ASTM B783-04
(Specification)Standard Specification for Materials for Ferrous Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Structural Parts
Standard Specification for Materials for Ferrous Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Structural Parts
ABSTRACT
This specification covers a variety of ferrous powder metallurgy structural materials and includes a classification system or material designation code. The classification system includes chemical composition, minimum offset yield strength for as-sintered materials, minimum ultimate tensile strength for heat-treated materials (sinter hardened or quenched and tempered), minimum density, and maximum coercive field strength requirements for iron-phosphorus materials. Structural parts shall be made by pressing and sintering metal powders with or without subsequent heat treatment. Parts may also be made by repressing or repressing and resintering sintered parts, if necessary, with or without subsequent heat treatment to produce finished parts conforming to the requirements of this specification. The material shall conform to the chemical composition requirements for iron, copper, carbon, nickel, molybdenum, chromium, manganese, silicon, sulfur, phosphorus, nitrogen, columbium, and oxygen. The material shall be subjected to chemical analysis and mechanical tests.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers a variety of ferrous P/M structural materials and includes a classification system or material designation code. The classification system used in this specification includes chemical composition, minimum tensile; 0.2 % offset yield strength for as-sintered materials and minimum ultimate tensile strength for heat-treated materials (sinter hardened or quenched and tempered). It also contains minimum density and maximum coercive field strength requirements for iron-phosphorus materials. Material classification is governed by the designation code which is explained in Appendix X1. The data provided display typical mechanical properties achieved under commercial manufacturing procedures. Physical and mechanical property performance characteristics can change as a result of subsequent processing steps beyond those designated in this standard. These changes could improve or degrade the properties.
1.2 Property values stated in inch-pound units are the standard. Conversion factors to SI units may be approximate.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B783 – 04
Standard Specification for
Materials for Ferrous Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Structural
1
Parts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B783; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope E8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Sulfur,
1.1 This specification covers a variety of ferrous P/M
Nitrogen, and Oxygen in Steel, Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt
structural materials and includes a classification system or
Alloys by Various Combustion and Fusion Techniques
material designation code. The classification system used in
2.2 Other Standard:
this specification includes chemical composition, minimum
MPIF Standard 35 Materials Standard for P/M Structural
tensile; 0.2 % offset yield strength for as-sintered materials and
4
Parts
minimum ultimate tensile strength for heat-treated materials
(sinter hardened or quenched and tempered). It also contains
3. Terminology
minimum density and maximum coercive field strength re-
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of powder metallurgy terms
quirements for iron-phosphorus materials. Material classifica-
can be found in Terminology B243. Additional descriptive
tion is governed by the designation code which is explained in
information is available in the Related Materials section of Vol
Appendix X1. The data provided display typical mechanical
02.05 of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards.
properties achieved under commercial manufacturing proce-
dures. Physical and mechanical property performance charac-
4. Ordering Information
teristics can change as a result of subsequent processing steps
4.1 Materials for parts conforming to this specification shall
beyond those designated in this standard. These changes could
be ordered by material designation code.
improve or degrade the properties.
4.2 Orders for parts under this specification may include the
1.2 Property values stated in inch-pound units are the
following information:
standard. Conversion factors to SI units may be approximate.
4.2.1 Certification, if required (see Section 11),
4.2.2 Test methods and mechanical properties other than
2. Referenced Documents
2 strength (see 8.2 and 8.3),
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2.3 Density (see 7.1),
A839 SpecificationforIron-PhosphorusPowderMetallurgy
4.2.4 Porosity or oil content (see 7.2), and
(P/M) Parts for Soft Magnetic Applications
4.2.5 Special packaging if required.
B243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
B328 Test Method for Density, Oil Content, and Intercon-
5. Materials and Manufacture
nected Porosity of Sintered Metal Structural Parts and
5.1 Structural parts shall be made by pressing and sintering
3
Oil-Impregnated Bearings
metal powders with or without subsequent heat treating. Parts
B528 Test Method for Transverse Rupture Strength of
may also be made by repressing or repressing and resintering
Metal Powder Specimens
sintered parts, if necessary, with or without subsequent heat
treatment to produce finished parts conforming to the require-
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee B09 on Metal
ments of this specification.
Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
mittee B09.05 on Structural Parts.
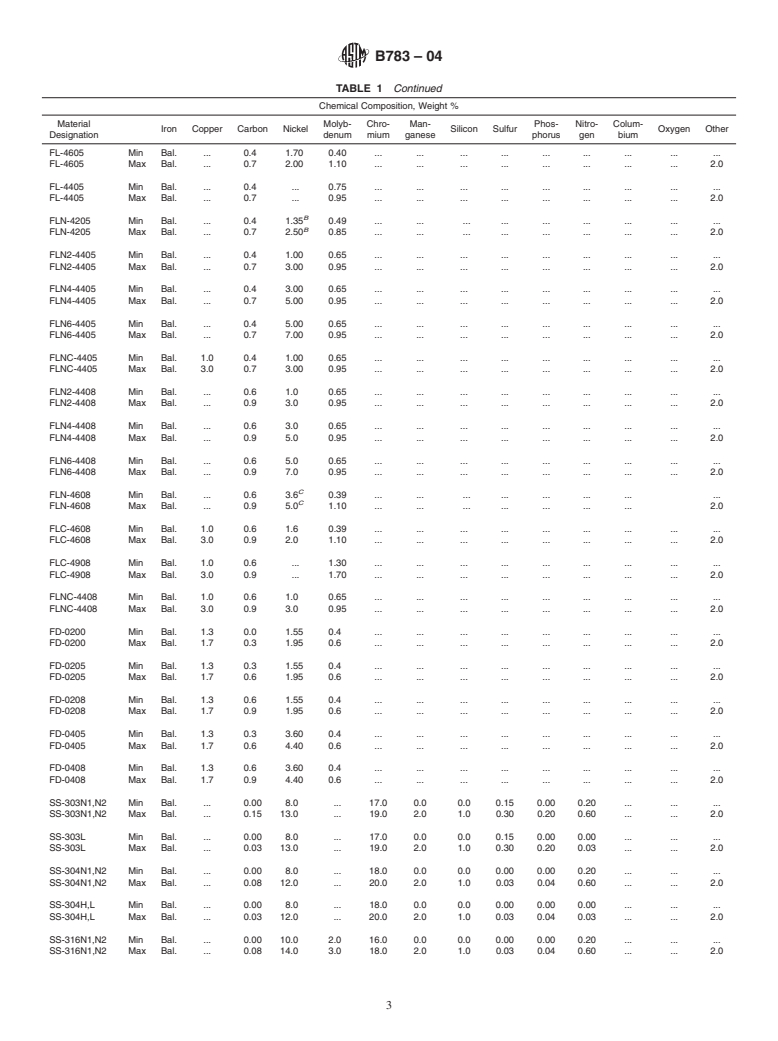
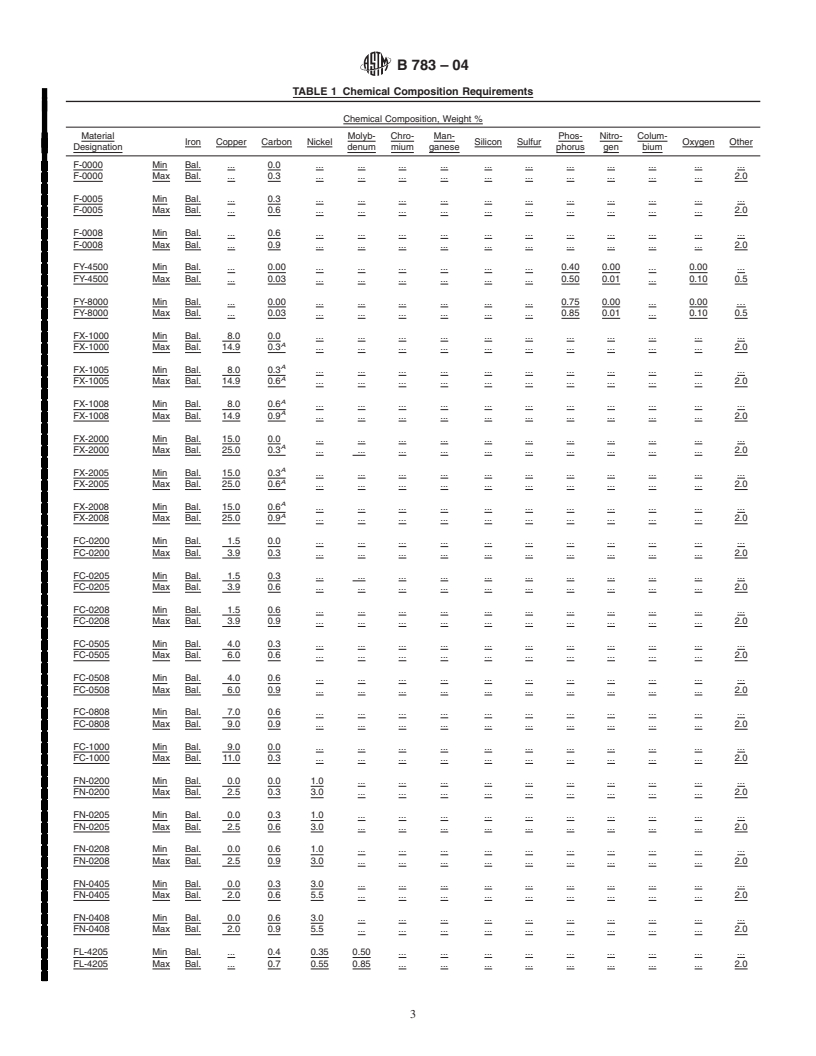
6. Chemical Composition
Current edition approved May 1, 2004. Published June 2004. Originally
´1
approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as B783 – 99 . DOI: 6.1 The material shall conform to the requirements of Table
10.1520/B0783-04.
1.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.2 Chemical analysis, if required, shall be made by meth-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
ods agreed upon by the producer and the user.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website.
3
Withdrawn. The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced
4
on www.astm.org. Available from MPIF, 105 College Road East, Princeton, NJ 08540.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B783 – 04
TABLE 1 Chemical Composition Requirements
Chemical Composition, Weight %
Material Molyb- Chro- Man- Phos- Nitro- Colum-
Iron Copper Carbon Nickel Silicon Sulfur Oxygen Other
Designation denum mium ganese phorus gen bium
F-0000 Min Bal. . 0.0 . . . . . . . . . . .
F-0000 Max Bal. . 0.3 . . . . . . . . . . 2.0
F-0005 Min Bal. . 0.3 . . . . . . .
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
e1
Designation:B783–99 Designation: B 783 – 04
Standard Specification for
Materials for Ferrous Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Structural
1
Parts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B 783; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1
e NOTE—Editorial changes were made to this standard in March 2000.
1. Scope
1.1This specification covers a variety of ferrous P/M structural materials and includes a classification system or material
designation code. The classification system used in this specification includes chemical composition, minimum tensile yield
strength for parts in the as-sintered condition, and minimum ultimate tensile strength for materials in the heat-treated condition.
1.2Property values stated in inch-pound units are the standard. Conversion factors to SI units may be approximate.
NOTE1—Paragraphs 5.1 and 7.1 will govern material classification by the designation code. The classification system is explained in
1.1 This specification covers a variety of ferrous P/M structural materials and includes a classification system or material
designationcode.Theclassificationsystemusedinthisspecificationincludeschemicalcomposition,minimumtensile;0.2 %offset
yield strength for as-sintered materials and minimum ultimate tensile strength for heat-treated materials (sinter hardened or
quenchedandtempered).Italsocontainsminimumdensityandmaximumcoercivefieldstrengthrequirementsforiron-phosphorus
materials. Material classification is governed by the designation code which is explained in Appendix X1. . The data provided
display typical mechanical properties achieved under commercial manufacturing procedures. Physical and mechanical property
performance characteristics can change as a result of subsequent processing steps beyond those designated in this standard. These
changes could improve or degrade the properties.
1.2 Property values stated in inch-pound units are the standard. Conversion factors to SI units may be approximate.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: ASTM Standards:
A 839 Specification for Iron-Phosphorus Powder Metallurgy (P/M) Parts for Soft Magnetic Applications
B 243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
B 328Test Method for Density, Oil Content, and Interconnected Porosity of Sintered Powder Metal Structural Parts and
2
Oil-Impregnated Bearings
E8Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials Test Method for Density, Oil Content, and Interconnected Porosity
of Sintered Powder Metal Structural Parts and Oil-Impregnated Bearings
B 528 Test Method for Transverse Rupture Strength of Metal Powder Specimens
E 8 Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials
E 1019 Test Methods for Determination of Carbon, Nitrogen and Oxygen in Iron, Nickel, and Cobalt Alloys
2.2 Other Standard:
3
MPIF Standard 35 Materials Standard for P/M Structural Parts
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of powder metallurgy terms can be found in Terminology B 243. Additional descriptive
information is available in the Related Materials section of Vol 02.05 of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards.
1
ThisspecificationisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeB-9onMetalPowderandMetalPowderProductsandisthedirectresponsibilityofSubcommitteeB09.05
on Structural Parts.
Current edition approved Sept. 10, 1999. Published December 1999. Originally published as B783–88. Last previous edition B783–93.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B09 on Metal Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
B09.05 on Structural Parts.
´1
Current edition approved May 1, 2004. Published June 2004. Originally approved in 1988. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as B 783 – 99 .
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 02.05.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.01.
3
Available from MPIF, 105 College Road East, Princeton, NJ 08540.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B783–04
4. Ordering Information
4.1 Materials for parts conforming to this spec
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.