ASTM D6213-97(2009)
(Practice)Standard Practice for Tests to Evaluate the Chemical Resistance of Geogrids to Liquids
Standard Practice for Tests to Evaluate the Chemical Resistance of Geogrids to Liquids
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This practice is intended to provide a list of standard procedures for test programs investigating the chemical resistance of a geogrid to a liquid. This practice should be used in the absence of other specifications required for the particular situation being addressed.
This practice is intended to provide a basis of standardization for those wishing to compare or investigate the chemical resistance of a geogrid. It should be recognized that chemical resistance is a user judgment evaluation and that this practice does not offer procedures for interpreting the results obtained from test procedures contained in this practice. As a practice, this does not produce a test result.
This practice is for the chemical resistance assessment of geogrids and is written in parallel to similar practices for geomembranes, geotextiles, geonets, and geopipes. Each practice is to be considered individually for the geosynthetic under investigation and collectively for all geosynthetics exposed to the potentially harsh chemical environment under consideration.
SCOPE
1.1 This practice covers the procedures for testing of geogrids for chemical resistance to liquids.
1.2 This practice describes methods for measuring changes in physical and mechanical properties caused by immersion in test solutions that may be representative of anticipated end-use conditions.
1.3 This practice describes procedures for required and recommended testing of geogrids.
1.4 Evaluation or interpretation of test data is beyond the scope of this practice.
1.5 This practice is intended to be used in conjunction with D 5322, or D 5496, or both. The scope of this practice is limited to testing and reporting procedures for unexposed and exposed geogrid coupons.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precautionary statements are given in Section 7.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D6213 − 97 (Reapproved 2009)
Standard Practice for
Tests to Evaluate the Chemical Resistance of Geogrids to
Liquids
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D6213; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1695 Terminology of Cellulose and Cellulose Derivatives
D4439 Terminology for Geosynthetics
1.1 This practice covers the procedures for testing of
D4595 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Geotextiles by
geogrids for chemical resistance to liquids.
the Wide-Width Strip Method
1.2 This practice describes methods for measuring changes
D4603 Test Method for Determining Inherent Viscosity of
in physical and mechanical properties caused by immersion in
Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) (PET) by Glass Capillary
test solutions that may be representative of anticipated end-use
Viscometer
conditions.
D5322 Practice for Laboratory Immersion Procedures for
1.3 This practice describes procedures for required and Evaluating the Chemical Resistance of Geosynthetics to
Liquids
recommended testing of geogrids.
D5496 Practice for In Field Immersion Testing of Geosyn-
1.4 Evaluation or interpretation of test data is beyond the
thetics
scope of this practice.
D5747 Practice for Tests to Evaluate the Chemical Resis-
1.5 This practice is intended to be used in conjunction with
tance of Geomembranes to Liquids
D5322,or D5496, or both. The scope of this practice is limited
E375 Definitions of Terms Relating to Resinography (With-
to testing and reporting procedures for unexposed and exposed
drawn 1992)
geogrid coupons.
3. Terminology
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1 Definitions:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
3.1.1 chemical resistance, n—for geosynthetics, the extent
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
to which a material or product retains its original physical and
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
chemical characteristics as a function of immersion in, or
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific precau-
contact with, a foreign substance. (D5747, D35)
tionary statements are given in Section 7.
3.1.2 coating, n—a liquid, liquefiable or mastic composition
2. Referenced Documents
that is converted to a solid protected, decorative, or functional
adherent film after application as a thin layer. (D16, D01)
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D16 TerminologyforPaint,RelatedCoatings,Materials,and
3.1.3 coupon, n—a portion of a material or laboratory
Applications
sample, from which multiple specimens can be taken for
D76 Specification for Tensile Testing Machines for Textiles
testing. (D5747, D35)
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
3.1.4 composite, n—a material made up of distinct parts
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
which contribute, either proportionately, or synergistically, to
D1238 Test Method for Melt Flow Rates of Thermoplastics
the properties of the combination. (E375, D20)
by Extrusion Plastometer
3.1.5 geogrid, n—a reinforcing geosynthetic comprised of
integrally connected elements with in-plane apertures between
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D35 on Geosyn-
elements. (D4439, D35)
thetics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D35.02 on Endurance
3.1.6 geosynthetic, n—a planar product manufactured from
Properties.
polymeric material used with soil, rock, earth, or other geo-
CurrenteditionapprovedJune1,2009.PublishedJuly2009.Originallyapproved
in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D6213 - 97 (2003). DOI:
technical engineering related material as an integral part of a
10.1520/D6213-97R09.
man made project, structure, or system. (D4439, D35)
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
the ASTM website. www.astm.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D6213 − 97 (2009)
3.1.7 inherent viscosity—the quotient of the natural loga- clamping power to prevent slipping or crushing (damage). The
rithm of relative viscosity by the concentration, that is inη /c. suggested style of clamp is wedge action type, commonly
rel
(D1695, D01) available from the manufacturer of the tensile testing machine.
3.1.8 integral, adj—in geosynthetics, forming a necessary
6.3 All other required equipment is specified in the refer-
part of the whole; a constituent. (D4439, D35)
enced test method standards. Refer to the appropriate standards
for a description of the apparatus necessary to perform those
3.1.9 relative viscosity—the ratio of the viscosity of a
tests.
solution to that of the pure solvent. (D1695, D01)
3.1.10 melt index, n—the flow rate of PE material when
7. Hazards
measured in accordance with Test Method D1238.
7.1 Geogrids may be exposed to liquids that may contain
3.1.11 polyester, n—a polymer in which the repeated struc-
hazardous chemicals. Appropriate precautions must be taken
tural unit in the chain is of the ester type. (D883, D20)
when handling hazardous waste, chemicals, and the immersion
3.1.12 polyolefin, n—a polymer prepared by the polymer-
solutions. Protective equipment suitable for the chemicals
ization of an olefin(s) as the sole monomer(s). (D883, D20)
being used must be worn by all personnel handling or exposed
3.1.13 sample, n—a portion of a lot of material that is taken to the chemicals. Particular care should be taken when opening
for incubation, testing, or for record purposes. (D123, D13) storage vessels at elevated temperatures due to the increased
volatility of organics and the increased activity of acids and
3.1.14 specimen, n—a specific portion of a material or
bases. Care must also be taken to prevent the spilling of
laboratory sample upon which a test is performed or which is
hazardous materials and provisions must be made to clean up
taken for that purpose. (D4439, D35)
any accidental spills that do occur.
4. Summary of Practice
7.2 Before carrying out any test, safety precautions and
4.1 This practice defines test methods and procedures for
disposal procedures for hazardous waste, chemicals or immer-
evaluating the resistance of geogrids to liquid exposure by
sion liquids, and any contaminated geogrid materials should be
monitoring physical and chemical properties of geogrid cou-
identified and implemented to provide full protection to all
pons after immersion in a test liquid.The physical condition of
personnel and to comply with applicable disposal regulations.
the geogrid is monitored as a function of cumulative exposure
8. Sample Preparation
time by means of visual observations, and mechanical and
chemical property tests.
8.1 Sample product as received.
5. Significance and Use
9. Sampling
5.1 This practice is intended to provide a list of standard
9.1 Geogrid:
procedures for test programs investigating the chemical resis-
9.1.1 Determine the number and dimensions of the test
tance of a geogrid to a liquid. This practice should be used in
specimens according to the requirements of property tests,
the absence of other specifications required for the particular
listed in Section 14, to be performed, the duration of the
situation being addressed.
immersion, and the number of test intervals.
5.2 This practice is intended to provide a basis of standard-
9.1.2 Sample—Sample in accordance with the respective
ization for those wishing to compare or investigate the chemi-
test methods selected for the geogrid.
cal resistance of a geogrid. It should be recognized that
9.1.3 Coupons—Cut coupons from geogrid sample repre-
chemical resistance is a user judgment evaluation and that this
sentative of the geogrids being evaluated so as to provide a
practice does not offer procedures for interpreting the results
sufficient number of specimens for each chosen property test
obtained from test procedures contained in this practice. As a
and test interval. Discard any coupons that contain scratches or
practice, this does not produce a test result.
other imperfections that might affect the test results, and cut
replacement coupons.
5.3 This practice is for the chemical resistance assessment
9.1.4 Mix the selected coupons in a random fashion and
of geogrids and is written in parallel to similar practices for
re-select coupons for the immersion and baseline testing.
geomembranes, geotextiles, geonets, and geopipes. Each prac-
9.1.5 Specimens—After exposure, test specimens are cut
tice is to be considered individually for the geosynthetic under
from the coupons.
investigation and collectively for all geosynthetics exposed to
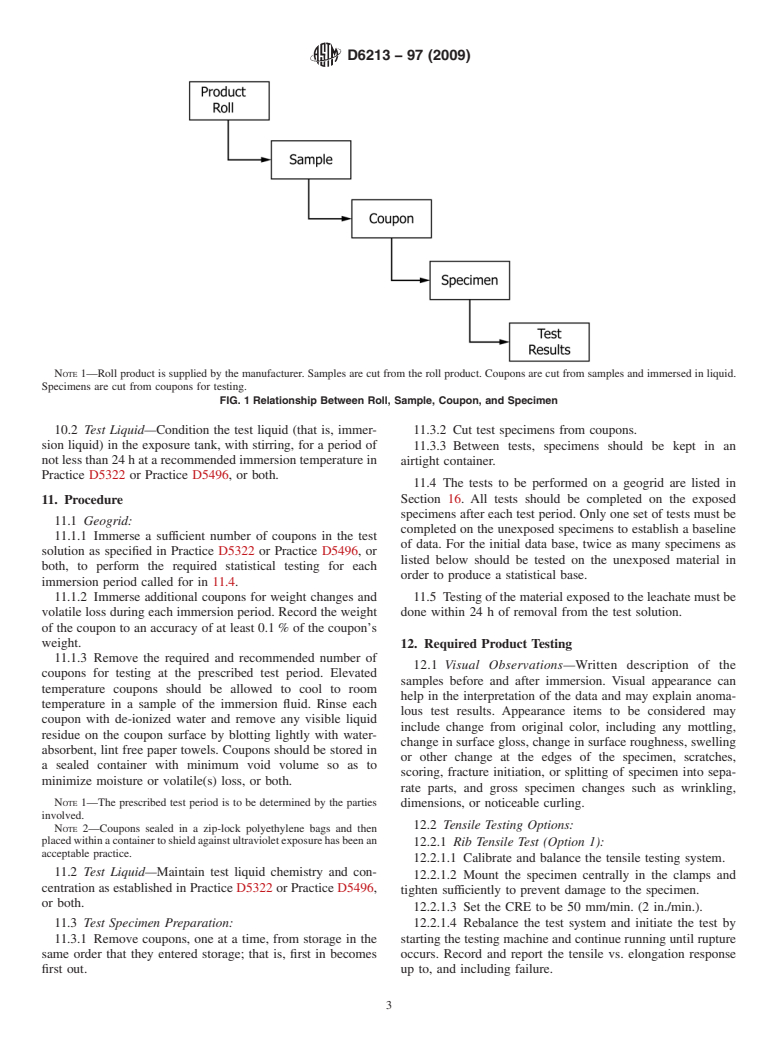
9.1.6 Interrelationship between product, sample, coupon,
the potentially harsh chemical environment under consider-
and specimen is illu
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.