-pound units given in such cases in the body of the standard
may be approximate.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B16/B16M Specification for Free-Cutting Brass Rod, Bar and Shapes for Use in Screw Machines
F22 Test Method for Hydrophobic Surface Films by the Water-Break Test
3
2.2 U.S. Military Specifications:
MIL-L-8937
MIL-P-16232F Phosphate Coatings, Heavy, Manganese or Zinc Base (for Ferrous Metals)
4
2.3 Other Standards:
42USC7671a Clean Air Act Amendments of 1990
Federal Test Method 791a Methods 3807 and 3812
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 dry solid film lubricants—dry coatings consisting of lubricating powders in a solid matrix bonded to one or both surfaces
to be lubricated.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 direct load, n—the load that is applied linearly, bisecting the angle of the vee block corrected to either the 800-lbf
(3550-N)800 lbf (3550 N) gauge reference or the 3000-lbf (13 300-N)3000 lbf (13 300 N) gauge reference.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee D02.L0.05 on Solid Lubricants.
Current edition approved March 1, 2010July 1, 2015. Published April 2010July 2015. Originally approved in 1967. Last previous edition approved in 20032010 as
D2625–94(2003).D2625 – 94 (2010). DOI: 10.1520/D2625-94R10.10.1520/D2625-94R15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Standardization Documents Order Desk, DODSSP, Bldg. 4, Section D, 700 Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5098, http://dodssp.daps.dla.mil.
4
Available from U.S. Government Printing Office Superintendent of Documents, 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
www.access.gpo.gov.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2625 − 94 (2015)
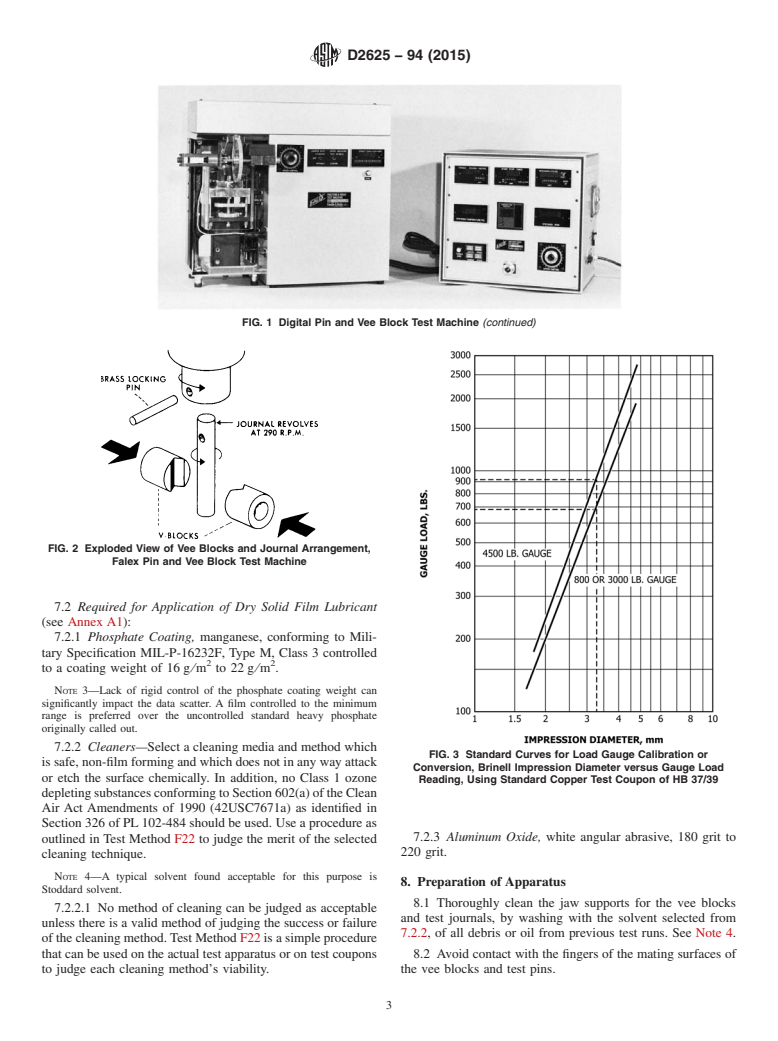
FIG. 1 Schematic Diagram of Falex Pin and Vee Block Test Machine
3.2.1.1 Discussion—
This load is equivalent to the true load times the cos 42°.
3.2.2 endurance (wear) life—the length of test time before failure under a constant loaded condition, in minutes, in which the
applied test lubricant performs its function.
3.2.3 gauge load, n—the value obtained from the gauge while running the test after being corrected to the standard curve using
the calibration procedure for the 4500-lbf (20 000-N)4500 lbf (20 000 N) reference gauge.
3.2.3.1 Discussion—
The gauge reading is irrespective of the particular gauge used, and corrections are made by comparison to the Brinell ball
impression diame
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.