ASTM B939-15
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Radial Crushing Strength, K, of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings and Structural Materials
Standard Test Method for Radial Crushing Strength, <emph type="bdit">K</emph>, of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings and Structural Materials
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The radial crushing strength test is a destructive procedure used to determine a material strength characteristic of PM bearings and hollow cylindrical test specimens. These data can be used to grade, classify, and evaluate the materials.
5.2 The PM bearing Specifications B438 and B439 require the use of this test method as an acceptance test for the strength of oil-impregnated sintered bearings.
5.3 This test method may be used by powder producers and parts manufacturers as a lot acceptance test for metal powders and lubricated powder mixtures intended for the production of porous parts.
5.4 Companies in the PM industry use this test as a manufacturing control test because it is appropriate for production practices.
5.5 Radial crushing strength is a property of the PM material but is not a design value. However, experience has shown that the radial crushing strength of a material is approximately twice the ultimate tensile strength.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the equipment and laboratory procedure for the determination of the radial crushing strength of materials using either a plain powder metallurgy (PM) bearing or a thin-walled hollow cylindrical test specimen. This is a destructive test that produces quantitative results.
1.2 Limitations:
1.2.1 The principle of this procedure is based on the material being tested having minimal ductility. The permanent deflection of the cylinder during the test should not exceed 10 % of the outside diameter.
1.2.2 The radial crushing strength test results should be used only as a guide if the test specimen has a wall thickness that is greater than one-third of the outside diameter. These test results should then only be used for comparison with data from the test specimens of like materials and similar dimensions.
1.3 With the exception of the values for density and the mass used to determine density, for which the use of the gram per cubic centimetre (g/cm3) and gram (g) units are the industry standard, the values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: B939 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Radial Crushing Strength,K, of Powder Metallurgy (PM)
1
Bearings and Structural Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B939; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* B438Specification for Bronze-Base Powder Metallurgy
(PM) Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
1.1 This test method covers the equipment and laboratory
B439Specification for Iron-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM)
procedure for the determination of the radial crushing strength
Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
of materials using either a plain powder metallurgy (PM)
B925Practices for Production and Preparation of Powder
bearing or a thin-walled hollow cylindrical test specimen.This
Metallurgy (PM) Test Specimens
is a destructive test that produces quantitative results.
E456Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
1.2 Limitations:
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
1.2.1 The principle of this procedure is based on the
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
material being tested having minimal ductility. The permanent
3
2.2 MPIF Standard:
deflection of the cylinder during the test should not exceed
MPIF Standard 55Determination of Radial Crush Strength
10% of the outside diameter.
(K) of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Test Specimens
1.2.2 Theradialcrushingstrengthtestresultsshouldbeused
only as a guide if the test specimen has a wall thickness that is
3. Terminology
greaterthanone-thirdoftheoutsidediameter.Thesetestresults
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of powder metallurgy (PM)
shouldthenonlybeusedforcomparisonwithdatafromthetest
terms can be found in Terminology B243. Additional descrip-
specimens of like materials and similar dimensions.
tive information is available in the related material section of
1.3 With the exception of the values for density and the
Vol 02.05 of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards.
mass used to determine density, for which the use of the gram
3
per cubic centimetre (g/cm ) and gram (g) units are the
4. Summary of Test Method
industry standard, the values stated in inch-pound units are to
4.1 Radial crushing strength is determined by subjecting a
be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are
plain sleeve bearing or a thin-walled cylindrical test specimen
mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for
to a controlled compressive force applied perpendicular to its
information only and are not considered standard.
central axis under uniformly increasing load until fracture
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
occurs.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4.2 The term “radial crushing strength,” as used in this test
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- method is the stress at fracture calculated from the breaking
load and the dimensions of the test specimen.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 The radial crushing strength test is a destructive proce-
B243Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
dureusedtodetermineamaterialstrengthcharacteristicofPM
bearings and hollow cylindrical test specimens.These data can
be used to grade, classify, and evaluate the materials.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B09 on Metal
Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcom-
5.2 The PM bearing Specifications B438 and B439 require
mittee B09.04 on Bearings.
theuseofthistestmethodasanacceptancetestforthestrength
Current edition approved April 1, 2015. Published April 2015. Originally
of oil-impregnated sintered bearings.
approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as B939–09. DOI:
10.1520/B0939-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from Metal Powder Industries Federation (MPIF), 105 College Rd.
the ASTM website. East, Princeton, NJ 08540, http://www.mpif.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B939 − 15
5.3 This test method may be used by powder producers and
parts manufacturers as a lot acceptance test for metal powders
and lubricated powder mixtures intended
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: B939 − 09 B939 − 15
Standard Test Method for
Radial Crushing Strength, K, of Powder Metallurgy (PM)
1
Bearings and Structural Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation B939; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the equipment and laboratory procedure for the determination of the radial crushing strength of
materials using either a plain powder metallurgy (PM) bearing or a thin-walled hollow cylindrical test specimen. This is a
destructive test that produces quantitative results.
1.2 Limitations:
1.2.1 The principle of this procedure is based on the material being tested having minimal ductility. The permanent deflection
of the cylinder during the test should not exceed 10 % of the outside diameter.
1.2.2 The radial crushing strength test results should be used only as a guide if the test specimen has a wall thickness that is
greater than one-third of the outside diameter. These test results should then only be used for comparison with data from the test
specimens of like materials and similar dimensions.
1.3 With the exception of density values, the values for density and the mass used to determine density, for which the g/cmuse
3
of the gram per cubic centimetre (g/cm unit is ) and gram (g) units are the industry standard, the values stated in inch-pound units
are to be considered theregarded as standard. The values in SI units, shown in parenthesis have been converted in accordance with
IEEE/ASTM Standard SI 10, may be approximate and are only included for information. given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B243 Terminology of Powder Metallurgy
B438 Specification for Bronze-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
B439 Specification for Iron-Base Powder Metallurgy (PM) Bearings (Oil-Impregnated)
B925 Practices for Production and Preparation of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Test Specimens
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.2 IEEE/ASTM Standard:
SI 10 American National Standard for Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
3
2.2 MPIF Standard:
MPIF Standard 55 Determination of Radial Crush Strength (K) of Powder Metallurgy (PM) Test Specimens
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of powder metallurgy (PM) terms can be found in Terminology B243. Additional descriptive
information is available in the related material section of Vol 02.05 of the Annual Book of ASTM Standards.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee B09 on Metal Powders and Metal Powder Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee B09.04
on Bearings.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2009April 1, 2015. Published January 2010April 2015. Originally approved in2005. in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 20052009
as B939 – 05.B939 – 09. DOI: 10.1520/B0939-09.10.1520/B0939-15.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Metal Powder Industries Federation (MPIF), 105 College Rd. East, Princeton, NJ 08540, http://www.mpif.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
B939 − 15
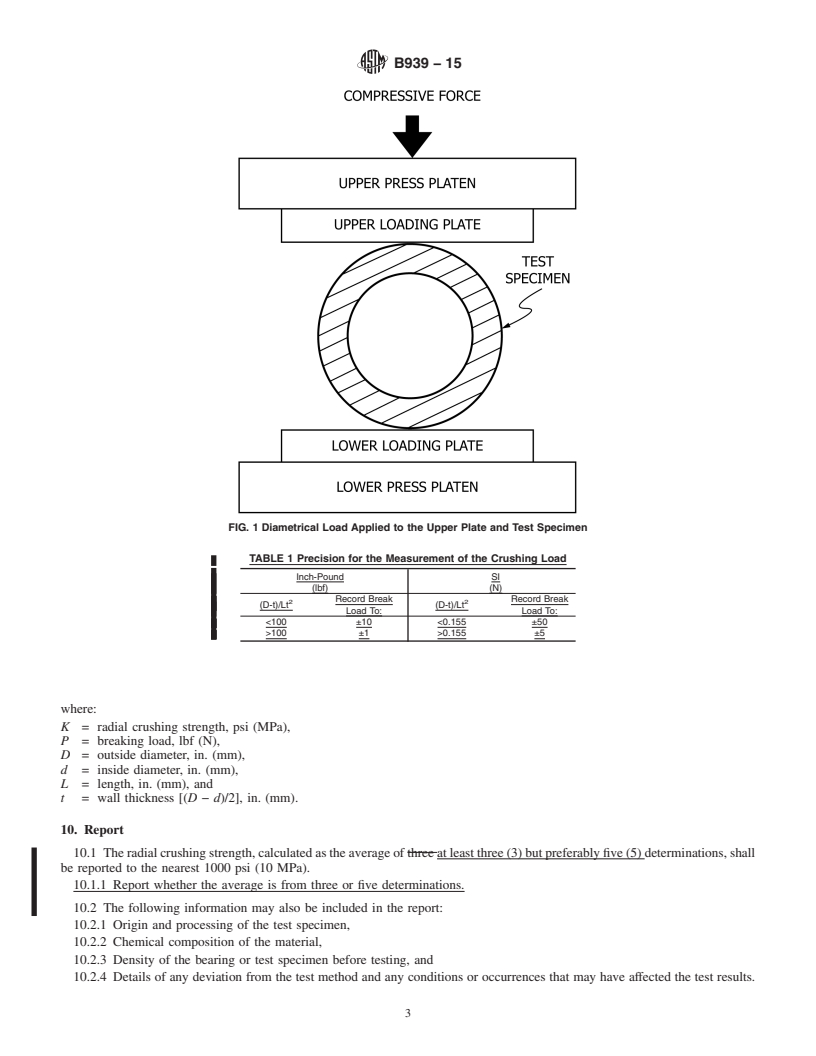
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Radial crushing strength is determined by subjecting a plain sleeve bearing or a thin-walled cylindrical test specimen to a
controlled compressive force applied perpendicular to its central axis under uniformly increasing load until fracture occurs.
4.2 The term radi
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.