ASTM D2809-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Cavitation Corrosion and Erosion-Corrosion Characteristics of Aluminum Pumps With Engine Coolants
Standard Test Method for Cavitation Corrosion and Erosion-Corrosion Characteristics of Aluminum Pumps With Engine Coolants
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method can be used to distinguish between coolants that contribute to cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion of aluminum automotive water pumps and those that do not. It is not intended that a particular rating number, as determined from this test, will be equivalent to a certain number of miles in a vehicle test; however, limited correlation between bench and field service tests has been observed with single-phase coolants. Field tests under severe operating conditions should be conducted as the final test if the actual effect of the coolant on cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion is to be appraised. It is also possible, with proper control of the test variables, to determine the effect of pump design, materials of construction, and pump operating conditions on cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion damage.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion characteristics of aluminum automotive water pumps with coolants.
Note 1—During the development of this test method, it was found that results obtained when testing two-phase coolants did not correlate with results from field tests. Therefore, the test method cannot be recommended as being a significant test for determining cavitation effects of two-phase coolants.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in 5.2.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2809 − 09
Standard Test Method for
Cavitation Corrosion and Erosion-Corrosion Characteristics
1
of Aluminum Pumps With Engine Coolants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2809; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the cavitation 3.1 This test method consists of pumping an aqueous
corrosion and erosion-corrosion characteristics of aluminum coolant solution at 113°C (235°F) through a pressurized
automotive water pumps with coolants. 103-kPa (15-psig) simulated automotive coolant system (Note
2).An aluminum automotive water pump, driven at 4600 r/min
NOTE 1—During the development of this test method, it was found that
by an electric motor, is used to pump the solution and to serve
results obtained when testing two-phase coolants did not correlate with
as the object specimen in evaluating the cavitation erosion-
resultsfromfieldtests.Therefore,thetestmethodcannotberecommended
as being a significant test for determining cavitation effects of two-phase
corrosion effect of the coolant under test. The pump is
coolants.
examined to determine the extent of cavitation erosion-
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the corrosion damage and is rated according to the system given in
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information Table 1. Photographs of typical eroded pumps after testing
only. appear in the Appendix.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
NOTE2—Testsrunatotherthan113°C(235°F)mightshowmoreorless
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the cavitation depending upon the coolant formulation.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning
4.1 This test method can be used to distinguish between
statements are given in 5.2.
coolants that contribute to cavitation corrosion and erosion-
corrosion of aluminum automotive water pumps and those that
2. Referenced Documents
do not. It is not intended that a particular rating number, as
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
determined from this test, will be equivalent to a certain
D1176 Practice for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous Solu-
number of miles in a vehicle test; however, limited correlation
tions of Engine Coolants orAntirusts forTesting Purposes
between bench and field service tests has been observed with
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in
single-phase coolants. Field tests under severe operating con-
ASTM Test Methods
ditions should be conducted as the final test if the actual effect
3
2.2 ASTM Adjunct:
of the coolant on cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion is
Pump test stand (7 drawings and Bill of Materials)
to be appraised. It is also possible, with proper control of the
testvariables,todeterminetheeffectofpumpdesign,materials
1
of construction, and pump operating conditions on cavitation
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D15 on Engine
Coolants and Related Fluids and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
corrosion and erosion-corrosion damage.
D15.09 on Simulated Service Tests.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2009. Published December 2009. Originally
5. Apparatus
approved in 1969 as D2809–69T. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as
ε1 3
D2809–04 . DOI: 10.1520/D2809-09.
5.1 Pump Test Stand— Detailed drawings are available.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
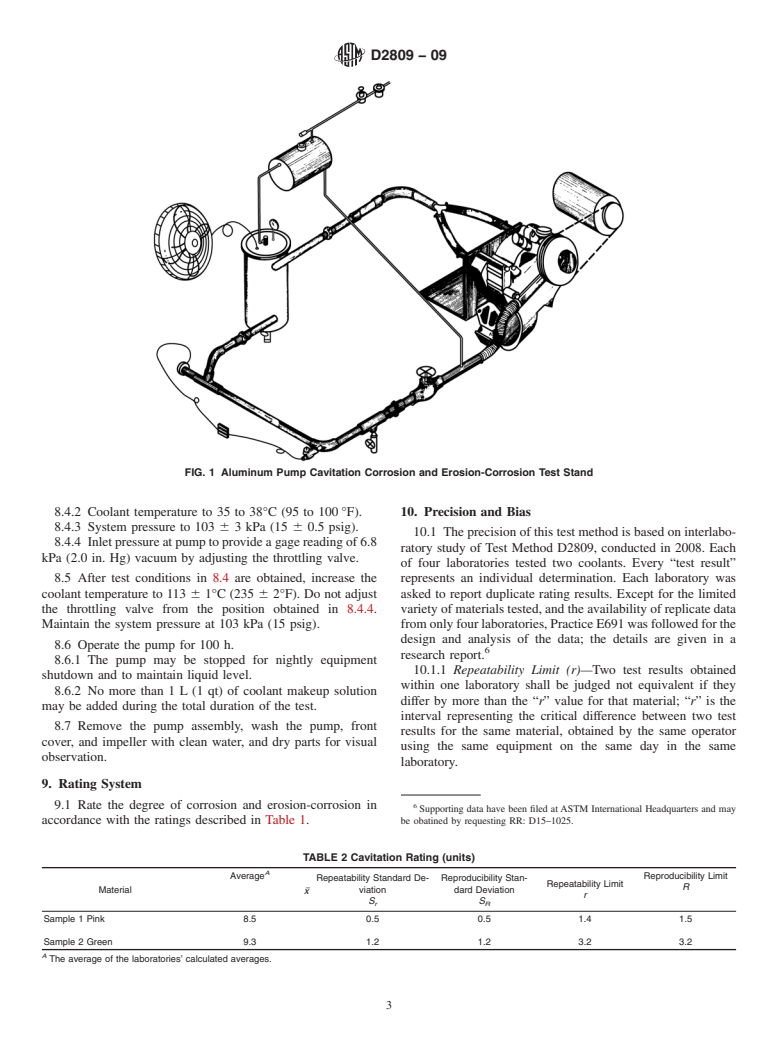
The copper, brass, and bronze flow circuit is illustrated in Fig.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1.The apparatus should be assembled upon a suitable platform
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. or structure, with provisions for mounting controls and gages.
3
Detail drawings of this apparatus and accompanying table of parts are available
5.2 Warning— The entire stand should be screened or
from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. ADJD2809. Original
adjunct produced in 1985. housed to protect personnel from hazardous scalding coolant
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2809 − 09
A,B
TABLE 1 Rating System
7. Sampling
Rating Condition
7.1 The coolant concentration shall be sampled in accor-
10 No corrosion or eros
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´2
Designation:D2809–04 Designation:D2809–09
Standard Test Method for
Cavitation Corrosion and Erosion-Corrosion Characteristics
1
of Aluminum Pumps With Engine Coolants
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2809; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
´ NOTE—Footnote 3 was updated editorially in August 2005.
2
´ NOTE—Adjunct references were corrected editorially in April 2006.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion characteristics of aluminum
automotive water pumps with coolants.
NOTE 1—During the development of this test method, it was found that results obtained when testing two-phase coolants did not correlate with results
from field tests. Therefore, the test method cannot be recommended as being a significant test for determining cavitation effects of two-phase coolants.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in 5.2.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1176 Practice for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous Solutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing Purposes Practice
for Sampling and Preparing Aqueous Solutions of Engine Coolants or Antirusts for Testing Purposes
E177 Practice for Use of the Terms Precision and Bias in ASTM Test Methods
3
2.2 ASTM Adjunct:
Pump test stand (7 drawings and Bill of Materials)
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 Thistestmethodconsistsofpumpinganaqueouscoolantsolutionat113°C(235°F)throughapressurized103-kPa(15-psig)
simulated automotive coolant system (Note 2). An aluminum automotive water pump, driven at 4600 r/min by an electric motor,
is used to pump the solution and to serve as the object specimen in evaluating the cavitation erosion-corrosion effect of the coolant
under test. The pump is examined to determine the extent of cavitation erosion-corrosion damage and is rated according to the
system given in Table 1. Photographs of typical eroded pumps after testing appear in the Appendix.
NOTE 2—Tests run at other than 113°C (235°F) might show more or less cavitation depending upon the coolant formulation.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 This test method can be used to distinguish between coolants that contribute to cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion
of aluminum automotive water pumps and those that do not. It is not intended that a particular rating number, as determined from
this test, will be equivalent to a certain number of miles in a vehicle test; however, limited correlation between bench and field
service tests has been observed with single-phase coolants. Field tests under severe operating conditions should be conducted as
the final test if the actual effect of the coolant on cavitation corrosion and erosion-corrosion is to be appraised. It is also possible,
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D15 on Engine Coolants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D15.09 on Simulated Service
Tests.
Current edition approved May 1, 2004. Published June 2004. Originally approved in 1969 as D2809–69T. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D2809–94(99). DOI:
10.1520/D2809-04E02.
´1
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2009. Published December 2009. Originally approved in 1969 as D2809–69T. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D2809–04 .
DOI: 10.1520/D2809-09.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Detail drawings of this apparatus and accompanying table of parts are available from ASTM International Headquarters. Order Adjunct No. ADJD2809.ADJD2809.
Original adjunct produced in 1985.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.