ASTM D6646-03(2014)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of the Accelerated Hydrogen Sulfide Breakthrough Capacity of Granular and Pelletized Activated Carbon
Standard Test Method for Determination of the Accelerated Hydrogen Sulfide Breakthrough Capacity of Granular and Pelletized Activated Carbon
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This method compares the performance of granular or pelletized activated carbons used in odor control applications, such as sewage treatment plants, pump stations, etc. The method determines the relative breakthrough performance of activated carbon for removing hydrogen sulfide from a humidified gas stream. Other organic contaminants present in field operations may affect the H2S breakthrough capacity of the carbon; these are not addressed by this test. This test does not simulate actual conditions encountered in an odor control application, and is therefore meant only to compare the hydrogen sulfide breakthrough capacities of different carbons under the conditions of the laboratory test.
5.2 This test does not duplicate conditions that an adsorber would encounter in practical service. The mass transfer zone in the 23 cm column used in this test is proportionally much larger than that in the typical bed used in industrial applications. This difference favors a carbon that functions more rapidly for removal of H2S over a carbon with slower kinetics. Also, the 1 % H2S challenge gas concentration used here engenders a significant temperature rise in the carbon bed. This effect may also differentiate between carbons in a way that is not reflected in the conditions of practical service.
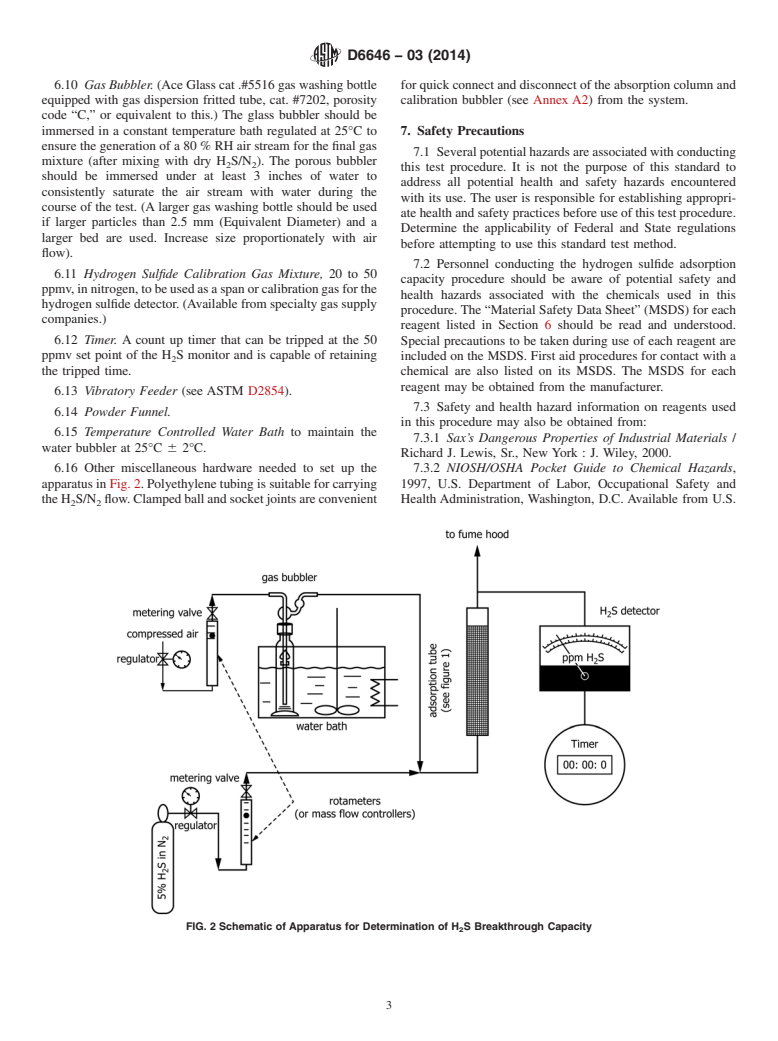
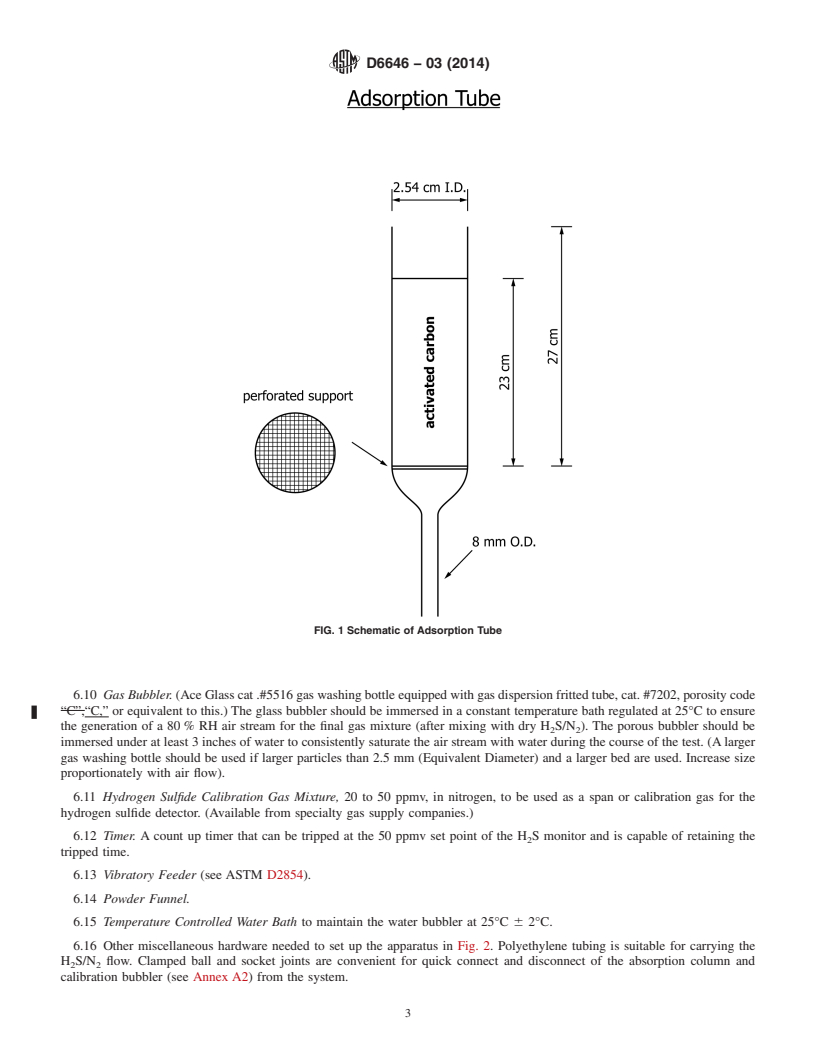
5.3 This standard as written is applicable only to granular and pelletized activated carbons with mean particle diameters less than 2.5 mm. Application of this standard to activated carbons with mean particle diameters (MPD) greater than 2.5 mm will require a larger diameter adsorption column. The ratio of column inside diameter to MPD should be greater than 10 in order to avoid wall effects. In these cases it is suggested that bed superficial velocity and contact time be held invariant at the conditions specified in this standard (4.77 cm/sec and 4.8 sec). Although not covered by this standard, data obtained from these tests may be reported as in paragraph 12 along with additio...
SCOPE
1.1 This test method is intended to evaluate the performance of virgin, newly impregnated or in-service, granular or pelletized activated carbon for the removal of hydrogen sulfide from an air stream, under the laboratory test conditions described herein. A humidified air stream containing 1 % (by volume) hydrogen sulfide is passed through a carbon bed until 50 ppm breakthrough of H2S is observed. The H2S adsorption capacity of the carbon per unit volume at 99.5 % removal efficiency (g H2S/cm3 carbon) is then calculated. This test is not necessarily applicable to non-carbon adsorptive materials.
1.2 This standard as written is applicable only to granular and pelletized activated carbons with mean particle diameters (MPD) less than 2.5 mm. See paragraph 5.3 if activated carbons with larger MPDs are to be tested.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D6646 −03 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of the Accelerated Hydrogen Sulfide
Breakthrough Capacity of Granular and Pelletized Activated
1
Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6646; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 Thistestmethodisintendedtoevaluatetheperformance
4.1 Breakthrough capacity is determined by passing a
of virgin, newly impregnated or in-service, granular or pellet- stream of humidified air containing 1 volume% hydrogen
izedactivatedcarbonfortheremovalofhydrogensulfidefrom
sulfide through a sample of granular or pelletized activated
an air stream, under the laboratory test conditions described carbon of known volume under specified conditions until the
herein. A humidified air stream containing 1% (by volume)
concentrationofhydrogensulfideintheeffluentgasreaches50
hydrogen sulfide is passed through a carbon bed until 50 ppm ppmv.
breakthrough of H S is observed.The H S adsorption capacity
2 2
of the carbon per unit volume at 99.5% removal efficiency (g
5. Significance and Use
3
H S/cm carbon) is then calculated.This test is not necessarily
2
5.1 This method compares the performance of granular or
applicable to non-carbon adsorptive materials.
pelletized activated carbons used in odor control applications,
1.2 This standard as written is applicable only to granular
such as sewage treatment plants, pump stations, etc. The
and pelletized activated carbons with mean particle diameters
method determines the relative breakthrough performance of
(MPD) less than 2.5 mm. See paragraph 5.3 if activated
activatedcarbonforremovinghydrogensulfidefromahumidi-
carbons with larger MPDs are to be tested.
fied gas stream. Other organic contaminants present in field
operations may affect the H S breakthrough capacity of the
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 2
carbon; these are not addressed by this test. This test does not
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
simulate actual conditions encountered in an odor control
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
application, and is therefore meant only to compare the
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
hydrogen sulfide breakthrough capacities of different carbons
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
under the conditions of the laboratory test.
2. Referenced Documents
5.2 This test does not duplicate conditions that an adsorber
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
wouldencounterinpracticalservice.Themasstransferzonein
D2652Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
the 23 cm column used in this test is proportionally much
D2854Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated
larger than that in the typical bed used in industrial applica-
Carbon
tions. This difference favors a carbon that functions more
D2867Test Methods for Moisture in Activated Carbon
rapidly for removal of H S over a carbon with slower kinetics.
2
E300Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
Also, the 1% H S challenge gas concentration used here
2
engendersasignificanttemperatureriseinthecarbonbed.This
3. Terminology
effect may also differentiate between carbons in a way that is
3.1 Terms relating to this standard are defined in D2652.
not reflected in the conditions of practical service.
5.3 This standard as written is applicable only to granular
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on
and pelletized activated carbons with mean particle diameters
Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas
less than 2.5 mm. Application of this standard to activated
Phase Evaluation Tests.
carbons with mean particle diameters (MPD) greater than 2.5
Current edition approved Aug. 15, 2014. Published September 2014. Originally
mmwillrequirealargerdiameteradsorptioncolumn.Theratio
approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in 2008 as D6646– 03 (2008).
DOI: 10.1520/D6646-03R14.
ofcolumninsidediametertoMPDshouldbegreaterthan10in
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
order to avoid wall effects. In these cases it is suggested that
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
bed superficial velocity and contact time be held invariant at
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. the conditions specified in this standard (4.77 cm/sec and 4.8
Copyright ©ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA19428-2959. United States
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D6646 − 03 (Reapproved 2008) D6646 − 03 (Reapproved 2014)
Standard Test Method for
Determination of the Accelerated Hydrogen Sulfide
Breakthrough Capacity of Granular and Pelletized Activated
1
Carbon
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6646; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method is intended to evaluate the performance of virgin, newly impregnated or in-service, granular or pelletized
activated carbon for the removal of hydrogen sulfide from an air stream, under the laboratory test conditions described herein. A
humidified air stream containing 1 % (by volume) hydrogen sulfide is passed through a carbon bed until 50 ppm breakthrough of
3
H S is observed. The H S adsorption capacity of the carbon per unit volume at 99.5 % removal efficiency (g H S/cm carbon) is
2 2 2
then calculated. This test is not necessarily applicable to non-carbon adsorptive materials.
1.2 This standard as written is applicable only to granular and pelletized activated carbons with mean particle diameters (MPD)
less than 2.5 mm. See paragraph 5.3 if activated carbons with larger MPDs are to be tested.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D2652 Terminology Relating to Activated Carbon
D2854 Test Method for Apparent Density of Activated Carbon
D2867 Test Methods for Moisture in Activated Carbon
E300 Practice for Sampling Industrial Chemicals
3. Terminology
3.1 Terms relating to this standard are defined in D2652.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 Breakthrough capacity is determined by passing a stream of humidified air containing 1 volume % hydrogen sulfide through
a sample of granular or pelletized activated carbon of known volume under specified conditions until the concentration of hydrogen
sulfide in the effluent gas reaches 50 ppmv.
5. Significance and Use
5.1 This method compares the performance of granular or pelletized activated carbons used in odor control applications, such
as sewage treatment plants, pump stations, etc. The method determines the relative breakthrough performance of activated carbon
for removing hydrogen sulfide from a humidified gas stream. Other organic contaminants present in field operations may affect
the H S breakthrough capacity of the carbon; these are not addressed by this test. This test does not simulate actual conditions
2
encountered in an odor control application, and is therefore meant only to compare the hydrogen sulfide breakthrough capacities
of different carbons under the conditions of the laboratory test.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D28 on Activated Carbon and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D28.04 on Gas Phase
Evaluation Tests.
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2008Aug. 15, 2014. Published September 2008September 2014. Originally approved in 2001. Last previous edition approved in
20032008 as D6646–03. DOI: 10.1520/D6646-03R08.– 03 (2008). DOI: 10.1520/D6646-03R14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D6646 − 03 (2014)
5.2 This test does not duplicate conditions that an adsorber would encounter in practical service. The mass transfer zone in the
23 cm column used in this test is proportionally much larger than that in the typical bed used in industrial applications. This
difference favors a carbon that functions more rapidly for removal of H S over a carbon with slower kinetics. Also, the 1 % H S
2 2
challenge gas concentration used here engenders a significant temperature rise in the carbon bed. This effect may also differentiate
between carbons in a way that is not reflected in the conditions of practical service.
5.3 This standard as written i
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.