ASTM D3867-09
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Nitrite-Nitrate in Water
Standard Test Methods for Nitrite-Nitrate in Water
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Both test methods use identical reagents and sample processing. The only difference between the two methods is that one test method is automated and the other is manual. The ranges and interferences are identical.
The automated test method is preferred when large numbers of samples are to be analyzed. The manual test method is used for fewer samples or when automated instrumentation is not available.
These test methods replace Test Methods D 1254 (Nitrite) and D 992 (Nitrate). The nitrite test method (Test Method D 1254) used a reagent that is considered to be a potential carcinogen. The nitrate test method (Test Method D 992) has been shown to have relatively large errors when used in wastewaters and also has greater manipulative difficulties than the test method described herein.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of nitrite nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, and combined nitrite-nitrate nitrogen in water and wastewater in the range from 0.05 to 1.0 mg/L nitrogen. Two test methods are given as follows:
Sections Test Method A—Automated Cadmium Reduction 9 to 18 Test Method B—Manual Cadmium Reduction19 to 28
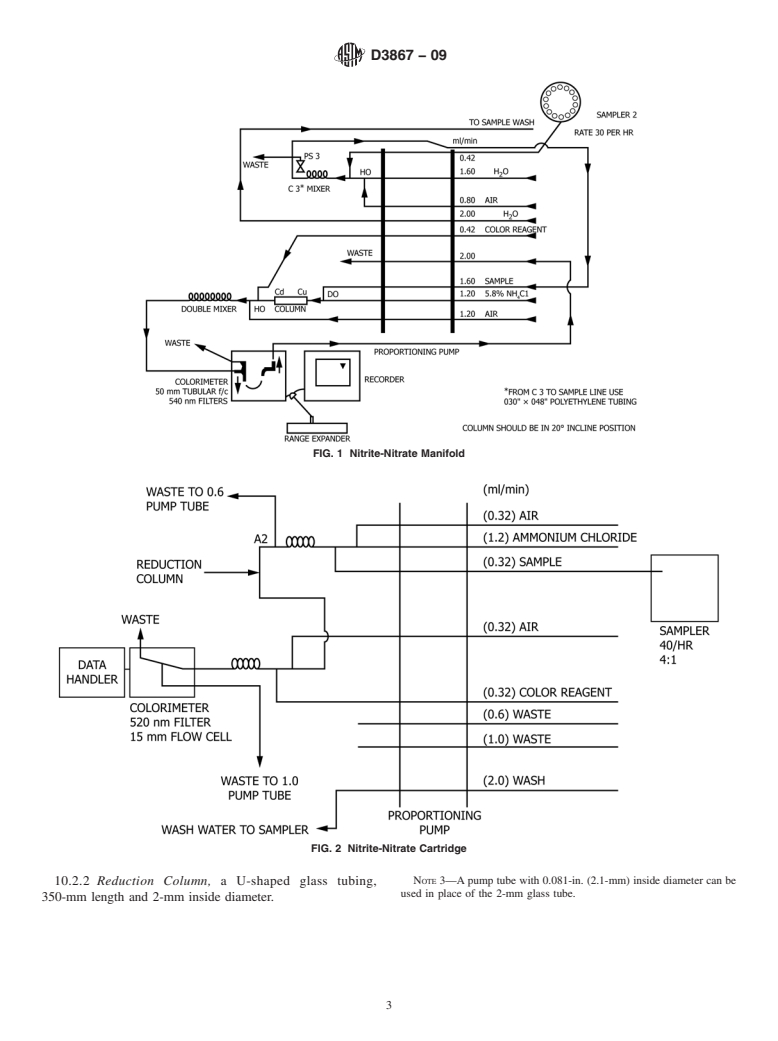
1.2 These test methods are applicable to surface, saline, waste, and ground waters. It is the user's responsibility to ensure the validity of these test methods for waters of untested matrices.
1.3 The values stated in either SI or inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Note 1 and Note 2.
9.1 The applicable range of this test method is from 0.05 to 1 mg/L of nitrite or nitrate nitrogen. The range may be extended upward by dilution of an appropriate aliquot. Many workers have found that this test method is reliable for nitrite and combined nitrite-nitrate levels to 0.01 mg N/L. However, the precision and bias data presented in this test method are insufficient to justify application of this test method in the 0.01 to 0.05 mg/L-N range.
9.2 This test method is applicable to surface, saline, waste, and ground waters. It is the user's responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for waters of untested matrices.
19.1 The applicable range of this test method is from 0.05 to 1 mg/L of nitrite or nitrate nitrogen. The range may be extended upward by dilution of an appropriate aliquot. Many workers have found that this test method is reliable for nitrite and combined nitrite-nitrate levels to 0.01 mg N/L. However, the precision and accuracy data presented in this test method are insufficient to justify application of this test method in the 0.01 to 0.05 mg/L-N range.
19.2 This test method is applicable to surface, saline, waste, and ground waters. It is the user's responsibility to ensure the validity of this test method for waters of untested matrices.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D3867 − 09
StandardTest Methods for
1
Nitrite-Nitrate in Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D3867; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications
for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of nitrite
E60 Practice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related
nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, and combined nitrite-nitrate nitrogen
Materials by Spectrophotometry
in water and wastewater in the range from 0.05 to 1.0 mg/L
2 E275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance of
nitrogen. Two test methods are given as follows:
Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometers
Sections
Test Method A—Automated Cadmium Reduction 9 to 18
3. Terminology
Test Method B—Manual Cadmium Reduction 19 to 28
1.2 These test methods are applicable to surface, saline,
3.1 Definitions: For definitions of terms used in these test
waste, and ground waters. It is the user’s responsibility to
methods, refer to Terminology D1129.
ensure the validity of these test methods for waters of untested
matrices. 4. Summary of Test Methods
1.3 The values stated in either SI or inch-pound units are to
4.1 Total Oxidized Nitrogen—a filtered sample is passed
be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses through a column containing copper-coated cadmium granules
are for information only.
to reduce nitrate ion to nitrite ion. The combined nitrite-nitrate
nitrogen is determined by diazotizing the total nitrite ion with
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
sulfanilamide and coupling with N-(1-
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride to form a highly
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
colored azo dye that is measured spectrophotometrically.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific hazard
4.2 Nitrite—the nitrite ion originally present in the sample
statements, see Note 1 and Note 2.
canbedeterminedseparatelybycarryingouttheprocedureand
omitting the cadmium reduction step.
2. Referenced Documents
4.3 Nitrate—the nitrate ion can be calculated as the differ-
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
ence between the combined nitrite-nitrate nitrogen and the
D1129 Terminology Relating to Water
nitrite nitrogen.
D1141 Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean
Water
5. Significance and Use
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
5.1 Both test methods use identical reagents and sample
D2777 Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias of
processing. The only difference between the two methods is
Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
that one test method is automated and the other is manual. The
D3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
ranges and interferences are identical.
D5810 Guide for Spiking into Aqueous Samples
5.2 The automated test method is preferred when large
numbers of samples are to be analyzed. The manual test
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D19 on
method is used for fewer samples or when automated instru-
Water and are the responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic Constituents
mentation is not available.
in Water.
Current edition approved May 15, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally
5.3 These test methods replace Test Methods D1254 (Ni-
approved in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D3867 – 04. DOI:
trite) and D992 (Nitrate). The nitrite test method (Test Method
10.1520/D3867-09.
2
D1254) used a reagent that is considered to be a potential
Methods similar to these appear in Methods of Chemical Analysis of Water and
Wastes, 2nd edition, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
carcinogen. The nitrate test method (Test Method D992) has
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
been shown to have relatively large errors when used in
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
wastewaters and also has greater manipulative difficulties than
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. the test method described herein.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3867 − 09
6. Interferences 8. Sampling and Sample Preservation
6.1 Turbi
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D 3867–04 Designation:D3867–09
Standard Test Methods for
1
Nitrite-Nitrate in Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 3867; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of nitrite nitrogen, nitrate nitrogen, and combined nitrite-nitrate nitrogen in
2
water and wastewater in the range from 0.05 to 1.0 mg/L nitrogen. Two test methods are given as follows:
Sections
Test Method A—Automated Cadmium Reduction 9to16
Test Method A—Automated Cadmium Reduction 9to18
Test Method B—Manual Cadmium Reduction17 to 24 19 to 28
Test Method B—Manual Cadmium Reduction 19 to 28
1.2 These test methods are applicable to surface, saline, waste, and ground waters. It is the user’s responsibility to ensure the
validity of these test methods for waters of untested matrices.
1.3
1.3 The values stated in either SI or inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are
for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific hazard statements, see Note 1 and Note 2.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3
D992Test Method for Nitrate Ion in Water ASTM Standards:
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
D 1141 Practice for the Preparation of Substitute Ocean Water D1192Specification for Equipment for Sampling Water and
4
Steam in Closed Conduits
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
4
D1254Test Method for Nitrite Ion in Water
D2777Practice for Determination of Precision and Bias ofApplicable Methods of Committee D19 on Water 2777 Practice for
Determination of Precision and Bias of Applicable Test Methods of Committee D19 on Water
D 3370 Practices for Sampling Water from Closed Conduits
D5810Guide for Spiking Into Aqueous Samples
D5847
D 5810 Guide for Spiking into Aqueous Samples
D 5847 Practice for Writing Quality Control Specifications for Standard Test Methods for Water Analysis
E60 PracticesPractice for Analysis of Metals, Ores, and Related Materials by Molecular Absorption Spectrometry
E 275 Practice for Describing and Measuring Performance of Ultraviolet, Visible, Ultraviolet and Near InfraredVisible
Spectrophotometers
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions: For definitions of terms used in these test methods, refer to Terminology D 1129.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D19 on Water and are the responsibility of Subcommittee D19.05 on Inorganic Constituents in Water.
Current edition approved July 1, 2004. Published July 2004. Originally approved in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 1999 as D3867–99.
Current edition approved May 15, 2009. Published May 2009. Originally approved in 1979. Last previous edition approved in 2004 as D 3867 – 04.
2
Methods similar to these appear in Methods of Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes, 2nd edition, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
3
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D3867–09
4. Summary of Test Methods
4.1 Total Oxidized Nitrogen—a filtered sample is passed through a column containing copper-coated cadmium granules to
reduce nitrate ion to nitrite ion. The combined nitrite-nitrate nitrogen is determined by diazotizing the total nitrite ion with
sulfanilamideandcouplingwith N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediaminedihydrochloridetoformahighlycoloredazodyethatismeasured
spectrophotometrically.
4.2 Nitrite—the nitrite ion originally present in the sample can be determined separately by carrying out the procedure and
omitting the cadmium reduction step.
4.3 Nitrate—the nitrate ion can be calculated as the difference between the combined nitrite-nitrate nitrogen and th
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.