ASTM F2136-18(2024)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Notched, Constant Ligament-Stress (NCLS) Test to Determine Slow-Crack-Growth Resistance of HDPE Resins or HDPE Corrugated Pipe
Standard Test Method for Notched, Constant Ligament-Stress (NCLS) Test to Determine Slow-Crack-Growth Resistance of HDPE Resins or HDPE Corrugated Pipe
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 This test method does not purport to interpret the data generated.
4.2 This test method is intended to compare slow-crack-growth (SCG) resistance for a limited set of HDPE resins.
4.3 This test method may be used on virgin HDPE resin compression-molded into a plaque or on extruded HDPE corrugated pipe that is chopped and compression-molded into a plaque (see 7.1.1 for details).
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is used to determine the susceptibility of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resins or corrugated pipe to slow-crack-growth under a constant ligament-stress in an accelerating environment. This test method is intended to apply only to HDPE of a limited melt index (0.947 g/cm3 to 0.955 g/cm3). This test method may be applicable for other materials, but data are not available for other materials at this time.
1.2 This test method measures the failure time associated with a given test specimen at a constant, specified, ligament-stress level.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412, and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D1600, unless otherwise specified.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F2136 − 18 (Reapproved 2024)
Standard Test Method for
Notched, Constant Ligament-Stress (NCLS) Test to
Determine Slow-Crack-Growth Resistance of HDPE Resins
or HDPE Corrugated Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2136; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.1 This test method is used to determine the susceptibility
of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) resins or corrugated pipe D1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plas-
tics (Withdrawn 2024)
to slow-crack-growth under a constant ligament-stress in an
accelerating environment. This test method is intended to apply D1822 Test Method for Determining the Tensile-Impact
Resistance of Plastics
only to HDPE of a limited melt index (<0.4 to 0.15) and
3 3
density range (>0.947 g ⁄cm to 0.955 g ⁄cm ). This test method D4703 Practice for Compression Molding Thermoplastic
Materials into Test Specimens, Plaques, or Sheets
may be applicable for other materials, but data are not available
for other materials at this time. D5397 Test Method for Evaluation of Stress Crack Resis-
tance of Polyolefin Geomembranes Using Notched Con-
1.2 This test method measures the failure time associated
stant Tensile Load Test
with a given test specimen at a constant, specified, ligament-
E4 Practices for Force Calibration and Verification of Test-
stress level.
ing Machines
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
F412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems
and are not considered standard.
3. Summary of Test Method
1.4 Definitions are in accordance with Terminology F412,
and abbreviations are in accordance with Terminology D1600,
3.1 This test method subjects a dumbbell-shaped, notched
unless otherwise specified. test-specimen (Fig. 1) to a constant ligament-stress in the
presence of a surface-active agent at an elevated temperature.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
It differs from Test Method D5397 in that a constant ligament
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
stress is used instead of a constant tensile load.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
4. Significance and Use
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1 This test method does not purport to interpret the data
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
generated.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.2 This test method is intended to compare slow-crack-
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
growth (SCG) resistance for a limited set of HDPE resins.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
4.3 This test method may be used on virgin HDPE resin
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
compression-molded into a plaque or on extruded HDPE
1 2
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.40 on Test contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Methods. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved Feb. 1, 2024. Published February 2024. Originally the ASTM website.
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2018 as F2136 – 18. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/F2136-18R24. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F2136 − 18 (2024)
T = thickness.
W = specimen width.
NOTE 1—The test specimen is intended to have the same geometry used for Test Method D5397 specimens. The length of the specimen can be changed
to suit the design of the test apparatus. However, there should be a constant neck section with length at least 0.5 in. (13 mm) long.
NOTE 2—It is preferable to modify the specimen die so that the attachment holes are punched out at the same time as the specimen rather than punching
or machining them into the specimen at a later time. If the attachment holes are introduced at a later time, it is extremely important that they be carefully
aligned so as to avoid adding a twisting component to the stress being placed on the specimen.
FIG. 1 Notching Position
corrugated pipe that is chopped and compression-molded into method for producing a constant ligament stress. Determine the
a plaque (see 7.1.1 for details). zero-load offset and lever-arm ratio for each test station, using
a force standard that complies with Practices E4. The load on
5. Apparatus
the specimen shall be accurate to 0.5 % of the calculated or
applied load. The bath solution temperature shall be set at
5.1 Blanking Die—A die suitable for cutting test specimens.
122 °F 6 2 °F (50 °C 6 1 °C).
Acceptable dies are: the type L die per Test Method D1822,
with holes drilled or punched in the tab areas after die cutting;
5.3 Notching Device—Notch depth is an important variable
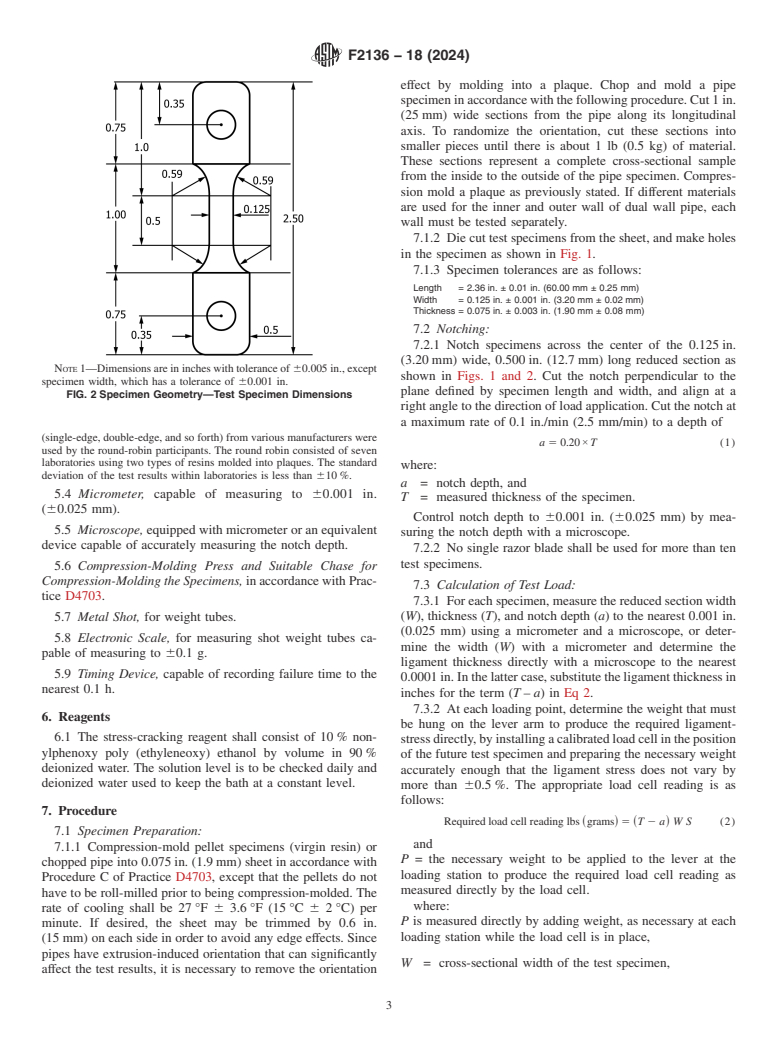
a die with the dimensions and tolerances specified in Fig. 2.
that must be controlled. Paragraph 7.2.1 describes the notching
procedure and type of apparatus used. The approximate thick-
5.2 Stress-Crack Testing Apparatus—A lever loading
ness of the blade should be 0.2 mm to 0.3 mm.
machine, with a lever arm ratio of 2:1 to 5:1 similar to that
described in Test Method D5397. Alternatively, the tensile load
NOTE 1—A round robin was conducted to determine the effect of types
may be applied directly using dead weights or any other of blades on the notch depth. In this study, several types of steel blades
F2136 − 18 (2024)
effect by molding into a plaque. Chop and mold a pipe
specimen in accordance with the following procedure. Cut 1 in.
(25 mm) wide sections from the pipe along its longitudinal
axis. To randomize the orientation, cut these sections into
smaller pieces until there is about 1 lb (0.5 kg) of material.
These sections represent a complete cross-sectional sample
from the inside to the outside of the pipe specimen. Compres-
sion mold a plaque as previously stated. If different materials
are used for the inner and outer wall of dual wall pipe, each
wall must be tested separately.
7.1.2 Die cut test specimens from the sheet, and make holes
in the specimen as shown in Fig. 1.
7.1.3 Specimen tolerances are as follows:
Length = 2.36 in. ± 0.01 in. (60.00 mm ± 0.25 mm)
Width = 0.125 in. ± 0.001 in. (3.20 mm ± 0.02 mm)
Thickness = 0.075 in. ± 0.003 in. (1.90 mm ± 0.08 mm)
7.2 Notching:
7.2.1 Notch specimens across the center of the 0.125 in.
(3.20 mm) wide, 0.500 in. (12.7 mm) long reduced section as
NOTE 1—Dimensions are in inches with tolerance of 60.005 in., except
shown in Figs. 1 and 2. Cut the notch perpendicular to the
specimen width, which has a tolerance of 60.001 in.
plane defined by specimen length and width, and align at a
FIG. 2 Specimen Geometry—Test Specimen Dimensions
right angle to the direction of load application. Cut the notch at
a maximum rate of 0.1 in./min (2.5 mm/min) to a depth of
(single-edge, double-edge, and so forth) from various manufacturers were
a 5 0.20 × T (1)
used by the round-robin participants. The round robin consisted of seven
laboratories using two types of resins molded into plaques. The standard
where:
deviation of the test results within laboratories is less than 610 %.
a = notch depth, and
5.4 Micrometer, capable of measuring to 60.001 in.
T = measured thickness of the specimen.
(60.025 mm).
C
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.