ASTM D1238-13
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion Plastometer
Standard Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion Plastometer
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method is particularly useful for quality control tests on thermoplastics.
4.2 The data produced by this test method serves to indicate the uniformity of the flow rate of the polymer as made by an individual process. It is not to be used as an indication of uniformity of other properties without valid correlation with data from other tests.
4.3 The flow rate obtained with the extrusion plastometer is not a fundamental polymer property. It is an empirically defined parameter critically influenced by the physical properties and molecular structure of the polymer and the conditions of measurement. The rheological characteristics of polymer melts depend on a number of variables. It is possible that the values of these variables occurring in this test will differ substantially from those in large-scale processes, which would result in data that does not correlate directly with processing behavior.
4.4 Measure the flow rate of a material using any of the conditions listed for the material in X4.1. For many materials, there are specifications that require the use of this test method, but with some procedural modifications that take precedence when adhering to the specification. Therefore, it is advisable to refer to that material specification before using this test method. Table 1 in Classification D4000 lists the ASTM materials standards that currently exist. An alternative test method for poly (vinyl chloride) (PVC) compounds is found in Test Method D3364.
4.5 Additional characterization of a material can be obtained if more than one condition is used. In the case that two or more conditions are employed, a Flow Rate Ratio (FRR) is obtained by dividing the flow rate at one condition by the flow rate at another condition. Procedure D provides one method to measure more than one condition in a single charge.
4.6 Frequently, variations in test technique, apparatus geometry, or test conditions, which defy all but the most careful scrutiny, exi...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the rate of extrusion of molten thermoplastic resins using an extrusion plastometer. After a specified preheating time, resin is extruded through a die with a specified length and orifice diameter under prescribed conditions of temperature, load, and piston position in the barrel. Four procedures are described. Comparable results have been obtained by these procedures in interlaboratory round-robin measurements of several materials and are described in Section 15.
1.2 Procedure A is used to determine the melt flow rate (MFR) of a thermoplastic material. The units of measure are grams of material/10 minutes (g/10 min). It is based on the measurement of the mass of material that extrudes from the die over a given period of time. It is generally used for materials having melt flow rates that fall between 0.15 and 50 g/10 min (see Note 1).
1.3 Procedure B is an automatically timed measurement used to determine the melt flow rate (MFR) as well as the melt volume rate (MVR) of thermoplastic materials. MFR measurements made with Procedure B are reported in g/10 minutes. MVR measurements are reported in cubic centimetres/ten minutes (cm3/10 min). Procedure B measurements are based on the determination of the volume of material extruded from the die over a given period of time. The volume is converted to a mass measurement by multiplying the result by the melt density value for the material (see Note 2). Procedure B is generally used with materials having melt flow rates from 0.50 to 1500 g/10 min.
1.4 Procedure C is an automatically timed measurement used to determine the melt flow rate (MFR) of polyolefin materials. It is generally used as an alternative to Procedure B on samples having melt flow rates greater than 75 g/10 min. Procedure C involves the use of a modified die, commonly referred to as a “half-die,” which has half the height and half the internal diameter of...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D1238 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion
1
Plastometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1238; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope* Procedure C involves the use of a modified die, commonly
referred to as a “half-die,” which has half the height and half
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the rate of
the internal diameter of the standard die specified for use in
extrusion of molten thermoplastic resins using an extrusion
Procedures A and B thus maintaining the same length to
plastometer.Afteraspecifiedpreheatingtime,resinisextruded
diameterratio.ThetestprocedureissimilartoProcedureB,but
throughadiewithaspecifiedlengthandorificediameterunder
the results obtained with Procedure C shall not be assumed to
prescribed conditions of temperature, load, and piston position
be half of those results produced with Procedure B.
in the barrel. Four procedures are described. Comparable
results have been obtained by these procedures in interlabora- 1.5 ProcedureDisamulti-weighttestcommonlyreferredto
tory round-robin measurements of several materials and are as a “Flow Rate Ratio” (FRR) test. Procedure D is designed to
described in Section 15. allow MFR determinations to be made using two or three
different test loads (either increasing or decreasing the load
1.2 Procedure A is used to determine the melt flow rate
during the test) on one charge of material. The FRR is a
(MFR) of a thermoplastic material. The units of measure are
dimensionless number derived by dividing the MFR at the
grams of material/10 minutes (g/10 min). It is based on the
higher test load by the MFR at the lower test load. Results
measurementofthemassofmaterialthatextrudesfromthedie
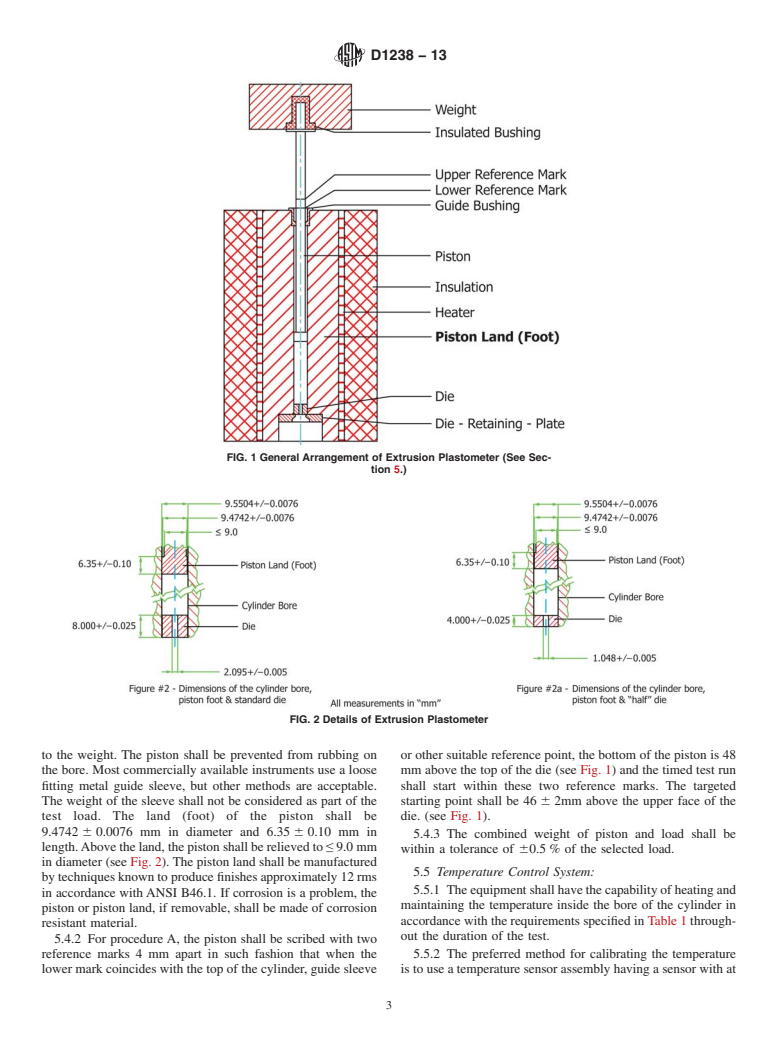
generated from multi-weight tests shall not be directly com-
over a given period of time. It is generally used for materials
pared with results derived from Procedure A or Procedure B.
having melt flow rates that fall between 0.15 and 50 g/10 min
NOTE1—Polymershavingmeltflowrateslessthan0.15orgreaterthan
(see Note 1).
900 g/10 min may be tested by the procedures in this test method;
however, precision data have not been developed.
1.3 Procedure B is an automatically timed measurement
NOTE 2—Melt density is the density of the material in it molten state.
usedtodeterminethemeltflowrate(MFR)aswellasthemelt
Itisnottobeconfusedwiththestandarddensityvalueofthematerial.See
volumerate(MVR)ofthermoplasticmaterials.MFRmeasure-
Table 3.
ments made with Procedure B are reported in g/10 minutes.
NOTE 3—This test method and ISO1133 address the same subject
MVR measurements are reported in cubic centimetres/ten matter, but differ in technical content.
3
minutes (cm /10 min). Procedure B measurements are based
1.6 This standard does not purport to address the safety
on the determination of the volume of material extruded from
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
thedieoveragivenperiodoftime.Thevolumeisconvertedto
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and
a mass measurement by multiplying the result by the melt
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
density value for the material (see Note 2). Procedure B is
limitations prior to use.
generallyusedwithmaterialshavingmeltflowratesfrom0.50
2. Referenced Documents
to 1500 g/10 min.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.4 Procedure C is an automatically timed measurement
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
used to determine the melt flow rate (MFR) of polyolefin
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
materials. It is generally used as an alternative to Procedure B
D3364TestMethodforFlowRatesforPoly(VinylChloride)
on samples having melt flow rates greater than 75 g/10 min.
with Molecular Structural Implications
D4000Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materi-
als
1
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20onPlastics
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties
2
(Section D20.30.08). For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2013. Published August 2013. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D1238-10. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D1238-13. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D1238 − 10 D1238 − 13
Standard Test Method for
Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics by Extrusion
1
Plastometer
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1238; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the rate of extrusion of molten thermoplastic resins using an extrusion
plastometer. After a specified preheating time, resin is extruded through a die with a specified length and orifice diameter under
prescribed conditions of temperature, load, and piston position in the barrel. Four procedures are described. Comparable results
have been obtained by these procedures in interlaboratory round-robin measurements of several materials and are described in
Section 15.
1.2 Procedure A is used to determine the melt flow rate (MFR) of a thermoplastic material. The units of measure are grams of
material/10 minutes (g/10 min). It is based on the measurement of the mass of material that extrudes from the die over a given
period of time. It is generally used for materials having melt flow rates that fall between 0.15 and 50 g/10 min (see Note 1).
1.3 Procedure B is an automatically timed measurement used to determine the melt flow rate (MFR) as well as the melt volume
rate (MVR) of thermoplastic materials. MFR measurements made with Procedure B are reported in g/10 minutes. MVR
3
measurements are reported in cubic centimetres/ten minutes (cm /10 min). Procedure B measurements are based on the
determination of the volume of material extruded from the die over a given period of time. The volume is converted to a mass
measurement by multiplying the result by the melt density value for the material (see Note 2). Procedure B is generally used with
materials having melt flow rates from 0.50 to 1500 g/10 min.
1.4 Procedure C is an automatically timed measurement used to determine the melt flow rate (MFR) of polyolefin materials.
It is generally used as an alternative to Procedure B on samples having melt flow rates greater than 75 g/10 min. Procedure C
involves the use of a modified die, commonly referred to as a “half-die,” which has half the height and half the internal diameter
of the standard die specified for use in Procedures A and B thus maintaining the same length to diameter ratio. The test procedure
is similar to Procedure B, but the results obtained with Procedure C shall not be assumed to be half of those results produced with
Procedure B.
1.5 Procedure D is a multi-weight test commonly referred to as a “Flow Rate Ratio” (FRR) test. Procedure D is designed to
allow MFR determinations to be made using two or three different test loads (either increasing or decreasing the load during the
test) on one charge of material. The FRR is a dimensionless number derived by dividing the MFR at the higher test load by the
MFR at the lower test load. Results generated from multi-weight tests shall not be directly compared with results derived from
Procedure A or Procedure B.
NOTE 1—Polymers having melt flow rates less than 0.15 or greater than 900 g/10 min may be tested by the procedures in this test method; however,
precision data have not been developed.
NOTE 2—Melt density is the density of the material in it molten state. It is not to be confused with the standard density value of the material. See Table
3.
NOTE 3—This test method and ISO 1133 address the same subject matter, but differ in technical content.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the
user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations
prior to use.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.30 on Thermal Properties (Section
D20.30.08).
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2010Aug. 1, 2013. Published March 2010August 2013. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 20042010 as
D1238 - 04c.D1238 - 10. DOI: 10.1520/D1238-10.10.1520/D1238-13.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
-------------
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.