ASTM D943-99
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils
Standard Test Method for Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils
SCOPE
1.1 This test method was developed for, and is used to evaluate the oxidation stability of inhibited steam-turbine oils in the presence of oxygen, water, and copper and iron metals at an elevated temperature. The test method is also used for testing other oils such as hydraulic oils and circulating oils having a specific gravity less than that of water and containing rust and oxidation inhibitors.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: D 943 – 99 An American National Standard
British Standard 4388
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
1
Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 943; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Specifications for IP Standard Thermometers
9
2.3 British Standard:
1.1 This test method is used to evaluate the oxidation
BS 1829
stability of inhibited steam-turbine oils in the presence of
oxygen, water, and copper and iron metals at an elevated
3. Summary of Test Method
temperature. The test method is also used for testing other oils
3.1 The oil sample is contacted with oxygen in the presence
such as hydraulic oils and circulating oils having a specific
of water and an iron-copper catalyst at 95°C. The test continues
gravity less than that of water and containing rust and oxidation
until the measured acid number of the oil is 2.0 mg KOH/g or
inhibitors.
above. The number of test hours required for the oil to reach
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2.0 mg KOH/g is the “ oxidation lifetime.”
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Significance and Use
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 This test method is widely used for specification pur-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific
poses and is considered of value in estimating the oxidation
precautionary statements, see Section 6.
stability of lubricants, especially those that are prone to water
contamination. It should be recognized, however, that correla-
2. Referenced Documents
tion between results of this method and the oxidation stability
2.1 ASTM Standards:
of a lubricant in field service may vary markedly with field
A 510 Specification for General Requirements for Wire
2 service conditions and with various lubricants. The precision
Rods and Coarse Round Wire, Carbon Steel
3 statement for this method was determined on steam turbine
B 1 Specification for Hard-Drawn Copper Wire
4
oils.
D 329 Specification for Acetone
4
D 770 Specification for Isopropyl Alcohol
NOTE 1—Furthermore, in the course of testing a lubricant by this
5
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water method, other signs of deterioration, such as sludge formation or catalyst
coil corrosion, may appear that are not reflected in the calculated oxidation
D 3244 Practice for Utilization of Test Data to Determine
6
lifetime. The subcommittee responsible for this method is investigating
Conformance with Specifications
the application of alternative criteria for evaluation of lubricants using this
D 3339 Test Method for Acid Number by Semi-Micro
test apparatus. Test Method D 4310 is now available for sludge measure-
6
Color Indicator Titration
ment.
D 4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
6
Petroleum Products 5. Apparatus
D 4310 Test Method for Determination of the Sludging and
5.1 Oxidation Cell, of borosilicate glass, as shown in Fig. 1,
6
Corrosion Tendencies of Inhibited Mineral Oils
consisting of a test tube, condenser, and oxygen delivery tube.
7
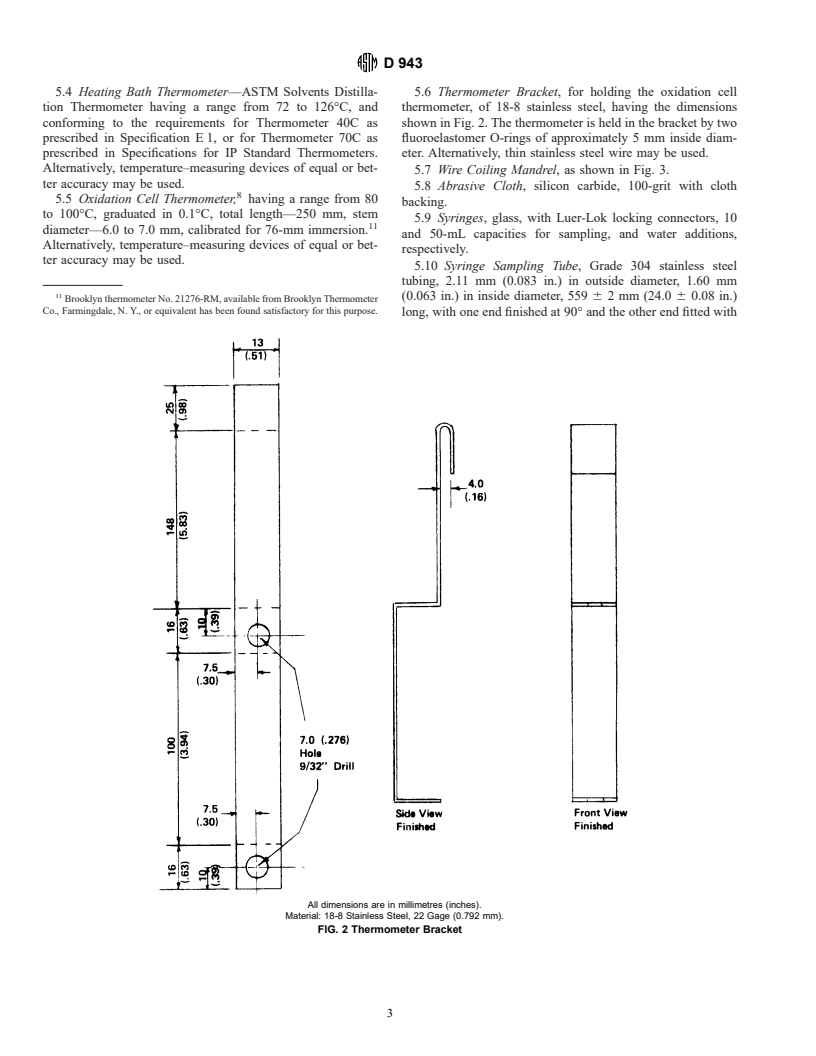
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers
The test tube has a calibration line at 300 mL (maximum error
8
2.2 IP Standards:
1 ml). This calibration applies to the test tube alone at 20°C.
5.2 Heating Bath, thermostatically controlled, capable of
1 maintaining the oil sample in the oxidation cell at a tempera-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-2 on
ture of 95 6 0.2°C, fitted with a suitable stirring device to
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.09 on Oxidation.
provide a uniform temperature throughout the bath, and large
Current edition approved June 10, 1999. Published August 1999. Originally
enough to hold the desired number of oxidation cells immersed
published as D 943 – 47. Last previous edition D 943 – 98.
in the heating bath to a depth of 390 6 10 mm and in the
In 1976, the method ceased to be a joint ASTM-IP standard.
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 01.03. heating liquid itself to a depth of 355 6 10 mm.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 02.03.
5.2.1 Studies have suggested that direct sunlight or artificial
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 06.04.
5
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 11.01.
6
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.02.
7
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
8 9
Available from the Institute of Petroleum, 61 New Cavendish St., London Available from British Standards Institute, 2 Park St., London, England
WIM, 8AR,
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.