ASTM A756-17
(Specification)Standard Specification for Stainless Anti-Friction Bearing Steel
Standard Specification for Stainless Anti-Friction Bearing Steel
ABSTRACT
This specification deals with the requirements for chromium-carbon bearing quality stainless steel to be used in the manufacture of anti-friction bearings. Chemical requirements shall conform to the required compositions of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, silicon, chromium, nickel, copper, and molybdenum. Heat analysis and product analysis shall made. Decarburization and surface imperfection limits are specified. When annealing will be made, the steel should have a completely spheroidized microstructure and the hardness is specified.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for chromium-carbon bearing quality stainless steel to be used in the manufacture of anti-friction bearings.
1.2 Supplementary Requirements of an optional nature are provided and when desired shall be so stated in the order.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
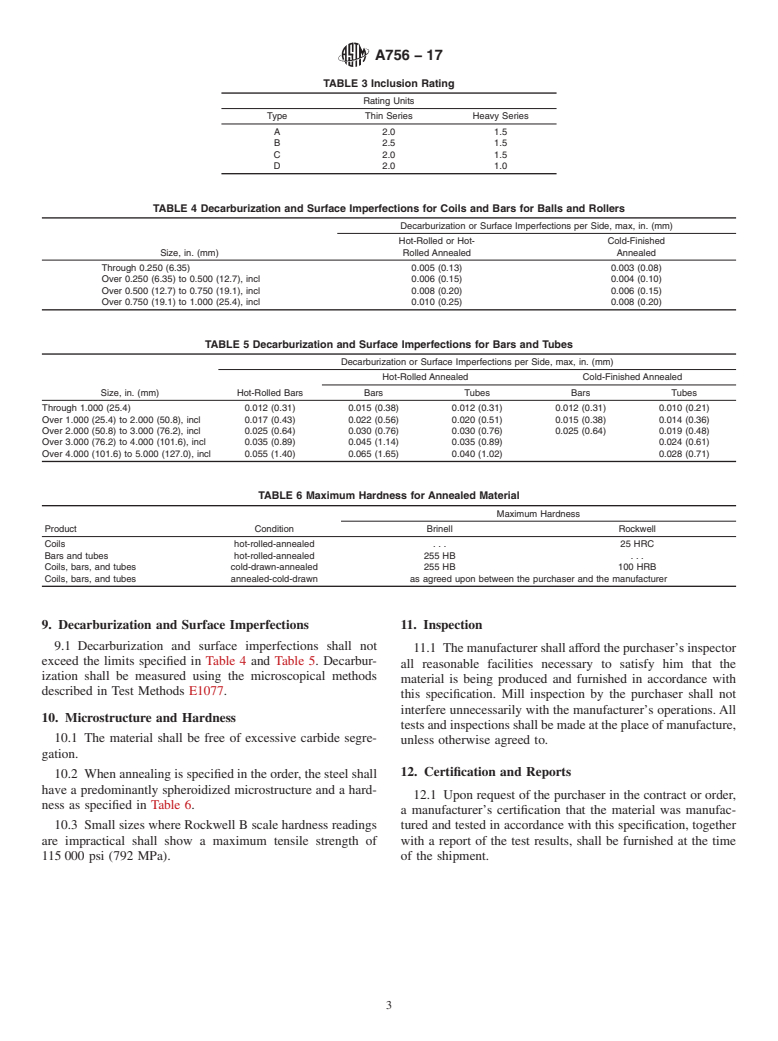
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:A756 −17
Standard Specification for
1
Stainless Anti-Friction Bearing Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A756; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 2.2 Other Standards:
3
ISO 683 Part 17 Ball and Roller Bearing Steels
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for
4
SAE J418a Grain Size Determination of Steel
chromium-carbon bearing quality stainless steel to be used in
the manufacture of anti-friction bearings.
3. Ordering Information
1.2 Supplementary Requirements of an optional nature are
3.1 Orders for material under specification should include
provided and when desired shall be so stated in the order.
the following information:
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded 3.1.1 Quantity,
3.1.2 Grade identification,
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only 3.1.3 Specification designation and year of issue,
3.1.4 Dimensions, shape, and
and are not considered standard.
3.1.5 Supplementary Requirements, if desired.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4. Process
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 The steel shall be made by a process that is capable of
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
providing a high-quality product meeting the requirements of
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
this specification.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
5. Chemical Composition
2. Referenced Documents
5.1 Typical examples of chemical compositions are shown
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
in Table 1. Other compositions may be specified.
A484/A484M Specification for General Requirements for
5.2 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the
Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
steel manufacturer in accordance withTest Methods, Practices,
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemi-
and Terminology A751. The chemical composition thus deter-
cal Analysis of Steel Products
mined shall conform to the requirements specified in Table 1
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of
for the ordered grade or to requirements agreed upon between
Steel
the manufacturer and the purchaser.
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets,
Blooms, and Forgings
5.3 Product analysis may be made by the purchaser in
E1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur,
accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology
Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt
A751. Permissible variations in product analysis shall be made
Alloys by Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques
in accordance with Specification A484/A484M.
E1077 Test Methods for Estimating the Depth of Decarbur-
ization of Steel Specimens 6. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
6.1 The size and shape of the material shall be agreed upon
between manufacturer and purchaser.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel,
6.2 Dimensional tolerances for hot-rolled or hot-rolled and
Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
annealed bars, in straight lengths or coils, and cold-finished
A01.28 on Bearing Steels.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2017. Published October 2017. Originally
ɛ1
approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as A756 – 09(2014) .
3
DOI: 10.1520/A0756-17. Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr.,Warrendale,
the ASTM website. PA 15096, http://www.sae.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A756−17
A, B
TABLE 1 Chemical Composition
P S Cu O
C
ISO Name C Mn Si Cr Ni Mo Al (max) Other
D
(max) (max) (max) (max)
... 440C 0.95–1.20 1.00 max 0.040 0.030 1.00 max 16.00–18.00 0.75 max 0.40–0.65 0.50 0.0020 0.050 ...
... X30CrMoN15-1 0.25–0.35 1.00 max 0.030 0.025 1.00 max 14.00–16.00 0.30–0.50
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: A756 − 09 (Reapproved 2014) A756 − 17
Standard Specification for
1
Stainless Anti-Friction Bearing Steel
This standard is issued under the fixed designation A756; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Table 1 was editorially corrected in October 2015.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This specification covers the requirements for chromium-carbon bearing quality stainless steel to be used in the manufacture
of anti-friction bearings.
1.2 Supplementary Requirements of an optional nature are provided and when desired shall be so stated in the order.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A484/A484M Specification for General Requirements for Stainless Steel Bars, Billets, and Forgings
A751 Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology for Chemical Analysis of Steel Products
E45 Test Methods for Determining the Inclusion Content of Steel
E381 Method of Macroetch Testing Steel Bars, Billets, Blooms, and Forgings
E1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur, Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys by
Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques
E1077 Test Methods for Estimating the Depth of Decarburization of Steel Specimens
2.2 Other Standards:
3
ISO 683 Part 17 Ball and Roller Bearing Steels
4
SAE J418a Grain Size Determination of Steel
3. Ordering Information
3.1 Orders for material under specification should include the following information:
3.1.1 Quantity,
3.1.2 Grade identification,
3.1.3 Specification designation and year of issue,
3.1.4 Dimensions, shape, and
3.1.5 Supplementary Requirements, if desired.
4. Process
4.1 The steel shall be made by a process that is capable of providing a high-quality product meeting the requirements of this
specification.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee A01 on Steel, Stainless Steel and Related Alloys and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee A01.28
on Bearing Steels.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2014Sept. 1, 2017. Published October 2014October 2017. Originally approved in 1978. Last previous edition approved in 20092014 as
ɛ1
A756 – 09.A756 – 09(2014) . DOI: 10.1520/A0756-09R14E01.10.1520/A0756-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’sstandard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20,ISO Central Secretariat, BIBC II, Chemin de
Blandonnet 8, CP 401, 1214 Vernier, Geneva, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org.
4
Available from SAE International (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001,15096, http://www.sae.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
A756 − 17
5. Chemical Composition
5.1 Typical examples of chemical compositions are shown in Table 1. Other compositions may be specified.
5.2 An analysis of each heat of steel shall be made by the steel manufacturer in accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and
Terminology A751. The chemical composition thus determined shall conform to the requirements specified in Table 1 for the
ordered grade or to requirements agreed upon between the manufacturer and the purchaser.
5.3 Product analysis may be made by the purchaser in accordance with Test Methods, Practices, and Terminology A751.
Permissible variations in product analysis shall be made in accordance with Specification A484/A484M.
6. Dimensions, Mass, and Permissible Variations
6.1 The
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.