ASTM D6563-05(2010)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Benzene, Toluene, Xylene (BTX) Concentrates Analysis by Gas Chromatography
Standard Test Method for Benzene, Toluene, Xylene (BTX) Concentrates Analysis by Gas Chromatography
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method was primarily developed to determine benzene, toluene, and xylenes in chemical intermediate and solvent streams such as reformate, BTX extracts, pyrolysis gasoline, hydrogenated pyrolysis gasoline, crude benzene, crude ethylbenzene, commercial toluene, and light blending aromatic feedstocks. This test method may not detect all components and there may be unknown components that would be assigned inappropriate response factors and thus, the results may not be absolute.
The relative distribution of C8 aromatics is useful for determining conformance to p-xylene feedstock specifications.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the total nonaromatic hydrocarbons, benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, xylenes, and total C9 + aromatic hydrocarbons in BTX concentrates by capillary column gas chromatography. This test method is applicable to materials with a final boiling point below 215°C.
1.2 This test method may also be used to determine the relative distribution of the individual C8 aromatic hydrocarbon isomers in mixed xylenes.
1.3 Individual components can be determined from 0.01 to 90 %.
1.4 In determining the conformance of the test results using this method to applicable specifications, results shall be rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of Practice E29.
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific precautionary statement, see Section 9.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation:D6563–05(Reapproved2010)
Standard Test Method for
Benzene, Toluene, Xylene (BTX) Concentrates Analysis by
Gas Chromatography
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6563; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
´ NOTE—Section 16 was corrected editorially in July 2010.
1. Scope* Procedures for Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Ma-
terials
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the total
E29 Practice for Using Significant Digits in Test Data to
nonaromatic hydrocarbons, benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene,
Determine Conformance with Specifications
xylenes, and total C + aromatic hydrocarbons in BTX con-
E355 Practice for Gas Chromatography Terms and Rela-
centrates by capillary column gas chromatography. This test
tionships
method is applicable to materials with a final boiling point
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
below 215°C.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.2 This test method may also be used to determine the
E1510 Practice for Installing Fused Silica Open Tubular
relative distribution of the individual C aromatic hydrocarbon
Capillary Columns in Gas Chromatographs
isomers in mixed xylenes.
2.2 Other Documents:
1.3 Individual components can be determined from 0.01 to
OSHA Regulations, 29 CFR paragraphs 1910.1000 and
90 %.
1910.1200
1.4 In determining the conformance of the test results using
this method to applicable specifications, results shall be
3. Terminology
rounded off in accordance with the rounding-off method of
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Practice E29.
3.1.1 extracted reformate, n—An aromatic concentrate ob-
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
tained by solvent extraction of reformate.
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.2 reformate, n—The product of a catalytic process that
standard.
increases the concentration of aromatic hydrocarbons.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.3 pyrolysis gasoline, n—Depentanized by-product re-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
covered from ethylene manufacture.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
3.1.4 synthetic blend, n—Blend of reagent hydrocarbons
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
that simulate a process product.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For a specific
3.1.5 hydrogenated pyrolysis gasoline, n—Pyrolysis gaso-
precautionary statement, see Section 9.
line that has been treated with hydrogen to reduce the olefins
2. Referenced Documents content.
2 3.1.6 crude ethylbenzene, n—Product produced from the
2.1 ASTM Standards:
reaction of impure fluid cat cracking, (FCC) ethylene and
D3437 Practice for Sampling and Handling Liquid Cyclic
benzene.
Products
3.1.6.1 Discussion—It typically contains greater than 40 %
D6809 Guide for Quality Control and Quality Assurance
of ethylbenzene and benzene.
3.1.7 light blending aromatics feedstock, n—Light aromat-
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D16 on ics fraction (with high amounts of benzene and toluene)
Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Related Chemicals and is the direct responsibility of
typically recovered from the isomerization of a p-xylene or
Subcommittee D16.01 on Benzene, Toluene, Xylenes, Cyclohexane and Their
m-xylene depleted C aromatics stream.
Derivatives.
3.1.8 mixed xylenes, n—a mixture of C aromatic hydrocar-
Current edition approved June 15, 2010. Published July 2010. Originally
approved in 2000. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D6463 – 05. DOI:
bon isomers including ethylbenzene, but excluding stryene.
10.1520/D6563-05R10E01.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM AvailablefromU.S.GovernmentPrintingOfficeSuperintendentofDocuments,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on 732 N. Capitol St., NW, Mail Stop: SDE, Washington, DC 20401, http://
the ASTM website. www.access.gpo.gov.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
´1
D6563–05 (2010)
TABLE 1 Instrument Parameters
4. Summary of Test Method
Column 50 or 60 m by 0.25 mm ID bonded
4.1 The specimen to be analyzed is injected into a gas
polyethylene glycol-fused silica capillary,
chromatographequippedwithaflameionizationdetector(FID)
internally coated to a 0.25-µm thickness
Carrier gas helium
and a capillary column. The peak area of each component is
Flow, linear velocity at 70°C, cm/s 20
measured and adjusted using effective carbon number (ECN)
Split ratio 200:1
response factors. The concentration of each component is
Detector gas
calculated based on its relative percentages of total adjusted Hydrogen flow rate, mL/min 30
Air flow rate, mL/min 300
peak area and normalized to 100.00. To determine the relative
Make-up flow rate, mL/min 30
distribution of C aromatic hydrocarbons, the peak areas of
8 Sample size, µL 0.5
Temperatures
those components only are normalized to 100.00.
Injector, °C 250
4.2 Results can be reported as either volume or weight
Detector, °C 300
percent. Volumetric results can be derived by dividing each
Column
Initial, °C 70
component’s weight percent by its relative density and re-
Hold, min 10
normalizing to 100 %.
Rate, °C/min 5
Final, °C 200
5. Significance and Use Hold, min 24
5.1 This test method was primarily developed to determine
benzene, toluene, and xylenes in chemical intermediate and
8.2 Detector Gas—Hydrogen with a minimum purity of
solvent streams such as reformate, BTX extracts, pyrolysis
99.99 mol %.
gasoline, hydrogenated pyrolysis gasoline, crude benzene,
8.3 Flame Support Gas—Air, total, hydrocarbon less than 5
crude ethylbenzene, commercial toluene, and light blending
ppm.
aromatic feedstocks. This test method may not detect all
9. Hazards
components and there may be unknown components that
would be assigned inappropriate response factors and thus, the
9.1 Consult current OSHA regulations, supplier’s Material
results may not be absolute.
Safety Data Sheets, and local regulations for all material used
5.2 The relative distribution of C aromatics is useful for
8 in this test method.
determining conformance to p-xylene feedstock specifications.
10. Sampling
6. Interferences
10.1 Sample material in accordance with Practice D3437.
6.1 Nonaromatic hydrocarbons may interfere with the de-
11. Preparation of Apparatus
termination of benzene and toluene when certain columns are
11.1 Chromatograph—Follow manufacturer’s instructions
used.
for mounting and conditioning the column in the chromato-
6.2 Styrene may be present in some samples. It will elute
graph. Adjust the instrument to the conditions as described in
with C + aromatics.
Table 1 to give the desired separation using the suggested
column. Other columns may require different conditions to
7. Apparatus
achieve the resolution requirements. Allow sufficient time for
7.1 Gas Chromatograph—Any gas chromatograph having a
the instrument to reach equilibrium as indicated by a stable
flame ionization detector and a splitter injector suitable for use
recorder/electronic baseline. See Practices E355 and E1510 for
with a fused silica capillary column may be used, provided the
additional information on gas chromatography practices and
system has sufficient sensitivity, linearity, and range to obtain a
terminology.
minimum peak height response for a 0.01 % peak of five times
the height of the signal background noise, while not exceeding
12. Procedure
the full scale of either the detector or the electronic integration
12.1 Bring the sample to ambient room temperature.
for the highest peak. The split injection system shall not
12.2 Inject an appropriate amount of sample into the chro-
discriminate over the boiling range of the samples analyzed.
matograph that meets the criteria outlined in 7.1. See Practices
The system shall be capable of operating at the conditions
E355 and E1510 for additional information on gas chromatog-
given in Table 1.
raphy practices and terminology.
7.2 Columns—The choice of column is based upon resolu-
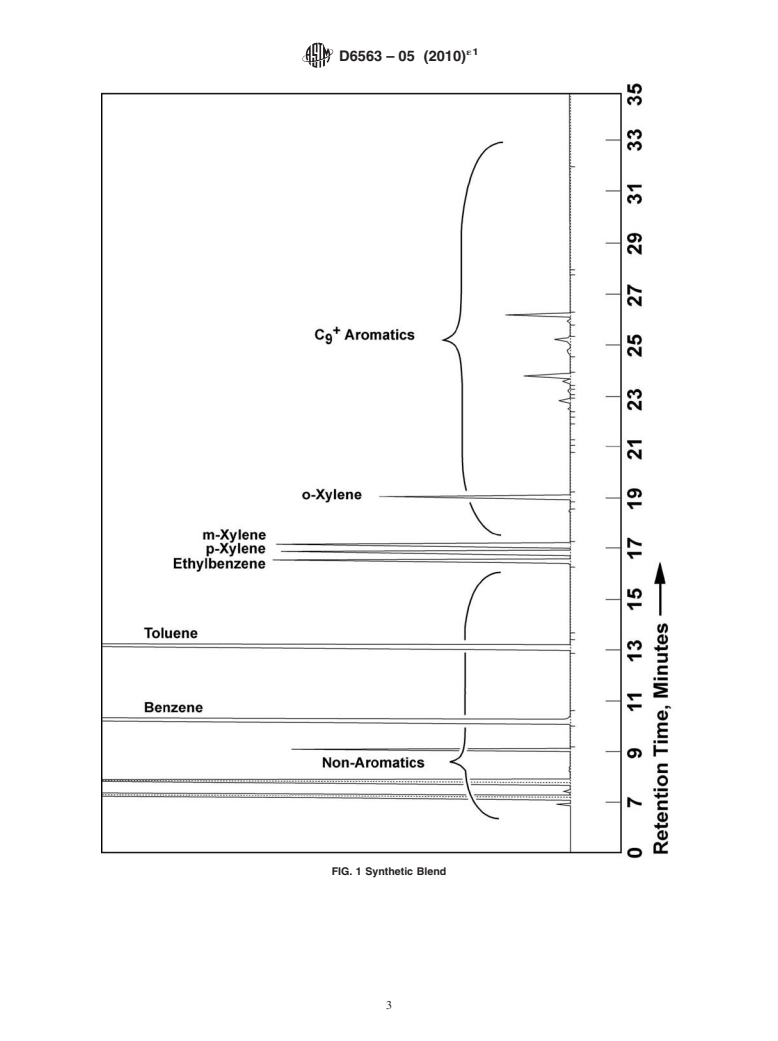
12.3 Sample chromatograms are illustrated in Figs. 1-4.
tion requirements. Any column may be used that is capable of
12.4 Measure the area of all peaks. The non-aromatics
resolving all the components of interest. The column and
fraction includes all peaks up to ethylbenzene (except for the
conditions described in Table 1 have been used successfully
peaks assigned to benzene and toluene). Sum together all the
and will be the referee in case of dispute.
non-aromatic peaks as a total area. The C + aromatics fraction
7.3 Recorder/Electronic Integration—Electronicintegration
includes all peaks eluting after m-xylene except for 0-xylene.
with tangent capabilities is recommended.
Sum together all the C + aromatic peaks as a total area.
8. Reagents 13. Calculation
8.1 Carrier Gas—Helium with a minimum purity of 99.99 13.1 Calculate the weight percent concentration of each
mol %. component as follows:
´1
D6563–05 (2010)
FIG. 1 Synthetic Blend
´1
D6563–05 (2010)
FIG. 2 Pyrolysis Gasoline
´1
D6563–05 (2010)
FIG. 3 Extracted Reformate
´1
D6563–05 (2010)
FIG. 4 Mixed Xylenes
´1
D6563–05 (2010)
100 3 A 3 ECN TABLE 2
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.