ASTM D4742-02
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Gasoline Automotive Engine Oils by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT)
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Gasoline Automotive Engine Oils by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT)
SCOPE
1.1 This test method evaluates the oxidation stability of engine oils for gasoline automotive engines. This test, run at 160°C, utilizes a high pressure reactor pressurized with oxygen along with a metal catalyst package, a fuel catalyst, and water in a partial simulation of the conditions to which an oil may be subjected in a gasoline combustion engine. This test method can be used for engine oils with viscosity in the range from 4 mm2/s (cSt) to 21 mm2/s (cSt) at 100°C, including re-refined oils.
1.2 This test method is not a substitute for the engine testing of an engine oil in established engine tests, such as Sequence IIID.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information purposes only.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
An American National Standard
Designation: D 4742 – 02
Standard Test Method for
Oxidation Stability of Gasoline Automotive Engine Oils by
1
Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4742; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
6
1. Scope Petroleum Products
7
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
1.1 This test method evaluates the oxidation stability of
E 144 Practice for Safe Use of Oxygen Combustion
engine oils for gasoline automotive engines. This test, run at
8
Bombs
160°C, utilizes a high pressure reactor pressurized with oxygen
along with a metal catalyst package, a fuel catalyst, and water
3. Terminology
in a partial simulation of the conditions to which an oil may be
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
subjected in a gasoline combustion engine. This test method
3.1.1 break point—the precise point of time at which rapid
can be used for engine oils with viscosity in the range from 4
2 2
oxidation of the oil begins.
mm /s (cSt) to 21 mm /s (cSt) at 100°C, including re-refined
3.1.2 oxidation induction time—the time until the oil begins
oils.
to oxidize at a relatively rapid rate as indicated by the decrease
1.2 This test method is not a substitute for the engine testing
of oxygen pressure.
of an engine oil in established engine tests, such as Sequence
3.1.3 oxygen uptake—oxygen absorbed by oil as a result of
IIID.
oil oxidation.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 The test oil is mixed in a glass container with three other
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
liquids that are used to simulate engine conditions: (1)an
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
oxidized/nitrated fuel component (Annex A2), (2) a mixture of
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
soluble metal naphthenates (lead, copper, iron, manganese, and
standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for
tin naphthenates (Annex A3)), and (3) reagant water.
information purposes only.
4.2 The glass container holding the oil mixture is placed in
a high pressure reactor equipped with a pressure gage. The high
2. Referenced Documents
pressure reactor is sealed, charged with oxygen to a pressure of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
620 kPa (90 psig), and placed in an oil bath at 160°C at an
A 314 Specification for Stainless Steel Billets and Bars for
2
angle of 30° from the horizontal. The high pressure reactor is
Forging
rotated axially at a speed of 100 r/min forming a thin film of oil
B 211 Specification for Aluminum and Aluminum-Alloy
3 within the glass container resulting in a relatively large
Bar, Rod, and Wire
oil-oxygen contact area.
D 664 Test Method for Acid Number of Petroleum Products
4
by Potentiometric Titration
NOTE 1—A pressure sensing device can be used in place of a pressure
5
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water gage.
D 2272 Test Method for Oxidation Stability of Steam-
4.3 The pressure of the high pressure reactor is recorded
4
Turbine Oil by Rotating Bomb
continuously from the beginning of the test and the test is
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
terminated when a rapid decrease of the high pressure reactor
pressure is observed (Point B, Fig. 1). The period of time that
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on elapses between the time when the high pressure reactor is
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
placed in the oil bath and the time at which the pressure begins
D02.09 on Oxidation.
to decrease rapidly is called the oxidation induction time and is
Current edition approved Feb 10, 2002. Published April 2002. Originally
used as a measure of the relative oil oxidation stability.
published as D 4742 – 88. Last previous edition D 4742 – 96.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.02.
4
6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
5
7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
8
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 4742
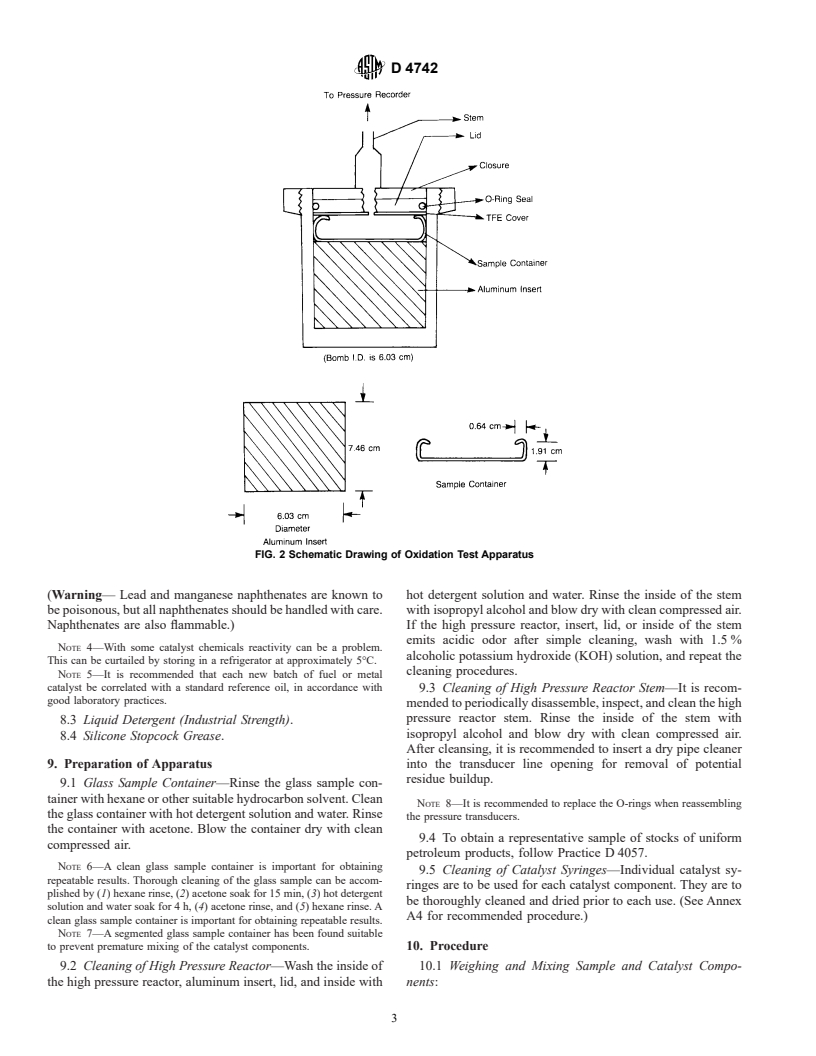
sories are shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 and described in Annex
A1.
9
NOTE 3—It is reported in literature that the oxidation high pressure
reactor can be modified from the Test Method D 2272 oxidation high
pressure reactor by insertion of an aluminum cylinder.
6.2 Precision Pressure Ga
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.