ASTM D4475-02(2008)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Apparent Horizontal Shear Strength of Pultruded Reinforced Plastic Rods By the Short-Beam Method
Standard Test Method for Apparent Horizontal Shear Strength of Pultruded Reinforced Plastic Rods By the Short-Beam Method
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
Apparent shear strength determined by this test method is useful for quality control and specification purposes. It is also applicable to research and development programs concerned with interlaminar-shear strength. The apparent shear strength obtained by this test method cannot be used for design purposes, but can be utilized for comparative testing of composite materials, if all failures are in horizontal shear.
It is recommended that control samples be fabricated with each research test series and that care be used to compare each set of controls with corresponding test series run at different times.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the apparent horizontal shear strength of fiber reinforced plastic rods. The specimen is a short beam in the form of lengths of pultruded rods. This test method is applicable to all types of parallel-fiber-reinforced plastic rod samples.
1.2 This test method is primarily used for quality control and specification purposes (see 4.1).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4475 −02(Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Apparent Horizontal Shear Strength of Pultruded Reinforced
Plastic Rods By the Short-Beam Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4475; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Significance and Use
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the appar- 4.1 Apparent shear strength determined by this test method
ent horizontal shear strength of fiber reinforced plastic rods. is useful for quality control and specification purposes. It is
The specimen is a short beam in the form of lengths of also applicable to research and development programs con-
pultruded rods. This test method is applicable to all types of cerned with interlaminar-shear strength. The apparent shear
parallel-fiber-reinforced plastic rod samples. strength obtained by this test method cannot be used for design
purposes, but can be utilized for comparative testing of
1.2 This test method is primarily used for quality control
composite materials, if all failures are in horizontal shear.
and specification purposes (see 4.1).
4.2 It is recommended that control samples be fabricated
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
with each research test series and that care be used to compare
standard.
each set of controls with corresponding test series run at
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
different times.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
5. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1 TestingMachine—Aproperly calibrated testing machine
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
that can be operated at a constant rate of crosshead motion, and
NOTE 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
in which the error in the load measuring system shall not
exceed 61 % of the maximum load expected to be measured.
2. Referenced Documents
The load-indicating mechanism shall be essentially free of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
inertia lag at the crosshead rate used. The accuracy of the
D618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
testing machine shall be verified in accordance with Practices
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
E4.
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
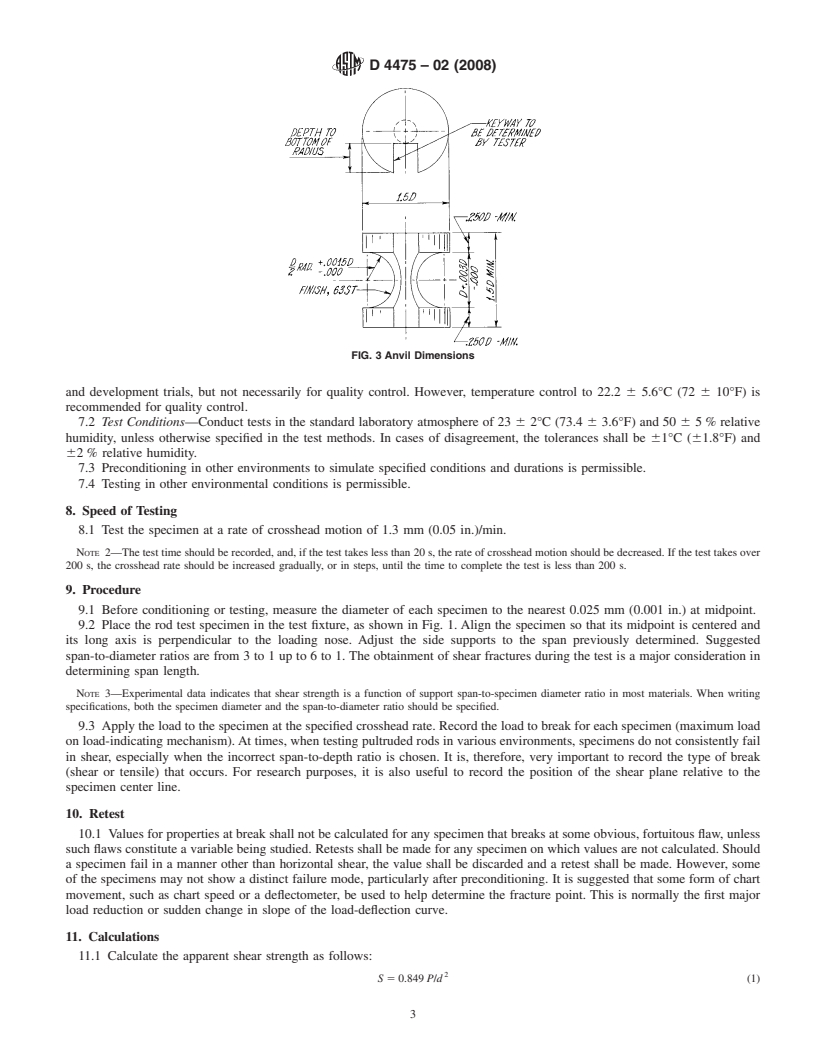
5.2 Loading Nose and Supports—Shown in Fig. 2 and Fig.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. The loading nose shall be a suitable steel rod with a groove
3. Summary of Test Method in the diameter of the pultruded rod machined in its lower end.
The groove diameter shall always have a plus tolerance and
3.1 The horizontal-shear test specimen is center-loaded as
zero negative tolerance.The bottom support shall be adjustable
shown in Fig. 1. The ends of the specimens rest on two
to allow for testing at various span/diameter ratios.The surface
supports that allow the specimen to bend, the load being
of the groove shall be free of indentation and burrs, with all
applied by means of a loading nose at midpoint along the
sharp edges relieved.
support span, as shown in Fig. 2.
5.3 Micrometers—Suitable micrometers for measuring the
3.2 The specimen is deflected until a shear failure occurs at
diameter of the test specimen to an incremental discrimination
the midplane of the horizontally supported rod.
of at least 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) shall be used.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D20 on Plastics
6. Test Specimen
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.18 on Reinforced Thermoset-
ting Plastics.
6.1 The specimen shall be cut from the pultruded rod to a
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published March 2008. Originally
length of one diameter greater than the test span and to a
approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D4475 - 02. DOI:
tolerance of plus or minus 0.1 times the diameter.
10.1520/D4475-02R08.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
6.2 Number of Specimens—The number of test specimens is
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
optional. However, a minimum of five specimens is required to
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. obtain a satisfactory average and standard deviation.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4475−02 (2008)
FIG. 3 Anvil Dimensions
7.3 Preconditioning in other environments to simulate
FIG. 1 Test Assembly
specified conditions and durations is permissible.
7.4 Testing in other environmental conditions is permis-
sible.
8. Speed of Testing
8.1 Test the specimen at a rate of crosshead motion of 1.3
mm (0.05 in.)/min.
NOTE 2—The test time should be recorded, and, if the test takes less
than 20 s, the rate of crosshead motion should be decreased. If the test
takes over 200 s, the crosshead rate should be increased gradually, or in
steps, until the time to complete the test is less than 200 s.
9. Procedure
9.1 Before conditioning or testing, measure the diameter of
each specimen to the nearest 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) at midpoint.
9.2 Place the rod test specimen in the test fixture, as shown
FIG. 2 Span Configuration for 3D Span. Span. May Also Be 4D,
in Fig. 1. Align the specimen so that its midpoint is centered
5D, or 6D, as Required to Achieve Shear Mode of Failure
and its long axis is perpendicular to the loading nose. Adjust
the side supports to the span previously determined. Suggested
span-to-diameter ratios are from 3 to 1 up to 6 to 1. The
7. Conditioning
obtainment of shear fractures during the test is a major
7.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens at 23 6
consideration in determining span length.
2°C(73.4 63.6°F)and50 65 %relativehumidityfornotless
NOTE3—Experimentaldataindicatesthatshearstrengthisafunctionof
than 40 h prior to test, in accordance with Procedure A of
support span-to-specimen diameter ratio in most materials. When writing
PracticeD618for those tests where conditioning is required. In
specifications, both the specimen diameter and the span-to-diameter ratio
cases of disagreement, the tolerances shall be 61°C (61.8°F)
should be specified.
and 62 % relative humidity. These conditions are recom-
9.3 Apply the load to the specimen at the specified cross-
mended for research and development trials, but not necessar-
head rate. Record the load to break for each specimen
ily for quality control. However, temperature control to 22.2 6
(maximum load on load-indicating mechanism). At times,
5.6°C (72 6 10°F) is recommended for quality control.
when testing pultruded rods in various environments, speci-
7.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the standard labora- mens do not consistently fail in shear, especially when the
tory atmosphere of 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5% incorrect span-to-depth ratio is chosen. It is, therefore, very
relat
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D4475–96 Designation: D 4475 – 02 (Reapproved 2008)
Standard Test Method for
Apparent Horizontal Shear Strength of Pultruded Reinforced
Plastic Rods By the Short-Beam Method
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4475; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the apparent horizontal shear strength of fiber reinforced plastic rods. The
specimen is a short beam in the form of lengths of pultruded rods. This test method is applicable to all types of
parallel-fiber-reinforced plastic rod samples.
1.2 This test method is primarily used for quality control and specification purposes (see 4.1).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
NOTE 1—There is no similar or equivalent ISO standard.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
E 4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
E 691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
3. Summary of Test Method
3.1 The horizontal-shear test specimen is center-loaded as shown in Fig. 1. The ends of the specimens rest on two supports that
allow the specimen to bend, the load being applied by means of a loading nose at midpoint along the support span, as shown in
Fig. 2.
3.2 The specimen is deflected until a shear failure occurs at the midplane of the horizontally supported rod.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 Apparent shear strength determined by this test method is useful for quality control and specification purposes. It is also
applicabletoresearchanddevelopmentprogramsconcernedwithinterlaminar-shearstrength.Theapparentshearstrengthobtained
by this test method cannot be used for design purposes, but can be utilized for comparative testing of composite materials, if all
failures are in horizontal shear.
4.2 It is recommended that control samples be fabricated with each research test series and that care be used to compare each
set of controls with corresponding test series run at different times.
5. Apparatus
5.1 Testing Machine—A properly calibrated testing machine that can be operated at a constant rate of crosshead motion, and
in which the error in the load measuring system shall not exceed 61 % of the maximum load expected to be measured. The
load-indicating mechanism shall be essentially free of inertia lag at the crosshead rate used. The accuracy of the testing machine
shall be verified in accordance with Practices E 4.
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-20 on Plastics and is the direct responsiblity of Subcommittee D20.18 on Reinforced Thermosetting
Plastics.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1996. Published May 1997. Originally published as D4475–85. Last previous edition D4475–85(1990).
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.18 on Reinforced Thermosetting
Plastics.
Current edition approved March 1, 2008. Published March 2008. Originally approved in 1985. Last previous edition approved in 2002 as D4475 - 02.
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D 4475 – 02 (2008)
FIG. 1 Test Assembly
FIG. 2 Span Configuration for 3D Span. Span. May Also Be 4D,
5D, or 6D, as Required to Achieve Shear Mode of Failure
5.2 Loading Nose and Supports—Shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. The loading nose shall be a suitable steel rod with a groove in
the diameter of the pultruded rod machined in its lower end. The groove diameter shall always have a plus tolerance and zero
negative tolerance. The bottom support shall be adjustable to allow for testing at various span/diameter ratios. The surface of the
groove shall be free of indentation and burrs, with all sharp edges relieved.
5.3 Micrometers—Suitable micrometers for measuring the diameter of the test specimen to an incremental discrimination of at
least 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) shall be used.
6. Test Specimen
6.1 The specimen shall be cut from the pultruded rod to a length of one diameter greater than the test span and to a tolerance
of plus or minus 0.1 times the diameter.
6.2 Number of Specimens—The number of test specimens is optional. However, a minimum of five specimens is required to
obtain a satisfactory average and standard deviation.
7. Conditioning
7.1 Conditioning—Condition the test specimens at 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5 % relative humidity for not less than
40 h prior to test, in accordance with Procedure A of Practice D 618 for those tests where conditioning is required. In cases of
disagreement, the tolerances shall be 61°C (61.8°F) and 62 % relative humidity.These conditions are recommended for research
D 4475 – 02 (2008)
FIG. 3 Anvil Dimensions
and development trials, but not necessarily for quality control. However, temperature control to 22.2 6 5.6°C (72 6 10°F) is
recommended for quality control.
7.2 Test Conditions—Conduct tests in the standard laboratory atmosphere of 23 6 2°C (73.4 6 3.6°F) and 50 6 5 % relative
humidity, unless otherwise specified in the test methods. In cases of disagreement, the tolerances shall be 61°C (61.8°F) and
62 % relative humidity.
7.3 Preconditioning in other environments to simulate specified conditions and durations is permissible.
7.4 Testing in other environmental conditions is permissible.
8. Speed of Testing
8.1 Test the specimen at a rate of crosshead motion of 1.3 mm (0.05 in.)/min.
NOTE 2—The test time should be recorded, and, if the test takes less than 20 s, the rate of crosshead motion should be decreased. If the test takes over
200 s, the crosshead rate should be increased gradually, or in steps, until the time to complete the test is less than 200 s.
9. Procedure
9.1 Before conditioning or testing, measure the diameter of each specimen to the nearest 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) at midpoint.
9.2 Place the rod test specimen in the test fixture, as shown in Fig. 1. Align the specimen so that its midpoint is centered and
its long axis is perpendicular to the loading nose. Adjust the side supports to the span previously determined. Suggested
span-to-diameter ratios are from 3 to 1 up to 6 to 1. The obtainment of shear fractures during the test is a major consideration in
determining span length.
NOTE 3—Experimental data indicates that shear strength is a function of support span-to-specimen diameter ratio in most materials. When writing
specifications, both the specimen diameter and the span-to-diameter ratio should be specified.
9.3 Apply the load to the specimen at the specified crosshead rate. Record the load to break for each specimen (maximum load
on load-indicating mechanism).At times, when testing pultruded rods in various environments, specimens do not consistently fail
in shear, especially when the incorrect span-to-depth ratio is chosen. It is, therefore, very important to record the type of break
(shear or tensile) that occurs. For research purposes, it is also useful to record the position of the shear plane relative to the
specimen center line.
10. Retest
10.1 Values for properties at break shall not be calculated for any specimen that breaks at so
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.