ASTM D2419-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Sand Equivalent Value of Soils and Fine Aggregate
Standard Test Method for Sand Equivalent Value of Soils and Fine Aggregate
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method assigns an empirical value to the relative amount, fineness, and character of claylike material present in the test specimen.
A minimum sand equivalent value may be specified to limit the permissible quantity of claylike fines in an aggregate.
This test method provides a rapid field method for determining changes in the quality of aggregates during production or placement.
Note 2—The quality of the results produced by this standard are dependant upon the competence of the personnel performing the procedure and the capability, calibration, and the maintenance of the equipment used. Agencies that meet the criteria of Practice D 3666 are generally considered capable of competent and objective testing/sampling/inspection/etc. Users of this standard are cautioned that compliance with Practice D 3666 alone does not completely assure reliable results. Reliable results depend on many factors: following the suggestions of Practice D 3666 or similar acceptable guideline provides a means of evaluating and controlling some of those factors.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended to serve as a rapid field-correlation test. The purpose of this test method is to indicate, under standard conditions, the relative proportions of clay-like or plastic fines and dust in granular soils and fine aggregates that pass the 4.75-mm (No. 4) sieve. The term “sand equivalent” expresses the concept that most granular soils and fine aggregates are mixtures of desirable coarse particles, sand, and generally undesirable clay or plastic fines and dust.
Note 1—Some agencies perform the test on material with a top size smaller than the 4.75-mm (No. 4) sieve. This is done to avoid trapping the clay-like or plastic fines and dust below flaky shaped 4.75 to 2.36 mm (No. 4 to 8) sized particles. Testing smaller top sized material may lower the numerical results of the test.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Regarding sieves, per Specification E 11 Section 1.2, “the values stated in SI units shall be considered standard for the dimensions of the wire cloth openings and the diameter of the wires used in the wire cloth. The values stated in inchpound units shall be considered standard with regard to the sieve frames.” When sieve mesh sizes are referenced, the alternate inch-pound designations are provided for information purposes and enclosed in parentheses.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2419 − 09
StandardTest Method for
1
Sand Equivalent Value of Soils and Fine Aggregate
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2419; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method is intended to serve as a rapid field- 2.1 ASTM Standards:
correlation test. The purpose of this test method is to indicate, C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
under standard conditions, the relative proportions of clay-like for Test Methods for Construction Materials
or plastic fines and dust in granular soils and fine aggregates C702 PracticeforReducingSamplesofAggregatetoTesting
that pass the 4.75-mm (No. 4) sieve. The term “sand equiva- Size
lent” expresses the concept that most granular soils and fine D8 Terminology Relating to Materials for Roads and Pave-
aggregates are mixtures of desirable coarse particles, sand, and ments
generally undesirable clay or plastic fines and dust. D75 Practice for Sampling Aggregates
D653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained
NOTE 1—Some agencies perform the test on material with a top size
Fluids
smaller than the 4.75-mm (No. 4) sieve.This is done to avoid trapping the
D3666 Specification for Minimum Requirements for Agen-
clay-like or plastic fines and dust below flaky shaped 4.75 to 2.36 mm
(No. 4 to 8) sized particles. Testing smaller top sized material may lower
cies Testing and Inspecting Road and Paving Materials
the numerical results of the test.
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded Sieves
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical 2.2 AASHTO Standard:
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only T 176 Standard Method of Test for Plastic Fines in Graded
3
and are not considered standard. Aggregates and Soils by Use of Sand Equivalent Test
1.2.1 Regarding sieves, per Specification E11 Section 1.2,
3. Terminology
“the values stated in SI units shall be considered standard for
3.1 Definitions:
the dimensions of the wire cloth openings and the diameter of
3
3.1.1 fine aggregate—aggregate passing the 9.5-mm ( ⁄8-in.)
thewiresusedinthewirecloth.Thevaluesstatedininchpound
sieve and almost entirely passing the 4.75-mm (No. 4) sieve
units shall be considered standard with regard to the sieve
and predominantly retained on the 75-µm (No. 200) sieve (see
frames.” When sieve mesh sizes are referenced, the alternate
Terminology D8).
inch-pounddesignations are provided for informationpurposes
and enclosed in parentheses.
3.1.2 sand equivalent—a measure of the amount of silt or
clay contamination in the fine aggregate (or soil) as determined
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
by test (see Terminology D653). (For further explanation, see
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Summary of Test Method and Significance and Use.)
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
3.1.3 soil—sediments or other unconsolidated accumula-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
tions of solid particles produced by the physical and chemical
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D04 on Road contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.51 on Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Aggregate Tests. the ASTM website.
3
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2009.PublishedJuly2009.Originallyapproved Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation
in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D2419 – 02. DOI: 10.1520/ Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 20001,
D2419-09. http://www.transportation.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2419 − 09
disintegration of rocks which may or may not contain organic 6.4.1 To remove this growth, prepare a cleaning solvent by
matter (see Terminology D653). diluting sodium hypochlorite solution (household chlorine
bleach) with an equal quantity of water.
4. Summary of Test Method 6.4.2 After discarding the contaminated solut
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D2419–02 Designation:D2419–09
Standard Test Method for
1
Sand Equivalent Value of Soils and Fine Aggregate
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 2419; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is intended to serve as a rapid field-correlation test. The purpose of this test method is to indicate, under
standard conditions, the relative proportions of clay-like or plastic fines and dust in granular soils and fine aggregates that pass the
4.75-mm (No. 4) sieve.The term “sand equivalent” expresses the concept that most granular soils and fine aggregates are mixtures
of desirable coarse particles, sand, and generally undesirable clay or plastic fines and dust.
NOTE 1—Someagenciesperformthetestonmaterialwithatopsizesmallerthanthe4.75-mm(No.4)sieve.Thisisdonetoavoidtrappingtheclay-like
or plastic fines and dust below flaky shaped 4.75 to 2.36 mm (No. 4 to 8) sized particles. Testing smaller top sized material may lower the numerical
results of the test.
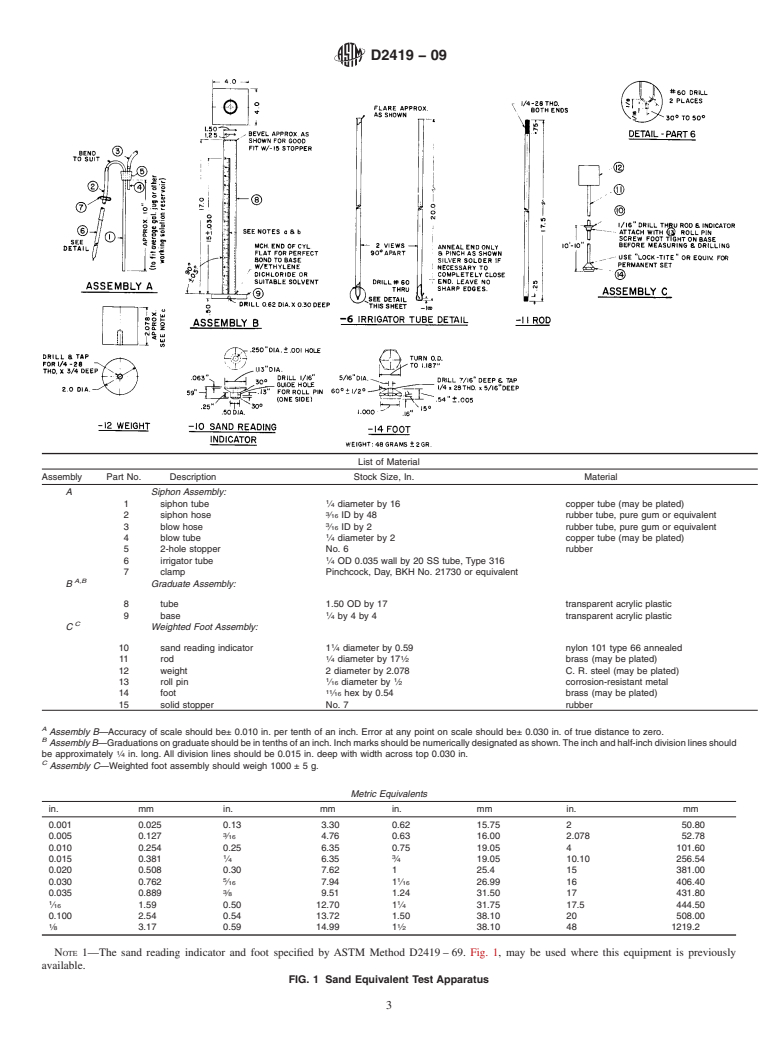
1.2Units of Measurement:
1.2.1The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard, with the exception of the dimensions of the special sand
equivalent test apparatus described in Fig. 1, in which the the inch dimensions are standard. Values in parentheses are for
information only.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.2.1 Regarding sieves, per Specification E 11 Section 1.2, “the values stated in SI units shall be considered standard for the
dimensions of the wire cloth openings and the diameter of the wires used in the wire cloth. The values stated in inchpound units
shall be considered standard with regard to the sieve frames.” When sieve mesh sizes are referenced, the alternate inch-pound
designations are provided for information purposes and enclosed in parentheses.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C 670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements for Test Methods for Construction Materials
C 702 Practice for Reducing Samples of Aggregate to Testing Size
D8 Terminology Relating to Materials for Roads and Pavements
D75 Practice for Sampling Aggregates
D 653 Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids Terminology Relating to Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids
D 3666 Specification for Minimum Requirements for Agencies Testing and Inspecting Road and Paving Materials
E11 Specification for Wire-Cloth and Sieves for Testing Purposes Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
Sieves
2.2 AASHTO Standard:
3
T 176 Standard Method of Test for Plastic Fines in Graded Aggregates and Soils by Use of Sand Equivalent Test
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D04 on Road and Paving Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D04.51 onAggregate
Tests.
Current edition approved July 10, 2002. Published September 2002. Originally published as D2419–65 T. Last previous edition D2419–96.
Current edition approved June 1, 2009. Published July 2009. Originally approved in 1965. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D 2419 – 02.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 04.02.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.03.
3
Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., NW, Suite 249, Washington, DC 20001,
http://www.transportation.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D2419–09
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.