ASTM D7252-17
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of Monomer and Isomers in Isocyanates
Standard Test Method for Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of Monomer and Isomers in Isocyanates
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is used for research or for quality control to characterize isocyanates used in polyurethane products.
SCOPE
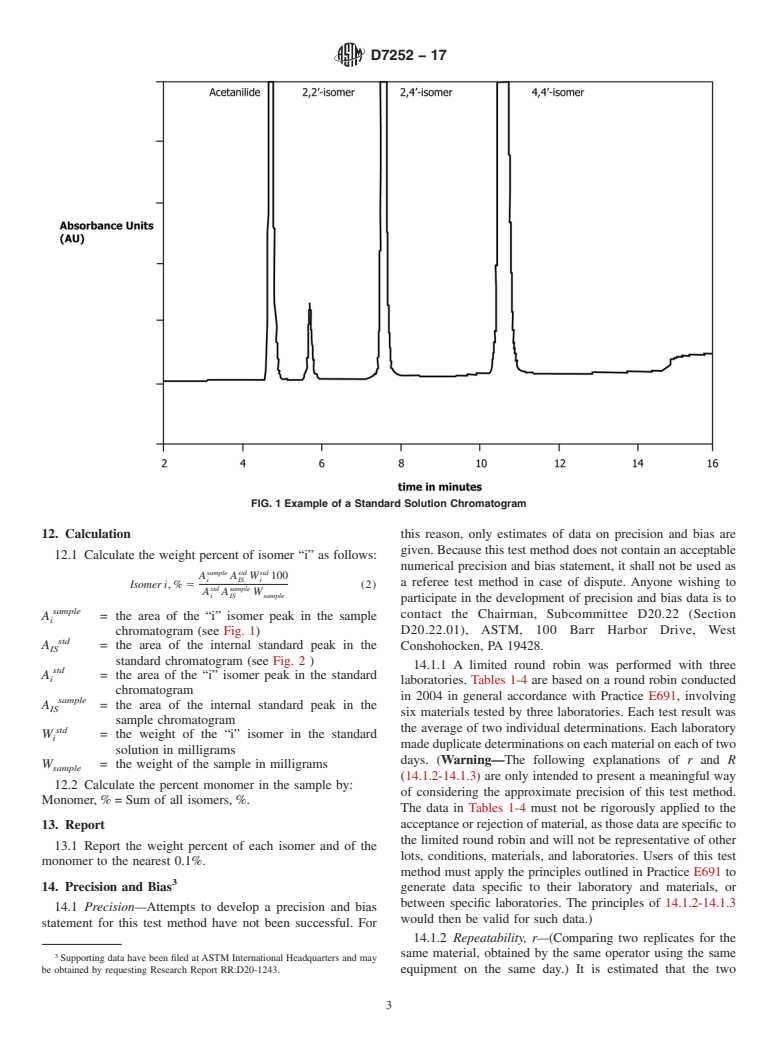
1.1 This test method determines the percent by weight of monomeric isomers and total monomer in crude or modified isocyanates. The test method is applicable to methylene di(phenylisocyanate) (MDI) and polymeric (methylene phenylisocyanate) (PMDI). (See Note 1.)
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1: There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D7252 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of Monomer and
1
Isomers in Isocyanates
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7252; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method determines the percent by weight of 4.1 The sample is reacted (derivatized) with methanol to
monomeric isomers and total monomer in crude or modified
form a mixture of methyl urethanes. The urethanes mixture is
isocyanates.Thetestmethodisapplicabletomethylenedi(phe- then separated by normal phase high performance liquid
nylisocyanate)(MDI)andpolymeric(methylenephenylisocya-
chromatography (HPLC). The separated, derivatized isomers
nate) (PMDI). (See Note 1.) are quantified through the use of an internal standard.
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded
5. Significance and Use
as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
5.1 This test method is used for research or for quality
standard.
control to characterize isocyanates used in polyurethane prod-
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ucts.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
6. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
6.1 High Performance Liquid Chromatograph, consisting
of:
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
6.1.1 Binary (or greater) solvent pump, capable of main-
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
taining a pulse-free flow rate of 1-3 milliliters per minute
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
6.1.2 Sample injector, automatic or manual, capable of
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
reproducibly injecting a 2 microliter volume
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
6.1.3 Column heater, capable of maintaining a temperature
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
of 30 6 0.2°C
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
6.1.4 UV detector, capable of measurements at 235 nm.
2. Referenced Documents 6.1.5 Chart recorder or Data system, capable of peak area
2
integration.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
6.2 HPLC analytical column, 250 mm by 4.6 mm by 5 µm
E682 Practice for Liquid Chromatography Terms and Rela-
cyano stationary phase.
tionships
NOTE 2—Other chromatographic columns are used provided it is
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
ascertained that similar chromatographic performance is obtained.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
6.3 Magnetic Stirring Hotplate.
3. Terminology
7. Reagents and Materials
3.1 For definitions of terms used in these test methods see
Terminology D883.
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent-grade chemicals are to be
used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
all reagents conform to the specifications of the Committee on
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Materials -
Analytical Reagents of theAmerican Chemical Society, where
Plastics and Elastomers.
such specifications are available. Other grades are used,
Current edition approved April 15, 2017. Published May 2017. Originally
ɛ1
provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently
approved in 2006. Last previous edition approved in 2011 as D7252 - 06(2011) .
DOI:10.1520/D7252-17.
high purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
the determination.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
7.1.1 Acetanilide, 99.9 % purity, to be used as an internal
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7252 − 17
7.1.2 Acetonitrile, dry. Dry this and reagents below over Eluent B = 100 %
molecular sieve for twenty-four hours. Hold for 10 minutes.
7.1.3 Ethanol, dry. Use of ethanol denatured with methanol (3)Re-equilibration
(such as SDA-30) is used if more readily available. Eluent A = 90 %
7.1.4 Hexane, dry. Eluent B = 10 %
7.1.5 Methanol, dry. Hold for 2.5 minutes
7.1.6 Eluent solution, Mix 1:1 by volume of dry meth
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D7252 − 06 (Reapproved 2011) D7252 − 17
Standard Test Method for
Polyurethane Raw Materials: Determination of Monomer and
1
Isomers in Isocyanates
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7252; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
ε NOTE—Reapproved with editorial changes in September 2011.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method determines the percent by weight of monomeric isomers and total monomer in crude or modified
isocyanates. The test method is applicable to methylene di(phenylisocyanate) (MDI) and polymeric (meththylene(methylene
phenylisocyanate) (PMDI). (See Note 1.)
1.2 Units—The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—There is no known ISO equivalent to this standard.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
E682 Practice for Liquid Chromatography Terms and Relationships
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms used in these test methods see Terminology D883.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The sample is reacted (derivatized) with methanol to form a mixture of methyl urethanes. The urethanes mixture is then
separated by normal phase high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The separated, derivatized isomers are quantified
through the use of an internal standard.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This test method can be is used for research or for quality control to characterize isocyanates used in polyurethane products.
6. Apparatus
6.1 High Performance Liquid Chromatograph, consisting of:
6.1.1 Binary (or greater) solvent pump, capable of maintaining a pulse-free flow rate of 1-3 millilitresmilliliters per minute
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.22 on Cellular Materials - Plastics
and Elastomers.
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2011April 15, 2017. Published October 2011May 2017. Originally approved in 2006. Last previous edition approved in 20062011 as
ɛ1
D7252 - 06.D7252 - 06(2011) DOI:10.1520/D7252-06R11E01. . DOI:10.1520/D7252-17.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D7252 − 17
6.1.2 Sample injector, automatic or manual, capable of reproducibly injecting a 2 microlitremicroliter volume
6.1.3 Column heater, capable of maintaining a temperature of 30 6 0.2°C
6.1.4 UV detector, capable of measurements at 235 nm.
6.1.5 Chart recorder or Data system, capable of peak area integration.
6.2 HPLC analytical column, 250 mm by 4.6 mm by 5 μm cyano stationary phasephase.
NOTE 2—Other chromatographic columns can be are used provided it is ascertained that similar chromatographic performance is obtained.
6.3 Magnetic Stirring Hotplate.
7. Reagents and Materials
7.1 Purity of Reagents—Reagent-grade chemicals are to be used in all tests. Unless otherwise indicated, it is intended that all
reagents conform to the specifications of the Committee on Analytical Reagents of the American Chemical Society, where such
specifications are available. Other grades can be are used, provided it is first ascertained that the reagent is of sufficiently high
purity to permit its use without lessening the accuracy of the d
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.