ASTM E2861-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measurement of Beam Divergence and Alignment in Neutron Radiologic Beams
Standard Test Method for Measurement of Beam Divergence and Alignment in Neutron Radiologic Beams
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 As discussed in Practice E748, traditional neutron radiography typically employs a high flux reactor source with a well defined collimation system to produce an image on film. The alignment of the imaging plane and the divergence angle are generally well defined and a small degree of misalignment or uncertainty in divergence angle makes little difference in the final image. These systems are well characterized by their physical dimension, the L/D ratio, and image quality indicators (Beam Purity Indicator and Sensitivity Indicator) described in Test Method E545. Neutron computed tomography is an example where it is important to know with some precision both the beam’s centerline and the degree of beam divergence, especially if the beam does not closely approximate a parallel beam. Portable or movable neutron imaging systems often utilize shorter collimation systems, a less precise alignment and poor symmetry in divergence angles, which may affect image analysis. In these example cases, direct measurement of the alignment and the divergence angles is desirable as calculation from system geometry would be less straightforward and accurate. Fabrication of the device is an extension of the Test Method E803 L/D device, providing different information through a similar approach.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the design, materials, manufacture, and use of a divergence and alignment indicator (DAI) for measuring the effective divergence of a thermal neutron beam used for neutron imaging as well as determining the alignment of the imaging plane relative (usually normal) to the centerline of the beam. This test method is applicable to thermal neutron imaging.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: E2861 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Beam Divergence and Alignment in
1
Neutron Radiologic Beams
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2861; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this guide
1.1 This test method covers the design, materials,
other than those defined in this section, refer to Terminology
manufacture, and use of a divergence and alignment indicator
E1316.
(DAI) for measuring the effective divergence of a thermal
neutron beam used for neutron imaging as well as determining
3.2 Definitions:
the alignment of the imaging plane relative (usually normal) to 3.2.1 neutron image—record in two dimensions of the
the centerline of the beam. This test method is applicable to intensity of neutron radiation. Examples include radiographs,
thermal neutron imaging. radioscopic images, computed radiography (CR) images, and
track etch images produced from a neutron source.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
3.2.2 neutron imaging—process of making a neutron image.
standard.
4. Summary of Test Method
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.1 The DAI allows the user to determine the alignment of
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
the imaging plane with the beam centerline and the beam
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
divergenceforathermalneutronbeam.Theusercandetermine
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
if the imaging system is aligned, aligned only in one direction
or completely misaligned and the angle of misalignment, as
2. Referenced Documents
well as the divergence angle for the imaging system. The DAI
is made using aluminum plate and rods, and incorporates
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
cadmium wires for contrast. Circular symmetry is utilized to
E543 Specification forAgencies Performing Nondestructive
simplify manufacture. An important feature of the DAI is
Testing
flexibility to adapt the “as-built” dimensions into the analysis.
E545 Test Method for Determining Image Quality in Direct
The DAI is placed with the five stand off posts against the film
Thermal Neutron Radiographic Examination
cassette or radioscopic imaging device in the physical center of
E748 Guide for Thermal Neutron Radiography of Materials
thebeam.TheDAIisperpendiculartotheselectedbeamradius
E803 TestMethodforDeterminingthe L/DRatioofNeutron
when the center S1 and center S4 cadmium wire images
Radiography Beams
overlap (see Figs. 1 and 2).The degree of misalignment can be
E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
measured by the cadmium wire image positions.After the DAI
2.2 Other Documents: is aligned, analysis of the cadmium wire “+” image spacing
3
ANSI Y14.5M Dimensioning and Tolerances yields the beam divergence.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 As discussed in Practice E748, traditional neutron radi-
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on
ography typically employs a high flux reactor source with a
Nondestructive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.05 on
Radiology (Neutron) Method.
well defined collimation system to produce an image on film.
Current edition approved June 1, 2016. Published June 2016. Originally
The alignment of the imaging plane and the divergence angle
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved as E2861-11. DOI:10.1520/
are generally well defined and a small degree of misalignment
E2861-16.
2
or uncertainty in divergence angle makes little difference in the
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
final image. These systems are well characterized by their
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
physical dimension, the L/D ratio, and image quality indicators
the ASTM website.
3
(Beam Purity Indicator and Sensitivity Indicator) described in
Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org. Test Method E545. Neutron computed tomography is an
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2861 − 16
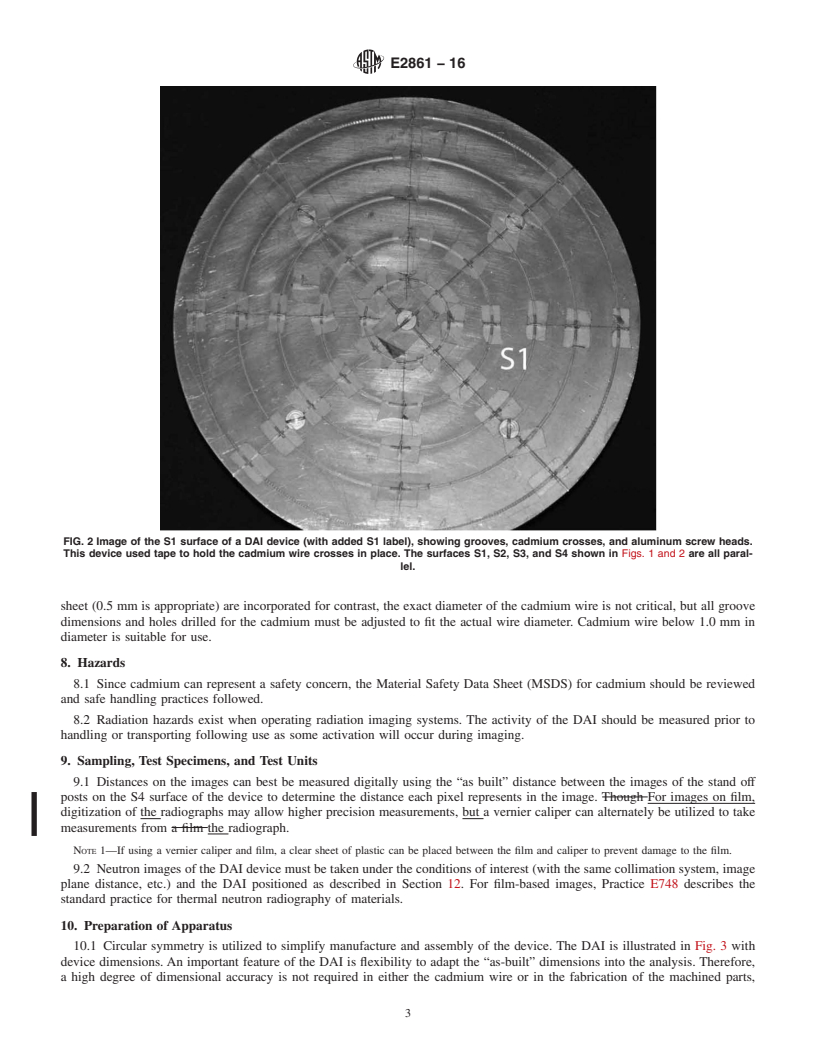
FIG. 1 Image of the DAI device with added labels to label the S2 sur
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: E2861 − 11 E2861 − 16
Standard Test Method for
Measurement of Beam Divergence and Alignment in
1
Neutron Radiologic Beams
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E2861; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the design, materials, manufacture, and use of a divergence and alignment indicator (DAI) for
measuring the effective divergence of a thermal neutron beam used for neutron imaging as well as determining the alignment of
the imaging plane relative (usually normal) to the centerline of the beam. This test method is applicable to thermal neutron imaging.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
E543 Specification for Agencies Performing Nondestructive Testing
E545 Test Method for Determining Image Quality in Direct Thermal Neutron Radiographic Examination
E748 Guide for Thermal Neutron Radiography of Materials
E803 Test Method for Determining the L/D Ratio of Neutron Radiography Beams
E1316 Terminology for Nondestructive Examinations
2.2 Other Documents:
3
ANSI Y14.5M Dimensioning and Tolerances
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this guide other than those defined in this section, refer to Terminology E1316.
3.2 Definitions:
3.2.1 neutron image—record in two dimensions of the intensity of neutron radiation. Examples include radiographs, radioscopic
images, computed radiography (CR) images, and track etch images produced from a neutron source.
3.2.2 neutron imaging—process of making a neutron image.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 The DAI allows the user to determine the alignment of the imaging plane with the beam centerline and the beam divergence
for a thermal neutron beam. The user can determine if the imaging system is aligned, aligned only in one direction or completely
misaligned and the angle of misalignment, as well as the divergence angle for the imaging system. The DAI is made using
aluminum plate and rods, and incorporates cadmium wires for contrast. Circular symmetry is utilized to simplify manufacture. An
important feature of the DAI is flexibility to adapt the “as-built” dimensions into the analysis. The DAI is placed with the five stand
off posts against the film cassette or radioscopic imaging device in the physical center of the beam. The DAI is perpendicular to
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee E07 on Nondestructive Testing and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E07.05 on Radiology
(Neutron) Method.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2011June 1, 2016. Published January 2012June 2016. DOI:10.1520/E2861-11. Originally approved in 2011. Last previous edition
approved as E2861-11. DOI:10.1520/E2861-16.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from American National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St., 4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
E2861 − 16
the selected beam radius when the center S1 and center S4 cadmium wire images overlap (see Figs. 1 and 2). The degree of
misalignment can be measured by the cadmium wire image positions. After the DAI is aligned, analysis of the cadmium wire “+”
image spacing yields the beam divergence.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 As discussed in Practice E748, traditional neutron radiography typically employs a high flux reactor source with a well
defined collimation system to produce an image on film. The alignment of the imaging plane and the divergence angle are generally
well defined and a small degree of misalignment or unc
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.