ASTM D7617/D7617M-11(2017)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Transverse Shear Strength of Fiber-reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite Bars
Standard Test Method for Transverse Shear Strength of Fiber-reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite Bars
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method for transverse shear strength is intended for use in laboratory tests in which the principal variable is the size or type of FRP bars. The test may be used for smooth round rods or on bars with a textured or undulating surface added to promote bond of the bars to Portland cement concrete. This test method establishes values of transverse shear strength for material specifications, quality control, quality assurance, research and development, and may also be used for structural design purposes.
5.2 Experience with this test method and the accompanying fixture is primarily with smooth rods and textured bars with diameters ranging from 6 mm to 25 mm [0.25 in. to 1 in.]. The method may be used for rods or bars of larger diameters, but the overall geometry of the test fixture may need to be increased.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method specifies the test requirements for (FRP) composite smooth round rods and textured bars for determining the transverse shear strength via a double shear fixture. FRP rods and bars are often loaded in transverse shear when these elements are used as dowels in concrete pavements, as stirrups in concrete beams, or as shear reinforcements in glued-laminated wood beams, for example.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.2.1 Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in brackets.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D7617/D7617M − 11 (Reapproved 2017)
Standard Test Method for
Transverse Shear Strength of Fiber-reinforced Polymer
1
Matrix Composite Bars
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D7617/D7617M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D3878 Terminology for Composite Materials
1.1 This test method specifies the test requirements for
D5229/D5229M TestMethodforMoistureAbsorptionProp-
(FRP) composite smooth round rods and textured bars for
erties and Equilibrium Conditioning of Polymer Matrix
determining the transverse shear strength via a double shear
Composite Materials
fixture. FRP rods and bars are often loaded in transverse shear
D7205/D7205M Test Method for Tensile Properties of Fiber
whentheseelementsareusedasdowelsinconcretepavements,
Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite Bars
as stirrups in concrete beams, or as shear reinforcements in
E4 Practices for Force Verification of Testing Machines
glued-laminated wood beams, for example.
E6 Terminology Relating to Methods of Mechanical Testing
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate,With
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
Lot or Process
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
E456 Terminology Relating to Quality and Statistics
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance
with the standard.
3. Terminology
1.2.1 Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in
brackets. 3.1 Terminology in D3878 defines terms relating to high-
modulus fibers and their composites. Terminology in D883
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
defines terms relating to plastics. Terminology in E6 defines
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
terms relating to mechanical testing. Terminology in E456
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
defines terms relating to statistics and the selection of sample
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
sizes. In the event of a conflict between terms, Terminology in
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
D3878 shall have precedence over the other terminology
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
standards.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.2.1 bar, n—a linear element, with a substantially round
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
cross section, often with surface undulations or a coating of
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
particles that promote mechanical interlock with concrete.
3.2.2 double shear fixture, n—atestfixturethatresultsinthe
2. Referenced Documents
desired shear force being applied to two distinct sections of the
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
specimen.
A615/A615M SpecificationforDeformedandPlainCarbon-
3.2.3 failure, n—cleavage of the bar under test into three
Steel Bars for Concrete Reinforcement
pieces or into two pieces where the second non-cleaved shear
plane is highly damaged.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D30 on
3.2.4 nominal cross sectional area, n—a measure of cross
Composite Materials and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D30.10 on
Composites for Civil Structures.
sectional area of a bar, determined over at least one represen-
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2017. Published September 2017. Originally
tative length, used to calculate stress.
approved in 2011. Last previous edition approved as D7617/D7617M–11. DOI:
10.1520/D7617_D7617M-11R17.
3.2.5 projected outer diameter, n—the smallest diameter of
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
a circle through which a bar, with its undulations or coatings,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
will pass. The bar may touch the circle but must pass through
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. without undue force.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. Un
...








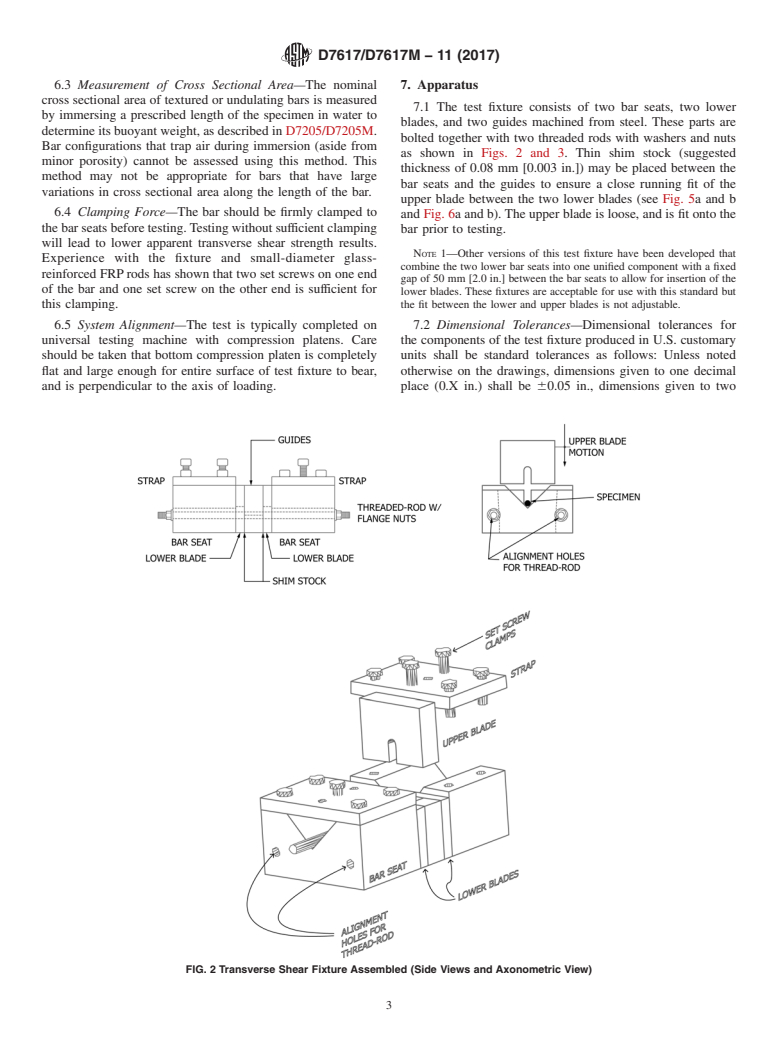
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.