ASTM C1662-17
(Practice)Standard Practice for Measurement of the Glass Dissolution Rate Using the Single-Pass Flow-Through Test Method
Standard Practice for Measurement of the Glass Dissolution Rate Using the Single-Pass Flow-Through Test Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This practice provides a prescriptive description of the design of a SPFT test apparatus and identifies aspects of the performance of SPFT tests and interpretation of test results that must be addressed by the experimenter to provide confidence in the measured dissolution rate.
5.2 The SPFT test method described in this practice can be used to characterize various aspects of glass corrosion behavior that can be utilized in a mechanistic model for calculating long-term behavior of a nuclear waste glass.
5.3 Depending on the values of test parameters that are used, the results of SPFT tests can be used to measure the intrinsic dissolution rate of a glass, the temperature and pH dependencies of the rate, and the effects of various dissolved species on the dissolution rate.
5.4 The reacted sample recovered from a test may be examined with surface analytical techniques, such as scanning electron microscopy, to further characterize the corrosion behavior. Such examinations may provide evidence regarding whether the glass is dissolving stoichiometrically, if particular leached layers and secondary phases were formed on the specimen surface, and so forth. These occurrences may impact the accuracy of the glass dissolution rate that is measured using this method. This practice does not address the analysis of solid reaction materials.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes a single-pass flow-through (SPFT) test method that can be used to measure the dissolution rate of a homogeneous silicate glass, including nuclear waste glasses, in various test solutions at temperatures less than 100°C. Tests may be conducted under conditions in which the effects from dissolved species on the dissolution rate are minimized to measure the forward dissolution rate at specific values of temperature and pH, or to measure the dependence of the dissolution rate on the concentrations of various solute species.
1.2 Tests are conducted by pumping solutions in either a continuous or pulsed flow mode through a reaction cell that contains the test specimen. Tests must be conducted at several solution flow rates to evaluate the effect of the flow rate on the glass dissolution rate.
1.3 This practice excludes static test methods in which flow is simulated by manually removing solution from the reaction cell and replacing it with fresh solution.
1.4 Tests may be conducted with demineralized water, chemical solutions (such as pH buffer solutions, simulated groundwater solutions, and brines), or actual groundwater.
1.5 Tests may be conducted with crushed glass of a known size fraction or monolithic specimens having known geometric surface area. The reacted solids may be examined to provide additional information regarding the behavior of the material in the test and the reaction mechanism.
1.6 Tests may be conducted with glasses containing radionuclides. However, this test method does not address safety issues for radioactive samples.
1.7 Data from these tests can be used to determine the values of kinetic model parameters needed to calculate the glass corrosion behavior in a disposal system over long periods (for example, see Practice C1174).
1.8 This practice must be performed in accordance with all quality assurance requirements for acceptance of the data.
1.9 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.10 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.11 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guid...
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1662 − 17
Standard Practice for
Measurement of the Glass Dissolution Rate Using the
1
Single-Pass Flow-Through Test Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1662; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 1.8 This practice must be performed in accordance with all
quality assurance requirements for acceptance of the data.
1.1 This practice describes a single-pass flow-through
(SPFT)testmethodthatcanbeusedtomeasurethedissolution 1.9 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
rate of a homogeneous silicate glass, including nuclear waste standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
glasses, in various test solutions at temperatures less than only.
100°C. Tests may be conducted under conditions in which the
1.10 This standard does not purport to address all of the
effects from dissolved species on the dissolution rate are
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
minimized to measure the forward dissolution rate at specific
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
valuesoftemperatureandpH,ortomeasurethedependenceof
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
the dissolution rate on the concentrations of various solute
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
species.
1.11 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.2 Tests are conducted by pumping solutions in either a
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
continuous or pulsed flow mode through a reaction cell that
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
contains the test specimen. Tests must be conducted at several
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
solution flow rates to evaluate the effect of the flow rate on the
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
glass dissolution rate.
1.3 This practice excludes static test methods in which flow
2. Referenced Documents
is simulated by manually removing solution from the reaction
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
cell and replacing it with fresh solution.
C92Test Methods for Sieve Analysis and Water Content of
1.4 Tests may be conducted with demineralized water,
Refractory Materials
chemical solutions (such as pH buffer solutions, simulated
C162Terminology of Glass and Glass Products
groundwater solutions, and brines), or actual groundwater.
C429Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Raw Materials for
Glass Manufacture
1.5 Tests may be conducted with crushed glass of a known
C693Test Method for Density of Glass by Buoyancy
sizefractionormonolithicspecimenshavingknowngeometric
C859Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
surface area. The reacted solids may be examined to provide
C1109Practice for Analysis of Aqueous Leachates from
additionalinformationregardingthebehaviorofthematerialin
Nuclear Waste Materials Using Inductively Coupled
the test and the reaction mechanism.
Plasma-Atomic Emission Spectroscopy
1.6 Tests may be conducted with glasses containing radio-
C1174PracticeforEvaluationoftheLong-TermBehaviorof
nuclides. However, this test method does not address safety
Materials Used in Engineered Barrier Systems (EBS) for
issues for radioactive samples.
Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste
1.7 Data from these tests can be used to determine the
C1220TestMethodforStaticLeachingofMonolithicWaste
values of kinetic model parameters needed to calculate the
Forms for Disposal of Radioactive Waste
glasscorrosionbehaviorinadisposalsystemoverlongperiods
C1285Test Methods for Determining Chemical Durability
(for example, see Practice C1174).
of Nuclear, Hazardous, and Mixed Waste Glasses and
MultiphaseGlassCeramics:TheProductConsistencyTest
(PCT)
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear
Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.13 on Spent Fuel
2
and High Level Waste. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2017. Published December 2017. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as C1662–10. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/C1662-17. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1662 − 17
C1463Practices for Dissolving Gl
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1662 − 10 C1662 − 17
Standard Practice for
Measurement of the Glass Dissolution Rate Using the
1
Single-Pass Flow-Through Test Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1662; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice describes a single-pass flow-through (SPFT) test method that can be used to measure the dissolution rate of
a homogeneous silicate glass, including nuclear waste glasses, in various test solutions at temperatures less than 100°C. Tests may
be conducted under conditions in which the effects from dissolved species on the dissolution rate are minimized to measure the
forward dissolution rate at specific values of temperature and pH, or to measure the dependence of the dissolution rate on the
concentrations of various solute species.
1.2 Tests are conducted by pumping solutions in either a continuous or pulsed flow mode through a reaction cell that contains
the test specimen. Tests must be conducted at several solution flow rates to evaluate the effect of the flow rate on the glass
dissolution rate.
1.3 This practice excludes static test methods in which flow is simulated by manually removing solution from the reaction cell
and replacing it with fresh solution.
1.4 Tests may be conducted with demineralized water, chemical solutions (such as pH buffer solutions, simulated groundwater
solutions, and brines), or actual groundwater.
1.5 Tests may be conducted with crushed glass of a known size fraction or monolithic specimens having known geometric
surface area. The reacted solids may be examined to provide additional information regarding the behavior of the material in the
test and the reaction mechanism.
1.6 Tests may be conducted with glasses containing radionuclides. However, this test method does not address safety issues for
radioactive samples.
1.7 Data from these tests can be used to determine the values of kinetic model parameters needed to calculate the glass corrosion
behavior in a disposal system over long periods (for example, see Practice C1174).
1.8 This practice must be performed in accordance with all quality assurance requirements for acceptance of the data.
1.9 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.10 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.11 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C92 Test Methods for Sieve Analysis and Water Content of Refractory Materials
C169C162 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Soda-Lime and Borosilicate GlassTerminology of Glass and Glass Products
C429 Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Raw Materials for Glass Manufacture
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C26 on Nuclear Fuel Cycle and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C26.13 on Spent Fuel and High
Level Waste.
Current edition approved June 1, 2010Nov. 15, 2017. Published July 2010December 2017. Originally approved in 2007. Last previous edition approved in 20072010 as
C1662 - 07.C1662 – 10. DOI: 10.1520/C1662-10.10.1520/C1662-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1662 − 17
C693 Test Method for Density of Glass by Buoyancy
C859 Terminology Relating to Nuclear Materials
C1109 Practice for Analysis of Aqueous Leachates from Nuclear Waste Materials Using Inductively Coupled Plas
...







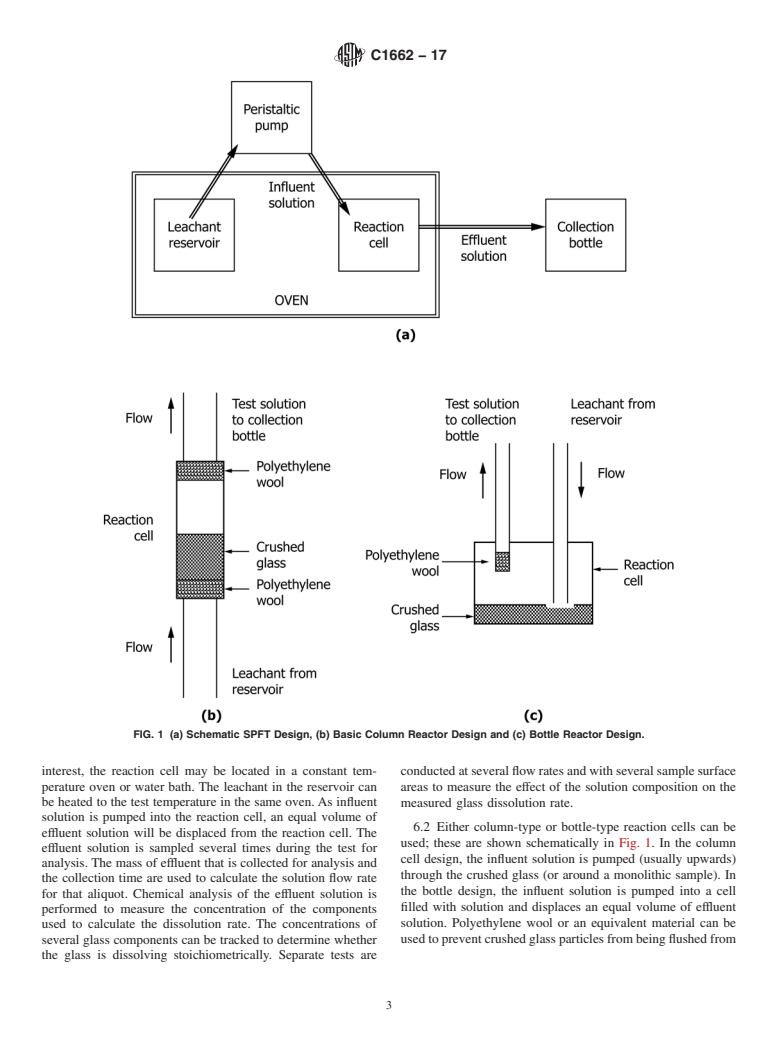


Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.