ASTM D2357-74(2003)
(Classification)Standard for Qualitative Classification of Surfactants by Infrared Absorption
Standard for Qualitative Classification of Surfactants by Infrared Absorption
SCOPE
1.1 This standard covers the qualitative classification of synthetic detergent products or mixtures of synthetic detergents. It is applicable to built detergent formulations as well as individual surfactant compositions.
Note 1—The organic active ingredient must be isolated from built syndet compositions in accordance with Test Method D 2358.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: D2357 – 74 (Reapproved 2003)
Standard for
Qualitative Classification of Surfactants by Infrared
Absorption
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2357; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Apparatus
1.1 This standard covers the qualitative classification of 4.1 Spectrophotometer, recording, infrared.
synthetic detergent products or mixtures of synthetic deter- 4.2 Dies and Press, for preparation of KBr disks.
gents. It is applicable to built detergent formulations as well as 4.3 Detergent Reference Spectra.
individual surfactant compositions.
5. Reagents
NOTE 1—The organic active ingredient must be isolated from built
5.1 Mineral Oil, USP.
syndet compositions in accordance with Test Method D2358.
5.2 Potassium Bromide (KBr), infrared quality, powdered.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
5.3 Additional Reagents, as specified in Test Method
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
D2358.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 6. Preparation of Sample
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
6.1 Sample in Pure Form—If the sample is in pure form or
contains only volatile solvents, dry the sample in accordance
2. Referenced Documents
with 5.8 of Test Method D2358, and obtain the infrared
2.1 ASTM Standards:
spectrum of the dried sample.
D2358 Test Method for Separation of Active Ingredient
6.2 For Built Surfactants and Synthetic Detergent
from Surfactant and Syndet Compositions
Compositions—Obtain the infrared spectrum of the active
ingredient(s)separatedinaccordancewithTestMethodD2358.
3. Summary of Classification
3.1 A portion of the active ingredient is scanned in the
7. Procedure
infrared region of the spectrum from at least 2 to 15 µm.
7.1 Whenever possible, the infrared spectrum should be
Qualitative identification of surfactant type is based on the
obtained directly from the organic material, by formation of a
presence of infrared absorption bands attributable to specific
film between salt blocks, and by recording the spectrum
functional groups.
between 2 and 15 µm. The film is satisfactory if the spectrum
3.2 A listing of absorption bands corresponding to the
shows 10 to 30 % transmittance in the strongest absorption
characteristic functional groups of some of the more common
region.
typesofcommercialsurfactantsisincludedinthismethod.Use
7.2 If the physical properties of the sample prevent use of
of available detergent reference spectra may provide additional
the film technique, the spectrum may be made from a mineral
information.
oil mull. Form the mull by adding 2 to 3 drops of mineral oil
to a small quantity of sample contained in a polished grinding
surface (agate) mortar, and grinding for a minimum of 5 min.
This classification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D12 on Soaps
This should produce a very fine syrupy dispersion. Use the
and Other Detergents and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D12.12 on
mull as a film between salt blocks and obtain the spectrum as
Analysis and Specifications of Soaps, Synthetics, Detergents and their Components.
in 7.1.
Current edition approved Feb. 10, 2003. Published March 2003. Originally
7.3 Ifthesamplecanbeobtainedindry,powderedform,the
published as D2357 – 65 T. Last previous edition D2357 – 74. DOI: 10.1520/
D2357-74R03.
KBr pressed-disk method may be used. Grind the sample
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
sufficiently fine to prevent radiation scatter, and add approxi-
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
mately 1 part sample to 19 parts of dry powdered KBr. Using
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. suitable equipment, form the disk at room temperature in
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
D2357 – 74 (2003)
vacuum, under pressure of 10 to 30 tons/in. Obtain the 8. Identification of Components
spectrum of the disk, sample between 2 and 15 µm as in 7.1.
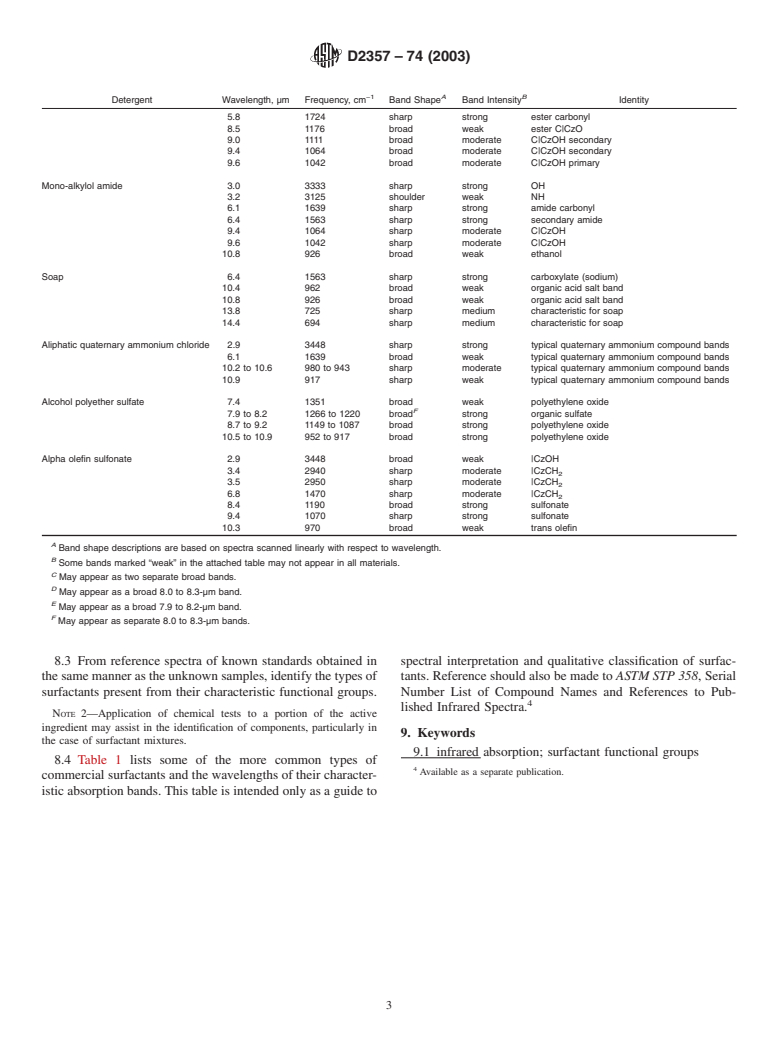
8.1 Notethewavelengthpositionofeachspecificabsorption
band.
For details of infrared experimental techniques, see Jones, R. N. and Sandorfy,
8.2 Identify the absorption bands in terms of functional
C., “The Application of Infrared and Raman Spectrometry to the Elucidation of
groups by the use of data in Table 1 or other appropriate
Molecular Structure.” Technique of Organic Chemistry, Vol IX, 1956. Interscience
reference source.
Publishers, Inc., New York, NY.
TABLE 1 Infrared Absorption Bands of Typical Commercial Detergents
−1 A B
Detergent Wavelength, µm Frequency, cm Band Shape Band Intensity Identity
Alkylbenzene sulfonate 6.7 1493 shoulder weak aromatic bands
C
8.1 to 8.5 1235 to 1176 broad strong sulfonate group
8.8 1136 sharp moderate sulfonate group
9.6 1042 sharp strong ABS bands
9.9 1010 sharp strong ABS bands
12.0 833 broad moderate para substitution
D
Fatty alcohol sulfate 8.0 1250 sharp strong organic sulfate group
D
8.3 1205 sharp strong organic sulfate group
9.2 1087 sharp moderate most characteristic alcohol sulfate band
10.3 971 broad weak characteristic alcohol sulfate bands
10.8 926 broad weak characteristic alcohol sulfate bands
Sulfonated amide (taurate) 6.1 1639 sharp strong amide carbonyl
6.4 1563 shoulder weak secondary amide
8.1 to 8.5 1235 to 1176 broad strong sulfonate group
9.4 1064 sharp strong C|CzN or alkyl sulfonate
Sulfonated ester (isethionate) 5.8 1724 sharp strong ester car
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.