ASTM D4618-92(2017)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Design and Fabrication of Flue Gas Desulfurization System Components for Protective Lining Application
Standard Specification for Design and Fabrication of Flue Gas Desulfurization System Components for Protective Lining Application
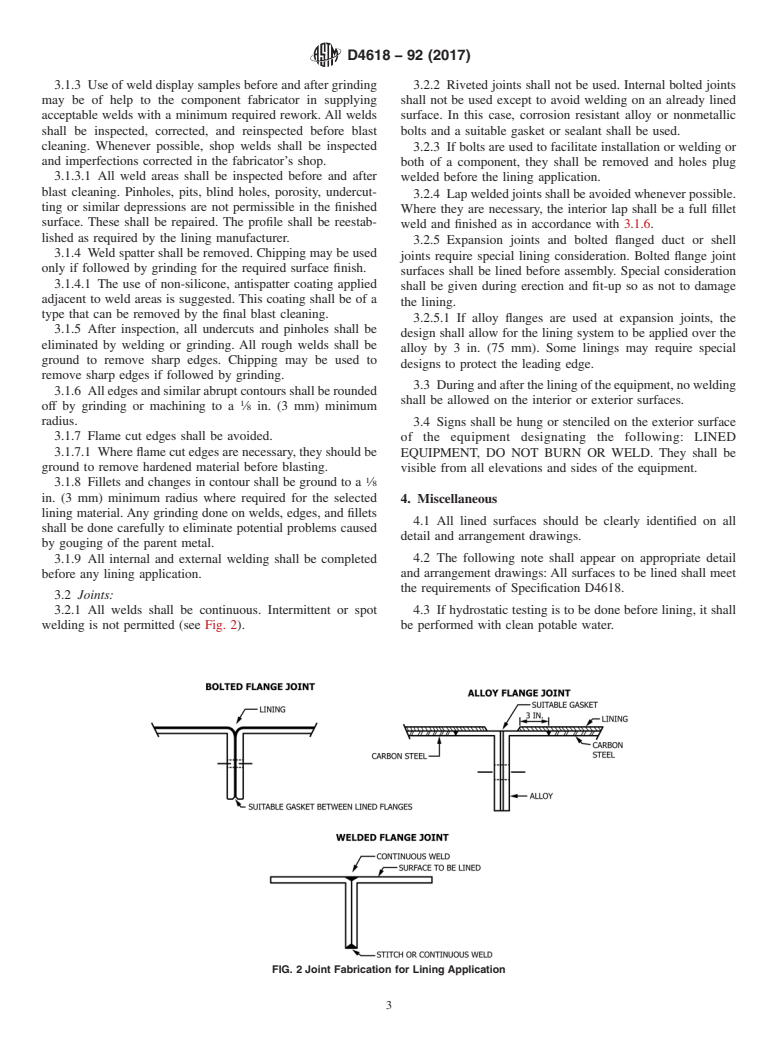
ABSTRACT
This specification covers the design and fabrication of metal components for flue gas desulfurization equipment, including absorber, tanks, chimney liners, ductwork, and associated equipment intended for use in protective lining applications, that are to be lined for corrosion or abrasion resistance, or both. It does not however cover the structural performance of the components and the use of metallic linings. Each of the components shall be designed in such a way that it conforms to the engineering requirements for rigidity wherein the effects of pressure, wind, seismic, and other design loads shall be considered; accessability to welding, grinding, surface preparation, and lining application; shell penetrations; appurtenances inside components such as agitators, anti-swirl baffles, gaging devices, internal piping, ladders, and support brackets; and structural reinforcement members and supports. All internal welds shall be continuous without imperfections and the degree of weld preparation prior to lining shall depend on the type of lining to be applied. Riveted joints and internal bolted joints shall not be used while lap bolted joints shall be avoided whenever possible. Intermittent or spot welding shall not be permitted as well.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers the design and fabrication of metal components for flue gas desulfurization (FGD) equipment, including absorbers, tanks, chimney liners, ductwork and associated equipment that are to be lined for corrosion or abrasion resistance, or both.
1.2 Limitations:
1.2.1 This specification is intended only to define the design considerations for successful application and performance of protective linings for FGD system components.
1.2.2 It does not cover structural performance of FGD components.
1.2.3 It does not cover use of metallic linings.
1.3 This specification represents the minimum requirements for lining work. In cases in which the manufacturer's instructions and recommendations differ from this specification, these differences shall be resolved before fabrication is started.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation:D4618 −92 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Specification for
Design and Fabrication of Flue Gas Desulfurization System
Components for Protective Lining Application
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4618; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Design/Engineering Requirements
2.1 Rigidity:
1.1 This specification covers the design and fabrication of
metal components for flue gas desulfurization (FGD) 2.1.1 The components shall be designed so that the interior
equipment, including absorbers, tanks, chimney liners, duct- metal surfaces are sufficiently rigid for the intended lining
work and associated equipment that are to be lined for materials. Manufacturer’s recommendations for maximum
corrosion or abrasion resistance, or both. strains or deflection limits for the lining material shall be
followed.
1.2 Limitations:
2.1.2 The weight of the lining system shall be considered in
1.2.1 This specification is intended only to define the design
the structural design of the component.
considerations for successful application and performance of
2.1.3 Thedesignshallconsidertheeffectsofpressure,wind,
protective linings for FGD system components.
seismic and other design loads.
1.2.2 It does not cover structural performance of FGD
2.1.4 Vibration may cause flexing or high surface strains on
components.
the lining.This is of particular concern to rigid lining materials
1.2.3 It does not cover use of metallic linings.
and shall be minimized.
2.1.5 Special consideration shall be given to all conditions
1.3 This specification represents the minimum requirements
of potentially excessive strain such as unsupported bottom
for lining work. In cases in which the manufacturer’s instruc-
areas, oil-canning, out of roundness, sidewall-to-bottom joints,
tions and recommendations differ from this specification, these
and so forth.
differences shall be resolved before fabrication is started.
2.1.5.1 Where a component is on a concrete foundation,
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
grouting shall be done if necessary to correct unsupported
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
bottom areas.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
2.1.5.2 Sand fill shall not be used for bottom support unless
and are not considered standard.
provisions are made to ensure that the sand cannot be lost as a
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
result of erosion.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
2.2 Accessibility:
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
2.2.1 All interior surfaces of the components shall be
priate safety, health and environmental practices and deter-
designed to be readily accessible for welding, grinding, surface
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
preparation, and lining application.
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
2.2.2 The minimum manway size for a working entrance
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
during lining application shall be 36 in. (900 mm) in diameter
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
or 24 in. (600 mm) width by 36 in. (900 mm) height.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
2.2.2.1 Closed components shall have a minimum of two
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
manways, one near the top and one near the bottom, preferably
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
located 180° apart to facilitate adequate ventilation for work-
ers.
2.2.2.2 Additional or larger openings may be required to
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D33 on
facilitate ventilation and material handling. The lining material
ProtectiveCoatingandLiningWorkforPowerGenerationFacilitiesandisthedirect
applicator should be consulted for specific requirements.
responsibility of Subcommittee D33.09 on Protective Lining forAir Quality Control
Systems.
2.3 Shell Penetrations:
Current edition approved Sept. 1, 2017. Published September 2017. Originally
ɛ
2.3.1 Openings such as, inlets, manholes, and outlet nozzles
approved in 1987. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as D4618 – 92 (2010) .
DOI: 10.1520/D4618-92R17. shall be flush with the interior wall.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D4618−92 (2017)
2.3.1.1 Inlet nozzles may extend into vessels if incoming complex shapes shall be avoided wherever possible. If they
fluids will be detrimental to lining materials. must be installed internally, these members shall be fully seal
2.3.2 Any exterior or interior connection shall be flanged to welded and the edges ground to a ⁄8 in. (3 mm) minimum
facilitate lining. radius.
2.3.3 The maximum length of flanged nozzles, 4 in. (100 2.5.3 If closed chambers are formed with internal box
mm) and greater in diameter, shall not exceed the dimensions beamsorpipes,theyshallbeventedtothevesselexterioratthe
in Table 1. lowest point, so that pressures are not developed during
2.3.3.1 Only 4 in. (100 mm) diameter and larger nozzles operation and possible curing procedures and so that corrosion,
shall be used for maximum reliability of the lining system. caused by localized lining failures, can be observed early.
2.3.3.2 As an alternative to lined nozzles, compatible
3. Fabrication
prefabricated, reinforced plastic, ceramic or alloy metal inserts
(sleeves) may be used if they offer superior corrosion and
3.1 Welds:
abrasion protection. Lining shall overlap onto prefabricated
3.1.1 All internal welds to be lined shall be continuous
liners.
without imperfections such as weld slag, weld spatter, rough
2.3.3.3 If an insert is used as an alternate, the lining shall
surfaces, undercutting, high peaks, porosity, sharp corners,
overlap unto the insert or some other means of ensuring an
sharp edges, and inadequate thickness. Imperfections shall be
adequate seal should be provided.
corrected (see Fig. 1).
2.3.4 Lining thickness may dictate changes in nozzle di-
3.1.2 The degree of weld preparation before lining depends
mensions to achieve design flow rates.
on the type of lining to be applied. The lining manufacturer
2.4 Appurtenances inside Components: shall be consulted for specific requirements for weld prepara-
tion during the design of the component and before start of
2.4.1 The requirements in Sections 2 and 3 apply to any
appurtenances that are being lined and installed inside a lined fabrication.
component, such as agitators, anti-swirl baffles, gauging
devices, internal piping, ladders, and support brackets.
2.4.2 If appurtenances inside the compo
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.