ASTM E1951-14(2019)
(Guide)Standard Guide for Calibrating Reticles and Light Microscope Magnifications
Standard Guide for Calibrating Reticles and Light Microscope Magnifications
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 These methods can be used to determine magnifications as viewed through the eyepieces of light microscopes.
4.2 These methods can be used to calibrate microscope magnifications for photography, video systems, and projection stations.
4.3 Reticles may be calibrated as independent articles and as components of a microscope system.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide covers methods for calculating and calibrating microscope magnifications, photographic magnifications, video monitor magnifications, grain size comparison reticles, and other measuring reticles. Reflected light microscopes are used to characterize material microstructures. Many materials engineering decisions may be based on qualitative and quantitative analyses of a microstructure. It is essential that microscope magnifications and reticle dimensions be accurate.
1.2 The calibration using these methods is only as precise as the measuring devices used. It is recommended that the stage micrometer or scale used in the calibration should be traceable to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) or a similar organization.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:E1951 −14 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Guide for
1
Calibrating Reticles and Light Microscope Magnifications
This standard is issued under the fixed designation E1951; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This guide covers methods for calculating and calibrat- 4.1 These methods can be used to determine magnifications
ing microscope magnifications, photographic magnifications, as viewed through the eyepieces of light microscopes.
video monitor magnifications, grain size comparison reticles,
4.2 These methods can be used to calibrate microscope
and other measuring reticles. Reflected light microscopes are
magnifications for photography, video systems, and projection
used to characterize material microstructures. Many materials
stations.
engineering decisions may be based on qualitative and quan-
4.3 Reticlesmaybecalibratedasindependentarticlesandas
titative analyses of a microstructure. It is essential that micro-
components of a microscope system.
scope magnifications and reticle dimensions be accurate.
1.2 Thecalibrationusingthesemethodsisonlyaspreciseas
5. Procedures
the measuring devices used. It is recommended that the stage
5.1 Nominal Magnification Calculations:
micrometer or scale used in the calibration should be traceable
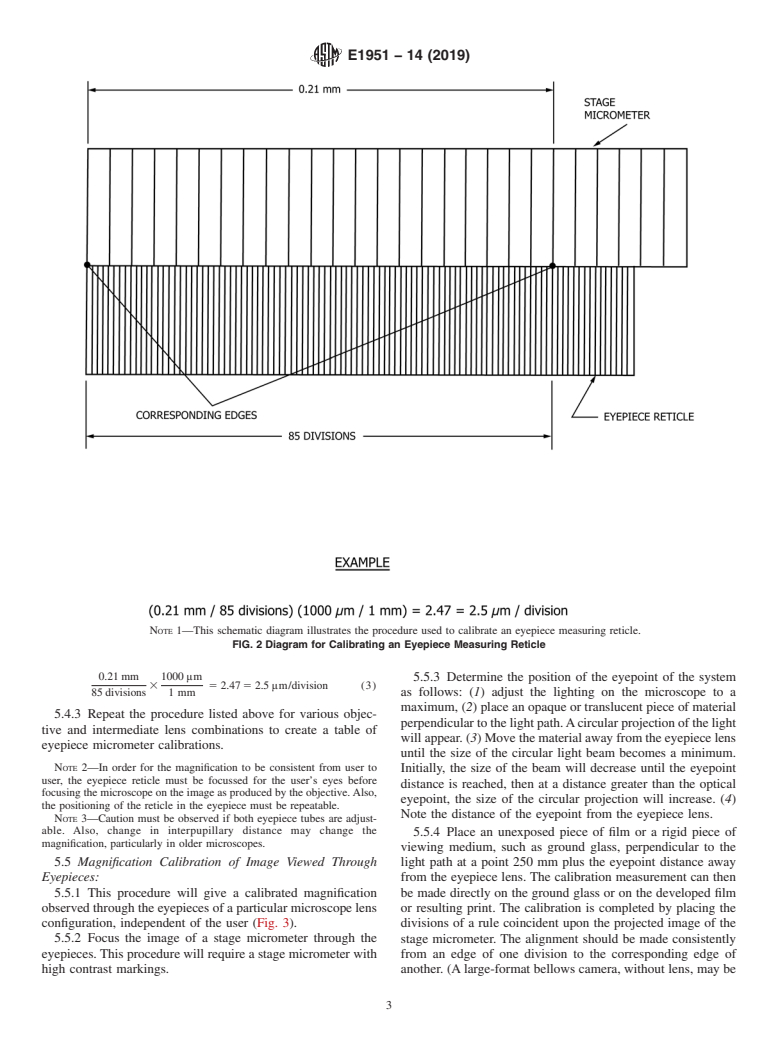
5.1.1 A calculated magnification, using the manufacturer’s
to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
or a similar organization. supplied ratings, is only an approximation of the true
magnification, since individual optical components may vary
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
from their marked magnification. For a precise determination
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
of the magnification observed through an eyepiece, see the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
procedure describe in 5.5.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
5.1.2 For a compound microscope, the total magnification
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
(M) of an image through the eyepiece is the product of the
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- t
objective lens magnification (M ), the eyepiece magnification
o
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
(M ), and, if present, a zoom system or other intermediate lens
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the e
magnification (M).An expression for the total magnification is
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- i
shown in Eq 1.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
M 5 M 3M 3M (1)
t o e i
5.1.3 Example 1—For a microscope configured with a 10X
2. Referenced Documents
objective, a 10X eyepiece, and a 1.25X intermediate lens, the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
total magnification observed through the eyepiece would be
E7 Terminology Relating to Metallography
calculated as follows.
E112 Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size
M 5 1031031.25 5 125 (2)
t
3. Terminology
5.2 Calibration for Photomicrography Magnifications:
3.1 Definitions—All terms used in this guide are defined in 5.2.1 The magnification of an image can be determined by
Terminology E7. photographing a calibrated stage micrometer using the desired
optical setup. First, photograph the stage micrometer using the
desired combination of objective, bellows extension, zoom and
1
ThisguideisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeE04onMetallography
intermediate lens, and then measure the apparent ruling length
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee E04.03 on Light Microscopy.
on the photomicrograph. The measurement should be made
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2019. Published November 2019. Originally
consistently from an edge or center of one division to the
approved in 1998. Last previous edition approved in 2014 as E1951–14. DOI:
10.1520/E1951-14R19.
corresponding edge or center of another (see Note 1). By
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
dividing this apparent length of ruling by the known dimension
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
of the micrometer, the magnification of the photomicrograph is
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. determined (see Fig. 1). The accuracy of the calibration is
Copyright © A
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.