ASTM D4194-95
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Operating Characteristics of Reverse Osmosis Devices
Standard Test Methods for Operating Characteristics of Reverse Osmosis Devices
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the operating characteristics of reverse osmosis devices using standard test conditions and are not necessarily applicable to natural waters. Two test methods are given, as follows: SectionsTest Method A-Brackish Water Reverse Osmosis Devices8-13 Test Method B-Seawater Reverse Osmosis Devices14-19
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4194 – 95
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Methods for
1
Operating Characteristics of Reverse Osmosis Devices
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4194; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope through the membrane.
3.2.7 permeate flow rate—the quantity of permeate pro-
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the
duced per unit time.
operating characteristics of reverse osmosis devices using
3.2.8 rejection—that portion of the salt in the feed which
standard test conditions and are not necessarily applicable to
does not pass through the reverse osmosis membrane, ex-
natural waters. Two test methods are given, as follows:
pressed as percent and is equal to (100 % − salt passage).
3.2.9 salt passage—the ratio of permeate salt concentration
Sections
to feed salt concentration, expressed as percent.
Test Method A—Brackish Water Reverse Osmosis De- 8-13
vices
4. Summary of Test Methods
Test Method B—Seawater Reverse Osmosis Devices 14-19
4.1 These test methods consist of determining the desalinat-
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ing ability and permeate flow rate of reverse osmosis devices.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
They are applicable to both new and used reverse osmosis
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
devices.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
5. Significance and Use
2. Referenced Documents 5.1 Reverse osmosis desalinating devices can be used to
produce potable water from brackish supplies (<10 000 mg/L)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
2 and seawater as well as to upgrade the quality of industrial
D 512 Test Methods for Chloride Ion in Water
water. These test methods permit the measurement of the
D 1125 Test Methods for Electrical Conductivity and Re-
2 performance of reverse osmosis devices using standard sets of
sistivity of Water
2 conditions and are intended for short-term testing (<24 h).
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
2 These test methods can be used to determine changes that may
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
have occurred in the operating characteristics of reverse
3. Terminology
osmosis devices but are not intended to be used for plant
design.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in these test
methods, refer to Terminology D 1129.
6. Reagents
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 concentrate, reject, or brine—that portion of feed 6.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent grade chemicals shall be
which does not pass through the membrane. used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
3.2.2 conversion or recovery—the ratio of permeate flow all reagents shall conform to the specifications of the Commit-
rate to feed flow rate, expressed as percent. tee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society,
3
3.2.3 desalination device—a single pressure vessel contain- where such specifications are available. Other grades may be
ing a reverse osmosis element or elements and supporting used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of
materials. sufficiently high purity to permit its use without lessening the
3.2.4 device pressure drop (DP)—the difference between accuracy of the determination.
the feed pressure and the concentrate pressure. 6.2 Purity of Water—Unless otherwise indicated, references
3.2.5 feed—the solution that enters the device. to water shall be understood to mean Type III reagent con-
3.2.6 permeate—that portion of the feed which passes forming to Specification D 1193.
1 3
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-19 on Reagent Chemicals, American Chemical Society Specifications, American
Water, and are the direct responsibilities of Subcommittee D19.08 on Membranes Chemical Society, Washington, DC. For suggestions on the testing of reagents not
and Ion Exchange Materials. listed by the American Chemical Society, see Analar Standards for Laboratory
Current edition approved April 15, 1995. Published June 1995. Originally Chemicals, BDH Ltd., Poole, Dorset, U.K., and the United States Pharmacopeia
published as D 4194 – 82. Last previous edition D 4194 – 89 (1994). and National Formulary, U.S. Pharmaceutical Convention, Inc. (USPC), Rockville,
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01. MD.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 4194
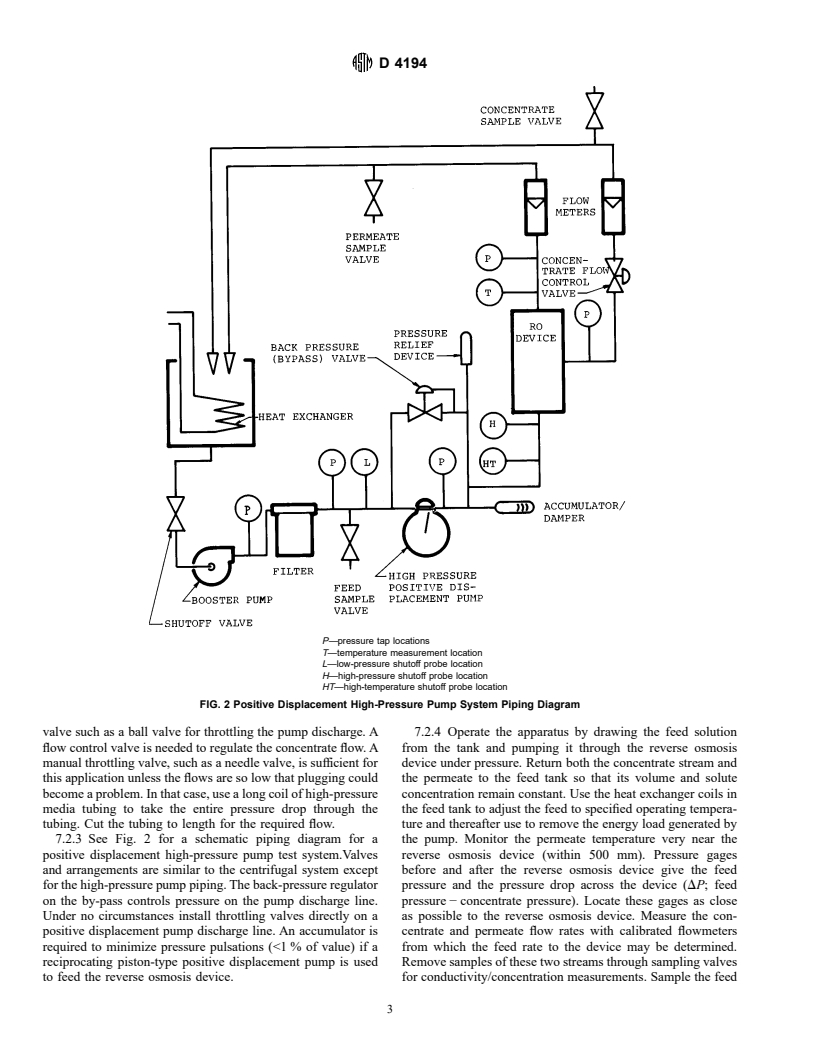
7. Appa
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.