ASTM C307-03
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength of Chemical-Resistant Mortar, Grouts, and Monolithic Surfacings
Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength of Chemical-Resistant Mortar, Grouts, and Monolithic Surfacings
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
It is recognized that chemical-resistant mortars, grouts, and monolithic surfacings are not usually under tension when in service; however, such data are useful for purposes of determining the rate of cure and other properties.
This test method is not recommended for mortars, grouts, and monolithic surfacings containing aggregate greater than ¼ in.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of tensile strength of cured chemical-resistant materials in the form of molded briquets. These materials include mortars, brick and tile grouts, machinery grouts, and monolithic surfacings. These materials shall be based on resin, silicate, silica, or sulfur binders.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:C307–03
Standard Test Method for
Tensile Strength of Chemical-Resistant Mortar, Grouts, and
1
Monolithic Surfacings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 307; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 4.2 This test method is not recommended for mortars,
grouts, and monolithic surfacings containing aggregate greater
1.1 This test method covers the determination of tensile
1
than ⁄4 in.
strength of cured chemical-resistant materials in the form of
molded briquets. These materials include mortars, brick and
5. Apparatus
tile grouts, machinery grouts, and monolithic surfacings.These
5.1 Weighing Equipment, shall be capable of weighing
materials shall be based on resin, silicate, silica, or sulfur
materials or specimens to 60.3 % accuracy.
binders.
5.2 Specimen Molds—The molds for making briquet test
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
specimens shall be sufficiently rigid to prevent deformation
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for
during molding and shall be made of corrosion-resistant
information only.
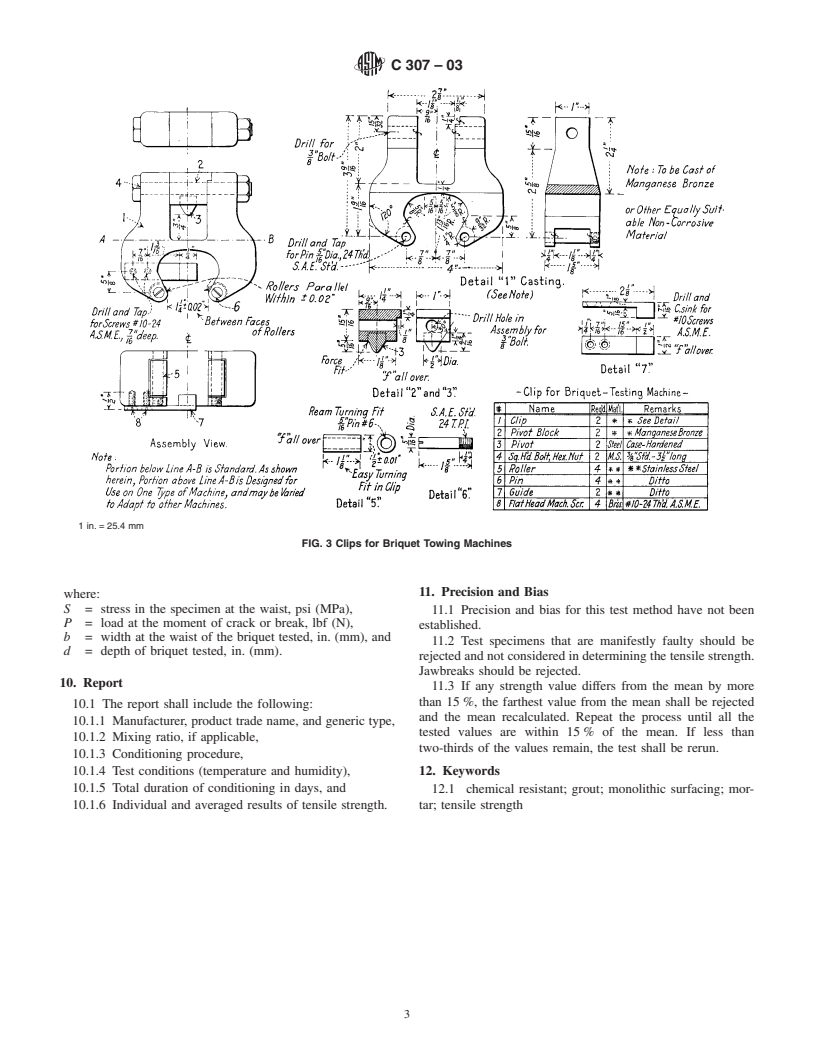
material.Gangmolds,whenused,shallbeofthetypeshownin
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
Fig. 1. The dimensions of the briquet molds shall be the width
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of the mold, between inside faces, at waist line of briquet, 1 in.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
The width and the depth of the briquet mold at the waist line
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
shall be 1 in. 6 0.02in. (25mm 6 0.5mm). The molds shall
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
conform to the dimensional requirements shown in Fig. 2.
2. Referenced Documents 5.3 Equipment for Mixing Materials, shall consist of a
2
container of suitable size, preferably corrosion resistant, and a
2.1 ASTM Standards:
strong, sturdy spatula, trowel, or mechanical mixer.
C 904 Terminology Relating to Chemical-Resistant Non-
5.4 The following additional equipment is required for
metallic Materials
sulfur mortars.
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
5.4.1 Melting Chamber, of sufficient volume and heat ca-
3. Terminology
pacity to melt the mortar sample and maintain the temperature
3
of the melt between 260 and 290°F (127 and 143°C).
3.1 Definitions:
5.4.2 Laboratory Mixer, of such a type and speed to be
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, see
capable of lifting the aggregate without beating air into the
Terminology C 904.
melt.
4. Significance and Use
5.4.3 Ladle, of sufficient capacity to completely pour one
briquet.
4.1 It is recognized that chemical-resistant mortars, grouts,
5.5 Testing Machine, the testing machine shall be of any
and monolithic surfacings are not usually under tension when
type sufficient to provide the required load and the rate of
in service; however, such data are useful for purposes of
crosshead movement prescribed. It shall have been verified to
determining the rate of cure and other properties.
have an accuracy of 1.0 % or better within 12 months of the
time of use in accordance with Practices E 4.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C03 on
Chemical-Resistant Nonmetallic Materials and is the direct responsibility of
Subcommittee C03.01 on Test Methods.
3
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 2003. Published November 2003. Originally The sole source of supply of the Forney capping compound melting chamber,
published in 1953. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as C 307–99. Model LA-0130, known to the committee at this time is Forney Industries, Inc.,
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or 1565 Broadway Ave., Hermitage, PA 16148. If you are aware of alternative
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM Headquarters. Your comments
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical
the ASTM website. committee, which you may attend.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C307–03
placed portion. Upon completion of the filling operations, the
tops of the specimens should extend slightly above the tops of
the molds. Wh
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.