ASTM D5483-95
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oxidation Induction Time of Lubricating Greases by Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Induction Time of Lubricating Greases by Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimetry
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of oxidation induction time of lubricating greases subjected to oxygen at 3.5 MPa (500 psig) and temperatures between 155 and 210°C.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 5483 – 95 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Oxidation Induction Time of Lubricating Greases by
1
Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimetry
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5483; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of oxidation
induction time of lubricating greases subjected to oxygen at 3.5
MPa (500 psig) and temperatures between 155 and 210°C.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
FIG. 1 PDSC Test Unit
2
E 473 Terminology Relating to Thermal Analysis
3. Terminology
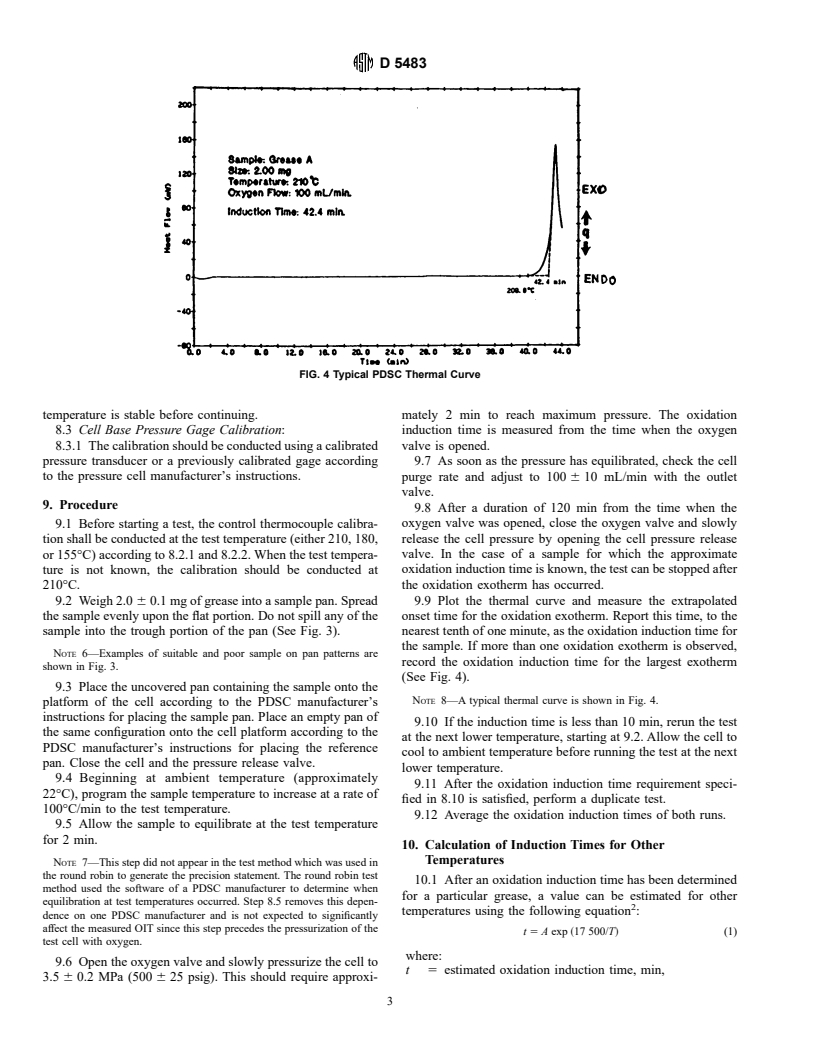
reported as the oxidation induction time for the grease under
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
the specified test temperature.
3.1.1 extrapolated onset time, n—a time determined on a
4.2 A kinetic equation incorporated with this test method
thermal curve, as the intersection of the extrapolated baseline
can estimate oxidation induction times at other temperatures.
and a line tangent to the oxidation exotherm constructed at its
5. Significance and Use
maximum rate.
3.1.2 oxidation induction time (OIT), n— the period of time
5.1 Oxidation induction time, as determined under the
from the first exposure to an oxidizing atmosphere until the
conditions of this test method, can be used as an indication of
3
extrapolated onset time.
oxidation stability. This test method can be used for research
3.1.3 pressure differential scanning calorimeter, (PDSC),
and development, quality control and specification purposes.
n—a differential scanning calorimeter, as defined in Terminol-
However, no correlation has been determined between the
ogy E 473, that is capable of maintaining the test sample at a
results of this test method and service performance.
controlled, elevated pressure.
6. Apparatus
3.1.4 thermal curve, n—a graph of sample heat flow versus
time.
6.1 Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimeter (PDSC),
4
equipped with the following items (See Fig. 1).
4. Summary of Test Method
6.1.1 Sample Enclosure, with capability to 3.5 MPa (500
4.1 A small quantity of grease is weighed into a sample pan
psig) at 210°C and pressure gage graduated at intervals of 200
and placed in a test cell. The cell is heated to a specified
kPa (28.6 psi) or less.
temperature and then pressurized with oxygen. The cell is held
at a regulated temperature and pressure until an exothermic
3
reaction occurs. The extrapolated onset time is measured and
Rhee, In-Sik, “Development of a New Oxidation Stability Test Method for
Greases Using a Pressure Differential Scanning Calorimeter (PDSC),” NLGI
Spokesman, Vol 55, No. 4, July 1991, pp. 123–132.
4
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on Available from TA Instruments, Inc., 109 Lukens Drive, New Castle, DE
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee 19720. At the time that the round robin data for this test method was generated, only
D02.O9.0E on Greases. this company manufactured equipment that met the requirements of 5.1. Subse-
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1995. Published December 1995. Originally quently, other companies have manufactured equipment meeting these require-
published as D 5483 – 93. Last previous edition D 5483 – 93. ments. Their use is permitted provided their performance is consistent with the
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.02. repeatability and reproducibility described in Section 10.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D 5483
FIG. 2 Calibration
8.1.2 Open the oxygen cylinder valve slightly and set a
pressure of 3.5 6 0.2 MPa (500 6 25 psig) on the cell inlet line
with the pressure regulator. Partially open the inlet valve on the
cell and allow the pressure to slowly build up in the cell. This
should require approximately 2 min. Using the outlet valve,
adjust the oxygen purge rate through the flowmeter to 100 6
10 mL/min. The open position of these valves should remain
fixed during the test.
FIG. 3 Sample Preparation on SFI Pan
8.1.3 Set the thermal analyzer to
...






Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.