ASTM E2954-15(2022)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Axial Compression Test of Reinforced Plastic and Polymer Matrix Composite Vertical Members
Standard Test Method for Axial Compression Test of Reinforced Plastic and Polymer Matrix Composite Vertical Members
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The compressive properties obtained by axial compression will provide information such as: modulus of elasticity, stress at proportional limit and compressive strength for the end support, and lateral bracing condition tested.
5.2 This test method addresses only full-sized specimens for determination of compressive strength and compressive modulus of elasticity intended for application to actual length members with end conditions and lateral bracing as intended.
Note 1: The effective length of the column with respect to buckling is affected by the end conditions. A fixed end condition results in an effective length for buckling that is less than the actual length of the column, by as much as 50 %.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of vertical members in axial compression for “full-sized” specimens with various end conditions with constant cross-sections throughout the length.
1.2 This test method is limited to reinforced plastic and polymer matrix composite materials and covers the determination of the compressive properties of structural members. The method is intended primarily for members of rectangular cross section, but is also applicable to irregularly shaped studs, round posts, or special sections.
1.3 This test method covers short-term axial load testing under standard indoor atmospheric conditions. It does not address: sampling, the ability of the material to carry a sustained long-term load, design load derivations, temperature effects, performance under freeze/thaw or salt spray exposure conditions, chemical/UV exposure effects, or engineering analysis/modeling needed to extrapolate the results to conditions other than those tested. Each of these factors, and potentially others, need to be considered by the design professional or product standard development committee before using the information generated by this test method to assess structural adequacy.
1.4 Short sections are not covered in this test method and should be tested using a material test standard such as Test Method D6108 or Test Methods D198.
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.7 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: E2954 − 15 (Reapproved 2022)
Standard Test Method for
Axial Compression Test of Reinforced Plastic and Polymer
Matrix Composite Vertical Members
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2954; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of vertical
1.7 This international standard was developed in accor-
members in axial compression for “full-sized” specimens with
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
various end conditions with constant cross-sections throughout
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
the length.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
1.2 This test method is limited to reinforced plastic and
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
polymer matrix composite materials and covers the determina-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
tion of the compressive properties of structural members. The
method is intended primarily for members of rectangular cross 2. Referenced Documents
section,butisalsoapplicabletoirregularlyshapedstuds,round 2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
posts, or special sections.
D198 Test Methods of Static Tests of Lumber in Structural
1.3 This test method covers short-term axial load testing
Sizes
under standard indoor atmospheric conditions. It does not D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
address: sampling, the ability of the material to carry a D2915 Practice for Sampling and Data-Analysis for Struc-
sustained long-term load, design load derivations, temperature tural Wood and Wood-Based Products
effects, performance under freeze/thaw or salt spray exposure D3878 Terminology for Composite Materials
conditions, chemical/UV exposure effects, or engineering D6108 Test Method for Compressive Properties of Plastic
analysis/modeling needed to extrapolate the results to condi- Lumber and Shapes
tions other than those tested. Each of these factors, and E4 Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Test-
potentially others, need to be considered by the design profes- ing Machines
sional or product standard development committee before
E6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Testing
using the information generated by this test method to assess E83 Practice for Verification and Classification of Exten-
structural adequacy.
someter Systems
E575 Practice for Reporting Data from Structural Tests of
1.4 Short sections are not covered in this test method and
Building Constructions, Elements, Connections, and As-
should be tested using a material test standard such as Test
semblies
Method D6108 or Test Methods D198.
E631 Terminology of Building Constructions
1.5 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical 3. Terminology
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
3.1 Definitions—Terminology D3878 defines terms relating
and are not considered standard.
to high-modulus fibers and their composites. Terminology
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D883definestermsrelatingtoplastics.TerminologyE6defines
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
terms relating to mechanical testing. In the event of a conflict
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
between terms, Terminology D3878 shall have precedence
over the other standards.
3.1.1 For definitions of terms in this standard, see Termi-
nology E631.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E06 on
Performance of Buildings and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E06.11
on Horizontal and Vertical Structures/Structural Performance of Completed Struc-
tures. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved May 1, 2022. Published May 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 2015. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as E2954–15. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/E2954-15R22. the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
E2954 − 15 (2022)
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard: 5. Significance and Use
3.2.1 full-sized specimen—full-sized specimens (meaning
5.1 The compressive properties obtained by axial compres-
full cross-sectional area) tested with standard lengths with
sion will provide information such as: modulus of elasticity,
various end conditions and bracing conditions about the weak
stress at proportional limit and compressive strength for the
and strong member axes. The end conditions addressed in-
end support, and lateral bracing condition tested.
clude: eccentricity, fixed, pinned.
5.2 Thistestmethodaddressesonlyfull-sizedspecimensfor
3.2.2 short sections (not considered in this test method)—
determination of compressive strength and compressive modu-
compressive test sections having a maximum length, L, less
lus of elasticity intended for application to actual length
than 17 times the least radius of gyration, r, where r = √(I/A).
members with end conditions and lateral bracing as intended.
3.3 Symbols:
NOTE 1—The effective length of the column with respect to buckling is
3.3.1 σ = compressive strength.
affectedbytheendconditions.Afixedendconditionresultsinaneffective
3.3.2 σ' = compressive stress at proportional limit. length for buckling that is less than the actual length of the column, by as
much as 50 %.
3.3.3 E = compressive modulus of elasticity.
3.3.4 E' = apparent modulus of elasticity.
6. Apparatus
3.3.5 A = cross-sectional area.
6.1 Drive Mechanism—Adrive mechanism for imparting to
3.3.6 ∆ = change in length from original gage length at
a movable loading head a uniform controlled velocity with
L
proportional limit.
respect to the stationary base.
3.3.7 L = gage length of compression column.
G
6.2 Load Indicator—A load-indicating mechanism capable
3.3.8 P = maximum load borne by column loaded to of showing the total compressive force on the specimen. This
max
failure.
force-measuring system shall be calibrated to ensure accuracy
in accordance with Practices E4.Aschematic representation of
3.3.9 P' = applied load at proportional limit, lbf (N).
the typical test set up is shown in Fig. 1.
4. Summary of Test Method
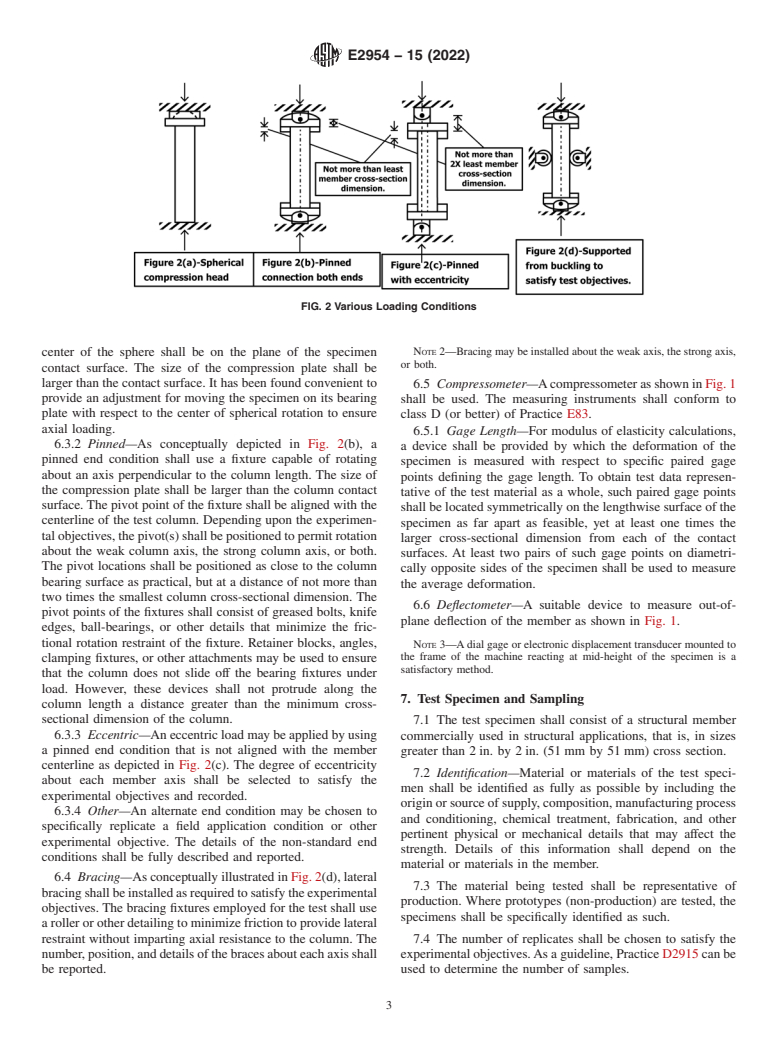
6.3 End Conditions—The end conditions used for the test
shall be chosen to satisfy the experimental objectives. Options
4.1 The structural member is subjected to a compressive
force distributed on the contact surface of the specimen in a include:
direction generally parallel to the longitudinal axis. The speci- 6.3.1 Fixed—With a fixed end condition as conceptually
mens are either loaded to failure or proof loaded. The test depicted in Fig. 2(a), a spherical bearing block may be used at
method is intended to determine the axial compressive strength either end of the column to ensure uniform contact. When
of standard full-size specimens tested with various end condi- spherical bearing blocks are used, the radius of the sphere shall
tions including: built-in eccentricity, pinned, fixed, or as be as small as practicable, in order to facilitate adjustment of
required to accomplish the experimental objective. Lateral the bearing plate to the specimen, and yet large enough to
bracing may be installed as required to accomplish the experi- provide adequate spherical bearing area. This radius is usually
mental objective. one to two times the greatest cross-section dimension. The
FIG. 1 Test Set-Up
E2954 − 15 (2022)
FIG. 2 Various Loading Conditions
NOTE 2—Bracing may be installed about the weak axis, the strong axis,
center of the sphere shall be on the plane of the specimen
or both.
contact surface. The size of the compression plate shall be
larger than the contact surface. It has been found convenient to
6.5 Compressometer—AcompressometerasshowninFig.1
provide an adjustment for moving the specimen on its bearing shall be used. The measuring instruments shall conform to
plate with respect to the center of spherical rotation to ensure
class D (or better) of Practice E83.
axial loading.
6.5.1 Gage Length—For modulus of elasticity calculations,
6.3.2 Pinned—As conceptually depicted in Fig. 2(b), a
a device shall be provided by which the deformation of the
pinned end condition shall use a fixture capable of rotating
specimen is measured with respect to specific paired gage
about an axis perpendicular to the column length. The size of
points defining the gage length. To obtain test data represen-
the compression plate shall be larger than the column contact
tative of the test material as a whole, such paired gage points
surface. The pivot point of the fixture shall be aligned with the
shall be located symmetrically on the lengthwise surface of the
centerline of the test column. Depending upon the experimen-
specimen as far apart as feasible, yet at least one times the
talobjectives,thepivot(s)shallbepositionedtopermitrotation
larger cross-sectional dimension from each of the contact
about the weak column axis, the strong column axis, or both.
surfaces. At least two pairs of such gage points on diametri-
The pivot locations shall be positioned as close to the column
cally opposite sides of the specimen shall be used to measure
bearing surface as practical, but at a distance of not more than
the average deformation.
two times the smallest column cross-sectional
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.