ASTM D6241-04
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for the Static Puncture Strength of Geotextiles and Geotextile-Related Products Using a 50-mm Probe
Standard Test Method for the Static Puncture Strength of Geotextiles and Geotextile-Related Products Using a 50-mm Probe
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is an index test used to measure the force required to puncture a geotextile and geotextile related products. The relatively large size of the plunger provides a multidirectional force on the geotextile.
1.2 The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6241–04
Standard Test Method for the
Static Puncture Strength of Geotextiles and Geotextile-
1
Related Products Using a 50-mm Probe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 6241; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 atmoshere for testing geotextiles, n—air maintained at
1.1 This test method is an index test used to measure the
a relative humidity of 50 to 70 % and a temperature of 21 6
force required to puncture a geotextile and geotextile-related
2°C (70 6 4°F).
products. The relatively large size of the plunger provides a
3.2.2 geotextile, n—a permeable geosynthetic composed
multidirectional force on the geotextile.
solely of textiles.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.2.3 puncture resistance, n—the inherent resisting mecha-
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
nism of the test specimen to the failure by a penetrating or
only.
puncturing object.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
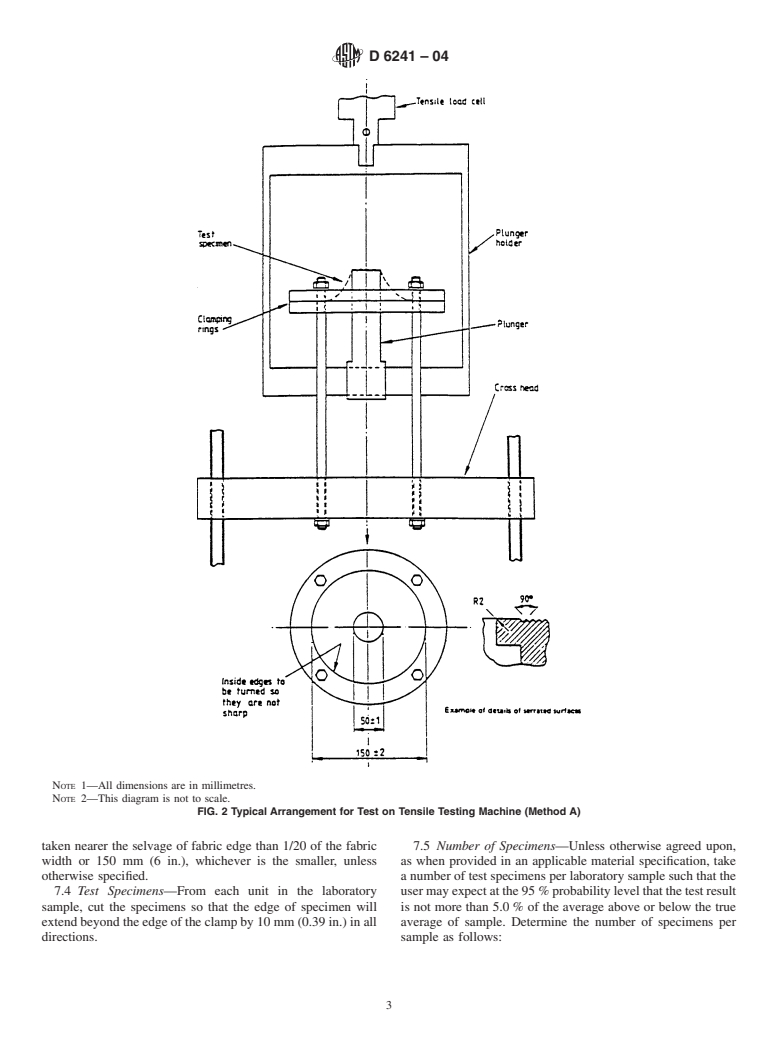
4. Summary of Test Method
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 A test specimen is clamped without tension between
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
circular plates and secured in a tensile or compression testing
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
machine, or both. A force is exerted against the center of the
2. Referenced Documents unsupported portion of the test specimen by a steel plunger
2
attached to the load indicator until rupture occurs. The maxi-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
mum force is the value of puncture strength.
D76 SpecificationforTensileTestingMachinesforTextiles
D 123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
5. Significance and Use
D 1776 Practice for Conditioning Textiles for Testing
5.1 This test method for determining the puncture strength
D 1883 Test Method for CBR (California Bearing Ratio) of
of geotextiles is to be used by the industry as an index of
Laboratory-Compacted Soils
puncture strength. The use of this test method is to establish an
D 4354 Practice for Sampling of Geotextiles for Testing
index value by providing standard criteria and a basis for
D 4439 Terminology for Geosynthetics
uniform reporting.
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
5.2 This test method is considered satisfactory for accep-
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
tance testing of commercial shipments of geotextiles.
NOTE 1—Test Method D 1883 describes a mold (CBR mold) that can
5.3 In case of a dispute arising from differences in reported
be used for this test method.
test results when using this test method for acceptance testing
of commercial shipments, the purchaser and the supplier
3. Terminology
should conduct comparative tests to determine if there is a
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of other textile terms used
statistical bias between their laboratories. Competent statistical
in this test method, refer toTerminology D 123. For definitions
assistance is recommended for the investigation of bias. As a
of other terms relating to geosynthetics used in this test
minimum, the two parties should take a group of test speci-
method, refer to Terminology D 4439.
mens that are as homogeneous as possible and that are from a
lot of the type in question. The test specimens then should be
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D35 on
randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for
Geosynthetics is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D35.01 on Mechanical
testing.Theaverageresultsfromthetwolaboratoriesshouldbe
Properties
compared using Student’s t-test for unpaired data and an
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2004. Published December 2004. Originally
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D 6241 – 99.
acceptable probability level chosen by the two parties before
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
the testing is begun. If a bias is found, either its cause must be
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6241–04
found and corrected, or the purchaser and the
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.