ASTM D6973-08
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a High Pressure Constant Volume Vane Pump
Standard Test Method for Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum Hydraulic Fluids in a High Pressure Constant Volume Vane Pump
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is an indicator of the wear characteristics of petroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a constant volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical industrial or mobile hydraulic applications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume high-pressure vane pump test procedure for indicating the wear characteristics of petroleum hydraulic fluids. See Annex A1 for recommended testing conditions for water-based synthetic fluids.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
An American National Standard
Designation:D6973–08
Standard Test Method for
Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum Hydraulic
1
Fluids in a High Pressure Constant Volume Vane Pump
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6973; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2.3 Other Documents:
4
SAE 100R13–20 Hydraulic Hose Specification
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume high-
ANSI/(NFPA) T2.13.1 R3-1998 Recommended Practice—
pressure vane pump test procedure for indicating the wear
Hydraulic Fluid Power—Use of Fire-Resistant Fluids in
characteristics of petroleum hydraulic fluids. SeeAnnexA1 for
5
Industrial Systems
recommended testing conditions for water-based synthetic
fluids.
3. Terminology
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
3.1.1 flushing, v—the process of cleaning the test system
only.
before testing to prevent cross-contamination.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 Hydraulic fluid in the amount of 190 6 4 L(50 6 1 gal)
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
is circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 50 h at a
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
pump speed of 2400 6 20 r/min and a pump outlet pressure of
20.7 6 0.2 MPa (3000 6 20 psig). Fluid temperature at the
2. Referenced Documents
2
pump inlet is 95 6 3°C (203 6 5°F).An ISO Grade 32 or 10W
2.1 ASTM Standards:
viscosity is required.
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
4.2 The cam ring and all ten vanes should be individually
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3 weighed before and after the test. The weight loss of the cam
2.2 ISO Standards:
ring should be reported with the combined weight loss of all
ISO 4021 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Particulate Contamina-
ten vanes. The intra-vanes (inserts) are not part of the required
tionAnalysis—Extraction of Fluid Samples from Lines of
weight loss measurements and should be separately measured
an Operating System
if desired. Other reported values are fluid cleanliness before
ISO 4406 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Fluids—Method for
and after the test, initial flow rate, and final flow rate.
Coding the Level of Contamination by Solids Particles
4.3 Prior to installing the hydraulic test fluid into the rig, a
ISO 7745 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Fire-Resistant (FR)
stand flush is required to remove any contaminants. A mini-
Fluids—Guidelines for Use
mum quantity of 190 6 4 L (50 6 1 gal) of fluid (see Note 1)
ISO 11171 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Calibration of Auto-
made of the same chemical formulation as the test fluid, is
matic Particle Counters for Liquids
required for the stand flush. Therefore the total quantity of oil
ISO 11500 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Determination of Par-
required for the test is 380 L (100 gal).
ticulate Contamination by Automatic Counting Using the
Light Extinction Principle
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method is an indicator of the wear character-
istics of petroleum hydraulic fluids operating in a constant
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
volume vane pump. Excessive wear in vane pumps could lead
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
to malfunction of hydraulic systems in critical industrial or
D02.N0.07 on Lubricating Properties.
mobile hydraulic applications.
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2008. Published March 2008. Originally
approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D 6973–05.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth
the ASTM website. Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
3 5
Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036. 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6973–08
Description of Components:
1 Reservoir (50 gal of oil; elevated abov
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard
Designation:D6973–05 Designation:D6973–08
Standard Test Method for
Indicating Wear Characteristics of Petroleum Hydraulic
1
Fluids in a High Pressure Constant Volume Vane Pump
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6973; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers a constant volume high-pressure vane pump test procedure for indicating the wear characteristics
of petroleum hydraulic fluids. See Annex A1 for recommended testing conditions for water-based synthetic fluids.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ISO Standards:ASTM Standards:
E 691 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Testing
3
2.2 ISO Standards:
ISO 4021 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Particulate Contamination Analysis—Extraction of Fluid Samples from Lines of an
Operating System
ISO 4406 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Fluids—Method for Coding the Level of Contamination by Solids Particles
ISO 7745 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Fire-Resistant (FR) Fluids—Guidelines for Use
ISO 11171 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Calibration of Automatic Particle Counters for Liquids
ISO 11500 Hydraulic Fluid Power—Determination of Particulate Contamination by Automatic Counting Using the Light
Extinction Principle
2.2
2.3 Other Documents:
4
SAE 100R13–20 Hydraulic Hose Specification
ANSI/(NFPA) T2.13.1 R3-1998 Recommended Practice—Hydraulic Fluid Power—Use of Fire-Resistant Fluids in Industrial
5
Systems
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 flushing, v—the process of cleaning the test system before testing to prevent cross-contamination.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Hydraulic fluid in the amount of 190 6 4 L(50 6 1 gal) is circulated through a rotary vane pump system for 50 h at a pump
speed of 2400 6 20 r/min and a pump outlet pressure of 20.7 6 0.2 MPa (3000 6 20 psig). Fluid temperature at the pump inlet
is 95 6 3°C (203 6 5°F). An ISO Grade 32 or 10W viscosity is required.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.N0.07
on Lubricating Properties.
Current edition approved MayFeb. 1, 2005.2008. Published May 2005.March 2008. Originally approved in 2003. Last previous edition approved in 20042005 as
e1
D6973–04 .D 6973–05.
2
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
4
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
4
Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
5
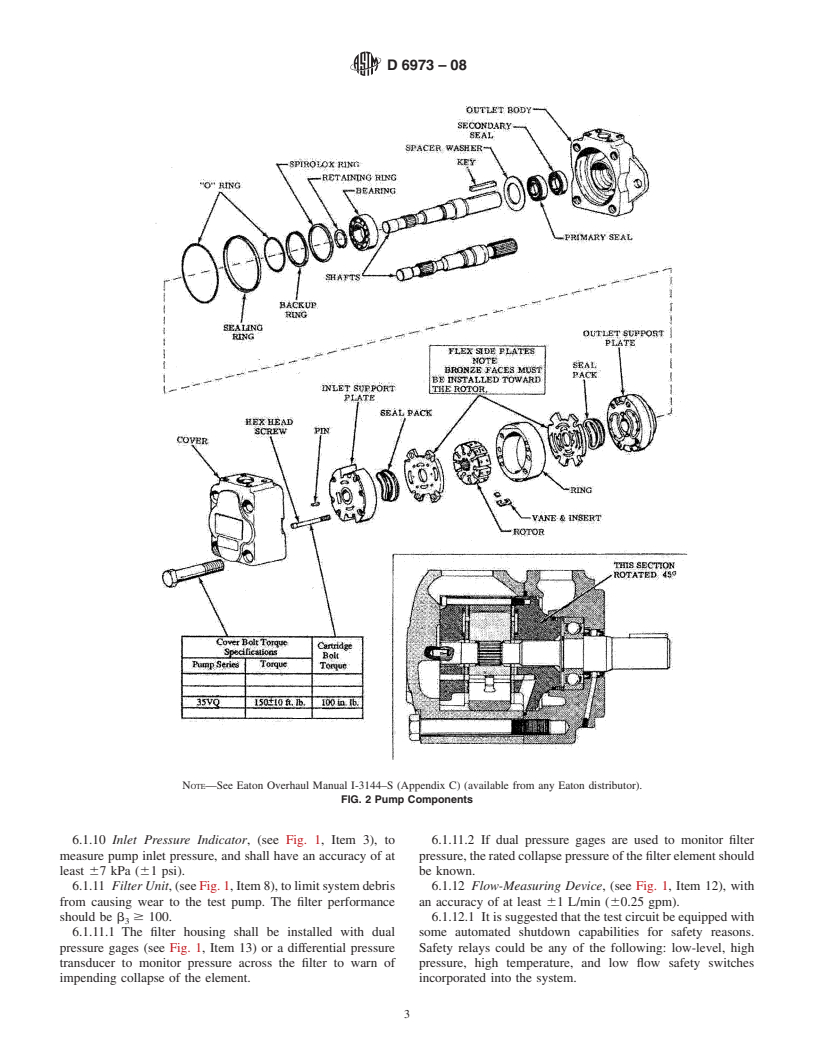
The replaceable cartridge consists of the inlet support plate, outlet support plate, flex side plates, seal pack, rotor, cam ring, intra-vane, and vanes.
5
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6973–08
4.2 The cam ring and all ten vanes should be individually weighed before and after the test. The weight loss of the cam ring
should be reported with the combined weight loss of all ten vanes.The intra-vanes (inserts) are not part of the required weight loss
measurements and should be separately measured if desired. Other reported values are fluid cleanli
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.