ASTM F623-99
(Specification)Standard Performance Specification for Foley Catheter
Standard Performance Specification for Foley Catheter
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes performance requirements for the short-term utilization of a single-use, balloon-retention catheter, French sizes 12 through 26 inclusive, used by the medical professions for providing a means of bladder drainage by means of the urethra. The product is manufactured in various sizes and materials such as latex, silicone, rubber, and various polymers (as well as combinations of these) and is provided nonsterile for sterilization and sterile for single use only. Catheters whose surface has been chemically treated to effect biocompatibility or microbial properties may be tested to this specification.
1.2 Exclusions—Long-term indwelling usage (over 30 days) is encountered with this product, but not commonly, and is therefore considered an exception to this specification. Similarly, the use of such catheters for nonurethral catheterization (such as for nephrostomy, suprapubic cystostomy, ureterostomy, gastrostomy, enemas, and so forth) is excluded from the scope of this specification. Likewise, three lumen catheters, 30-cm3 balloon and pediatric catheters, and catheters whose surface has been chemically treated to enhance their lubricity have not been tested to this specification and excluded from the scope of this specification and will require separate standard development.
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, operations, and equipment. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: F 623 – 99
Standard Performance Specification for
Foley Catheter
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 623; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
INTRODUCTION
The objective of this specification is to describe those product requirements and associated test
methods that will assure the safety and effectiveness of a disposable, 5-cm (mL) balloon,
retention-type catheter used in urinary bladder drainage.
This specification includes referee test methods that can be used to determine compliance with the
stated performance requirements. Note that the test methods are not to be construed as production
methods, quality control techniques, or manufacturer’s lot release criteria. The product parameters
addressed by the standard include those determined by the FDA Panel on Review of
Gastroenterological-Urological Devices to be pertinent to the proposed classification of the Foley
catheter to FDA Class II standards, plus other parameters determined by the ASTM task force to be
pertinent to the product.
This specification represents the state-of-the-art at this time and is a minimum performance
specification. It is recognized that the document must remain dynamic; suggestions for revision are
encouraged, and should be directed to Committee F04 Staff Manager, ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Dr., PO
Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428–2959.
1. Scope scope of this specification and will require separate standard
development.
1.1 This specification establishes performance requirements
1.3 This standard may involve hazardous materials, opera-
for the short-term utilization of a single-use, balloon-retention
tions, and equipment. This standard does not purport to
catheter, French sizes 12 through 26 inclusive, used by the
address all of the safety concerns associated with its use. It is
medical professions for providing a means of bladder drainage
the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish
by means of the urethra. The product is manufactured in
appropriate safety and health practices and determine the
various sizes and materials such as latex, silicone, rubber, and
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
various polymers (as well as combinations of these) and is
provided nonsterile for sterilization and sterile for single-use
2. Referenced Documents
only. Catheters whose surface has been chemically treated to
2.1 ASTM Standards:
effect biocompatibility or microbial properties may be tested to
F 748 Practice for Selecting Generic Biological Test Meth-
this specification.
ods for Materials and Devices
1.2 Exclusions—Long-term indwelling usage (over 30
2.2 Other Documents:
days) is encountered with this product, but not commonly, and
ISO/AAMI/ANSI 10993–1 Biological Testing of Medical
is therefore considered an exception to this specification.
and Dental Material and Devices — Part 1: Guidance on
Similarly, the use of such catheters for nonurethral catheter-
Selection of Tests
ization (such as for nephrostomy, suprapubic cystostomy,
U.S. Pharmacopeia
ureterostomy, gastrostomy, enemas, etc.) is excluded from the
scope of this specification. Likewise, three lumen catheters,
3 3. Terminology
30-cm balloon and pediatric catheters, and catheters whose
3.1 Definitions of Terms:
surface has been chemically treated to enhance their lubricity
have not been tested to this specification and excluded from the
1 2
This performance specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 13.01.
F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices and is the direct responsibility Available from American National Standards Institute, 25 W. 43rd St., 4th
of Subcommittee F04.34 on Urological Materials and Devices. Floor, New York, NY 10036.
Current edition approved October 10, 1999. Published December 1999. Origi- Available from U.S. Pharmacopeia, 12601 Twinbrook Pkwy., Rockville, MD
nally published as F 623 – 81. Last previous edition F 623 – 89. 20852.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 623
3.1.1 balloon (Foley) catheter—an indwelling catheter re- use this referee test method in his usual inspection and quality
tained in the bladder by a balloon that is inflated with liquid. control.
3.1.1.1 Discussion—A two-way balloon catheter has a 3.1.7 sterility—generally, the state of being free of micro-
drainage lumen and inflation lumen (see Fig. 1). Common organisms. For purposes of this specification, sterility is
3 3
balloon inflation sizes are 5 cm with the 5-cm balloon being defined as freedom from microorganisms when tested accord-
used to hold the catheter in place for normal usage, and 30 cm ing to the methodology defined by the USP for nonparenteral
where so designated when a larger balloon is used. A three-way devices.
balloon catheter is used for continuous bladder irrigation, and 3.1.8 tolerances—the allowable deviation from a standard
features both a drainage lumen and an irrigation lumen (but as size. In usual engineering practice, the maximum permitted
noted above is excluded from consideration in this specifica- size is denoted by a plus sign followed by the tolerance and the
tion). minimum permitted size denoted by a minus sign followed by
3.1.2 FDA—the abbreviation for the Food and Drug Admin- the tolerance. In this standard the label French size has
istration, the Federal agency under Health, Education, and tolerances given for several dimensions. For example, +3, −1
Welfare responsible for the regulation of medical device means that a nominal 14 label French size can be permitted to
products. go as high as 17, but not below 13. Another way of writing
3.1.3 French size—a scale used for denoting the size of tolerance, when both tolerances are equal, is: 62, meaning the
other tubular instruments and devices, each unit being roughly 14 label French size must be between 12 French and 16 French.
equivalent to 0.33 mm in diameter. Label French sizes are as 3.1.9 USP—U.S. Phaarmacopeia
follows:
4. Requirements
French Size Outside Diameter, in. (mm)
12 0.157 (4.0) 4.1 Flow Rate through Drainage Lumen—Label French size
13 0.171 (4.3)
catheters 14 through 24 inclusive shall have a minimum
14 0.184 (4.7)
average flow rate of 100 cm /min, and a label French size 12
15 0.197 (5.0)
16 0.210 (5.3) catheter shall have a flow rate of 70 cm /min. Tests shall be
17 0.223 (5.7)
conducted in accordance with 6.1.
18 0.236 (6.0)
4.2 Balloon Integrity (Resistance to Rupture)—The infla-
19 0.249 (6.3)
20 0.262 (6.7)
tion balloon must be inflated easily with distilled or deionized
21 0.276 (7.0)
water to labeled volume without showing any evidence of
22 0.289 (7.3)
breakage throughout the test period. Leakage and failure to
23 0.302 (7.7)
24 0.315 (8.0)
deflate are dealt with in 4.4 and 4.6. Tests shall be conducted
25 0.328 (8.3)
in accordance with 6.2.
26 0.341 (8.7)
4.3 Inflated Balloon Response to Traction—The entire bal-
3.1.4 lumen—the channel within a tube.
loon of catheters label French size 14 through 26 shall not pass
3.1.5 proximal—refers to the balloon end of the catheter,
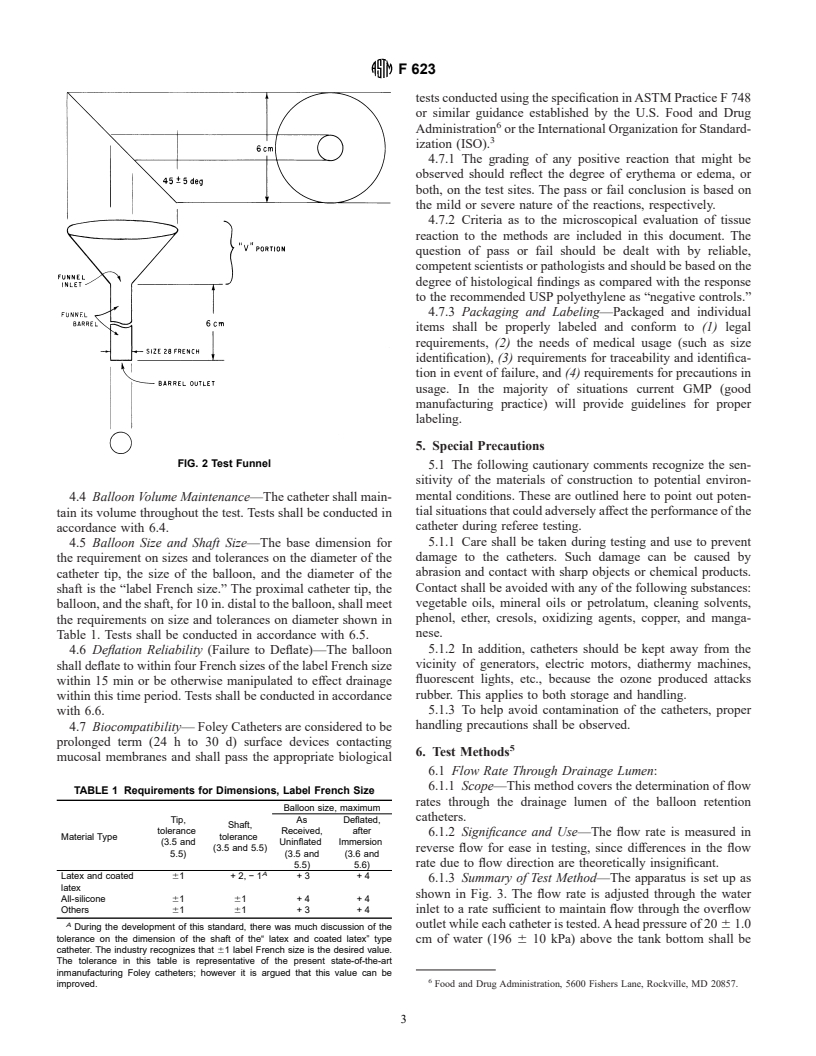
into or through the funnel barrel (Fig. 2). Tests shall be
since when in position for clinical use, the balloon end is
conducted in accordance with 6.3.
proximal or closest to the patient.
3.1.6 referee test method—the method cited in the published
Supporting data for this specification, which provides a rationale of the
specification for the device. This method and the correspond-
performance requirements and test methods, is available on loan from ASTM
ing requirements will be invoked when the performance of the
Headquarters, 100 Barr Harbor Dr., PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA
medical device will be questioned. The manufacturer need not
19428–2959. Request Research Report F04-1003.
FIG. 1 Balloon Retention (Foley) Type Catheter
F 623
tests conducted using the specification in ASTM Practice F 748
or similar guidance established by the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration or the International Organization for Standard-
ization (ISO).
4.7.1 The grading of any positive reaction that might be
observed should reflect the degree of erythema or edema, or
both, on the test sites. The pass or fail conclusion is based on
the mild or severe nature of the reactions, respectively.
4.7.2 Criteria as to the microscopical evaluation of tissue
reaction to the methods are included in this document. The
question of pass or fail should be dealt with by reliable,
competent scientists or pathologists and should be based on the
degree of histological findings as compared with the response
to the recommended USP polyethylene as “negative controls.”
4.7.3 Packaging and Labeling—Packaged and individual
items shall be properly labeled and conform to (1) legal
requirements, (2) the needs of medical usage (such as size
identification), (3) requirements for traceability and identifica-
tion in event of failure, and (4) requirements for precautions in
usage. In the majority of situations current GMP (good
manufacturing practice) will provide guidelines for proper
labeling.
5. Special Precautions
FIG. 2 Test Funnel
5.1 The following cautionary comments recognize the sen-
sitivity of the materials of construction to potential environ-
mental conditions. These are outlined here to point out poten-
4.4 Balloon Volume Maintenance—The catheter shall main-
tial situations that could adversely affect the performance of the
tain its volume throughout the test. Tests shall be conducted in
catheter during referee testing.
accordance with 6.4.
5.1.1 Care shall be taken during testing and use to prevent
4.5 Balloon Size and Shaft Size—The base dimension for
damage to the catheters. Such damage can be caused by
the requirement on sizes and tolerances on the diameter of the
abrasion and contact with sharp objects or chemical products.
catheter tip, the size of the balloon, and the diameter of the
Contact shall be avoided with any of the following substances:
shaft is the “label French size.” The proximal catheter tip, the
vegetable oils, mineral oils or petrolatum, cleaning solvents,
balloon, and the shaft, for 10 in. distal to the balloon, shall meet
phenol, ether, cresols, oxidizing agents, copper, and manga-
the requirements on size and tolerances on diameter shown in
nese.
Table 1. Tests shall be conducted in accordance with 6.5.
5.1.2 In addition, catheters should be kept away from the
4.6 Deflation Reliability (Failure to Deflate)—The balloon
vicinity of generators, electric motors, diathermy machines,
shall deflate to within four French sizes of the label French size
fluorescent lights, etc., because the ozone produced attacks
within 15 min or be otherwise manipulated to effect drainage
rubber. This applies to both storage and handling.
within this time period. Tests shall be conducted in accordance
5.1.3 To help avoid contamination of the catheters, proper
with 6.6.
handling precautions shall be observed.
4.7 Biocompatibility— Foley Catheters are considered to be
prolonged term (24 h to 30 d) surface devices contacting
6. Test Methods
mucosal membranes and shall pass the appropriate biological
6.1 Flow Rate Through Drainage Lumen:
6.1.1 Scope—This method covers the determination of flow
TABLE 1 Requirements for Dimensions, Label French Size
rates through the drainage lumen of the balloon retention
Balloon size, maximum
catheters.
Tip,
As Deflated,
Shaft,
tolerance Received, after
6.1.2 Significance and Use—The flow rate is measured in
Material Type tolerance
(3.5 and Uninflated Immersion
(3.5 and 5.5) reverse flow for ease in testing, since differences in the flow
5.5) (3.5 and (3.6 and
5.5) 5.6) rate due to flow direction are theoretically insignificant.
A
Latex and coated 61 +2,−1 +3 +4
6.1.3 Summary of Test Method—The apparatus is set up as
latex
shown in Fig. 3. The flow rate is adjusted through the water
All-silicone 61 61+4 +4
inlet to a rate sufficient to maintain flow through the overflow
Others 61 61+3 +4
A
outlet while each catheter is tested. A head pressure of 20 6 1.0
During the development of this standard, there was much discussion of the
tolerance on the dimension of the shaft of the“ latex and coated latex” type
cm of water (196 6 10 kPa) above the tank bottom shall be
catheter. The industry recognizes that 61 label French size is the desired value.
The tolerance in this table is representative of the present state-of-the-art
inmanufacturing Foley catheters; however it is argued that this value can be
improved. Food and Drug Administration, 5600 Fishers Lane, Rockville, MD 20857.
F 623
FIG. 3 Flow Rate Apparatus for Reverse Flow Technique
maintained throughout the test to approximate actual physi- 6.1.7.2 Inflate the retention balloon of the test specimen
ologic conditions. The overflow outlet should not be covered with distilled or deionized water to labeled volume. For
by water. example, a 5-cm balloon should be inflated with 5 + 2, − 0
6.1.4 Apparatus: cm of distilled or deionized water (or as recommended by the
6.1.4.1 Water Reservoir, capable of maintaining 20 6 1.0 individual manufacturer on the label).
cm (7.9 6 0.4 in.) of water (196 6 10 kPa) above the tip of the 6.1.7.3 Connect the catheter to catheter connector and open
catheter connection throughout the test as shown in Fig. 3. the stopcock. The tip of the catheter connection at the junction
6.1.4.2 Graduated Cylinder, calibrated for suitable mea- of catheter on-off valve should be level with the bottom of the
surement of the effluent. tank 61 cm and it should deliver fluid at 20 6 1 cm (196 6 10
6.1.4.3 Syringe, with appropriate tip for inflation of catheter kPa) head pressure at that junction.
balloon. 6.1.7.4 Establish the inflow and outflow equilibrium prior to
6.1.5 Precautions: test measurements.
6.1.5.1 Overflow should not be covered. Head pressure 6.1.7.5 Record the amount of water flowing through the
must be kept constant; water should always be exiting through catheter drainage lumen in 1 min. Express results in cubic
the overflow outlet. centimetres per minute as flow rate. Test each catheter three
6.1.5.2 Establish equilibrium prior to testing. times and calculate the average flow rate for each catheter.
6.1.5.3 Flow rates through all fittings must exceed that of 6.1.8 Interpretation of Results—Flow rates for catheters
the catheter be
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.