ASTM D5270-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Transmissivity and Storage Coefficient of Bounded, Nonleaky, Confined Aquifers
Standard Test Method for Determining Transmissivity and Storage Coefficient of Bounded, Nonleaky, Confined Aquifers
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers an analytical procedure for determining the transmissivity, storage coefficient, and possible location of boundaries for a bounded confined aquifer. This test method is used to analyze water-level or head data from one or more observation wells or piezometers during the pumping of water from a control well at a constant rate. This test method also applies to flowing artesian wells discharging at a constant rate. With appropriate changes in sign, this test method also can be used to analyze the effects of injecting water into a control well at a constant rate.
1.2 The analytical procedure in this test method is used in conjunction with the field procedure in Test Method D4050.
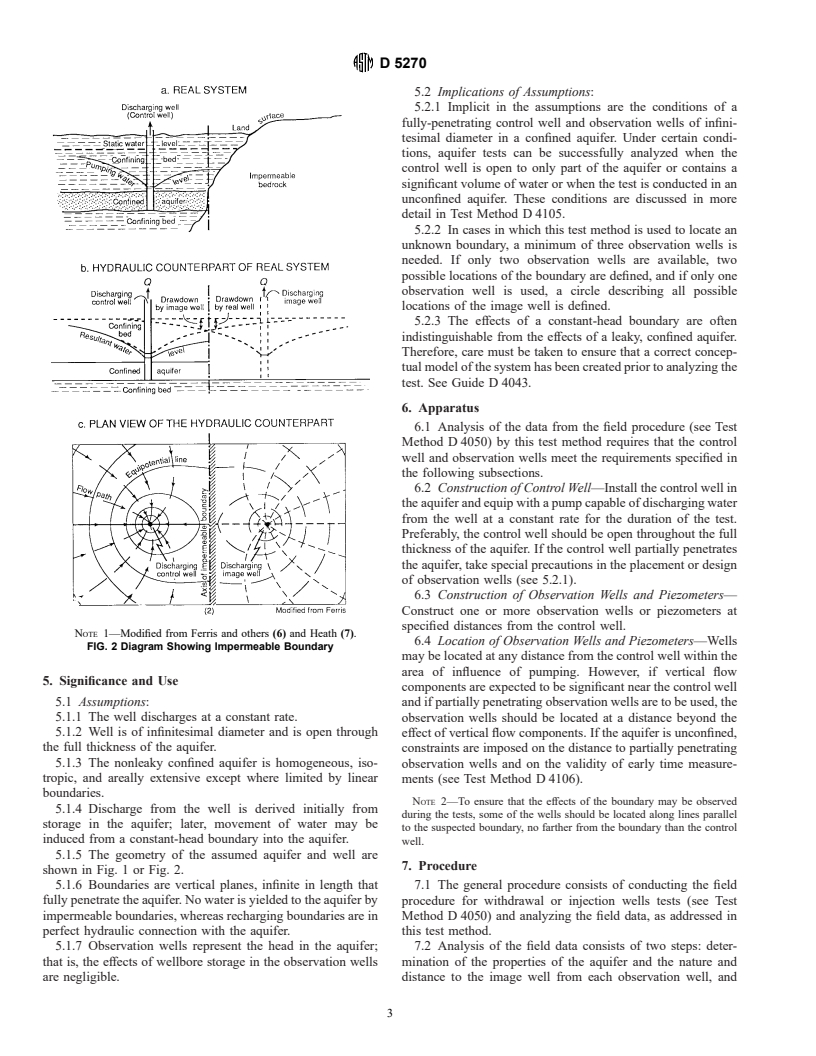
1.3 Limitations -The valid use of this test method is limited to determination of transmissivities and storage coefficients for aquifers in hydrogeologic settings with reasonable correspondence to the assumptions of the Theis nonequilibrium method (see Test Method D4106) (see 5.1), except that the aquifer is limited in areal extent by a linear boundary that fully penetrates the aquifer. The boundary is assumed to be either a constant-head boundary (equivalent to a stream or lake that hydraulically fully penetrates the aquifer) or a no-flow (impermeable) boundary (equivalent to a contact with a significantly less permeable rock unit). The Theis nonequilibrium method is described in Test Methods D 4105 and D 4106.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: D 5270 – 96
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Determining Transmissivity and Storage Coefficient of
1
Bounded, Nonleaky, Confined Aquifers
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 5270; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
2
1. Scope Determining Hydraulic Properties by Well Techniques
D 4050 Test Method (Field Procedure) for Withdrawal and
1.1 This test method covers an analytical procedure for
Injection Well Tests for Determining Hydraulic Properties
determining the transmissivity, storage coefficient, and possible
2
of Aquifer Systems
location of boundaries for a confined aquifer with a linear
D 4105 Test Method (Analytical Procedure) for Determin-
boundary. This test method is used to analyze water-level or
ing Transmissivity and Storage Coefficient of Nonleaky
head data from one or more observation wells or piezometers
Confined Aquifers by the Modified Theis Nonequilibrium
during the pumping of water from a control well at a constant
2
Method
rate. This test method also applies to flowing artesian wells
D 4106 Test Method (Analytical Procedure) for Determin-
discharging at a constant rate. With appropriate changes in
ing Transmissivity and Storage Coefficient of Nonleaky
sign, this test method also can be used to analyze the effects of
2
Confined Aquifers by the Theis Nonequilibrium Method
injecting water into a control well at a constant rate.
D 4750 Test Method for Determining Subsurface Liquid
1.2 The analytical procedure in this test method is used in
Levels in a Borehole or Monitoring Well (Observation
conjunction with the field procedure in Test Method D 4050.
2
Well)
1.3 Limitations—The valid use of this test method is limited
to determination of transmissivities and storage coefficients for
3. Terminology
aquifers in hydrogeologic settings with reasonable correspon-
3.1 Definitions:
dence to the assumptions of the Theis nonequilibrium method
3.1.1 constant-head boundary—the conceptual representa-
(see Test Method D 4106) (see 5.1), except that the aquifer is
tion of a natural feature such as a lake or river that effectively
limited in areal extent by a linear boundary that fully penetrates
fully penetrates the aquifer and prevents water-level change in
the aquifer. The boundary is assumed to be either a constant-
the aquifer at that location.
head boundary (equivalent to a stream or lake that hydrauli-
3.1.2 equipotential line—a line connecting points of equal
cally fully penetrates the aquifer) or a no-flow (impermeable)
hydraulic head. A set of such lines provides a contour map of
boundary (equivalent to a contact with a significantly less
a potentiometric surface.
permeable rock unit). The Theis nonequilibrium method is
3.1.3 image well—an imaginary well located opposite a
described in Test Methods D 4105 and D 4106.
control well such that a boundary is the perpendicular bisector
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
of a straight line connecting the control and image wells; used
standard.
to simulate the effect of a boundary on water-level changes.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.4 impermeable boundary—the conceptual representa-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
tion of a natural feature such as a fault or depositional contact
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
that places a boundary of significantly less-permeable material
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
laterally adjacent to an aquifer.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.5 See Terminology D 653 for other terms.
2. Referenced Documents 3.2 Symbols and Dimensions:
3.2.1 K [nd]—constant of proportionality, r /r .
l i r
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3 −1
3.2.2 Q [L T ]—discharge.
D 653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
2
3.2.3 r [L]—radial distance from control well.
Fluids
3.2.4 r [L]—distance from observation well to image well.
i
D 4043 Guide for Selection of Aquifer-Test Method in
3.2.5 r [L]—distance from observation well to control well.
r
3.2.6 S [nd]—storage coefficient.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-18 on Soil
3.2.7 s [L]—drawdown.
and Rock and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D18.21 on Ground Water
3.2.8 s [L]—component of drawdown due to image well.
and Vadose Zone Investigations. i
Current edition approved Oct. 10, 1996. Published February 1997. Originally
3.2.9 s [L]—drawdown at an observation well.
o
published as D 5270 – 92. Last previous edition D 5270 – 92.
3.2.10 s [L]—component of drawdown due to control we
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.