ASTM C1581/C1581M-16
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determining Age at Cracking and Induced Tensile Stress Characteristics of Mortar and Concrete under Restrained Shrinkage
Standard Test Method for Determining Age at Cracking and Induced Tensile Stress Characteristics of Mortar and Concrete under Restrained Shrinkage
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is for relative comparison of materials and is not intended to determine the age at cracking of mortar or concrete in any specific type of structure, configuration, or exposure.
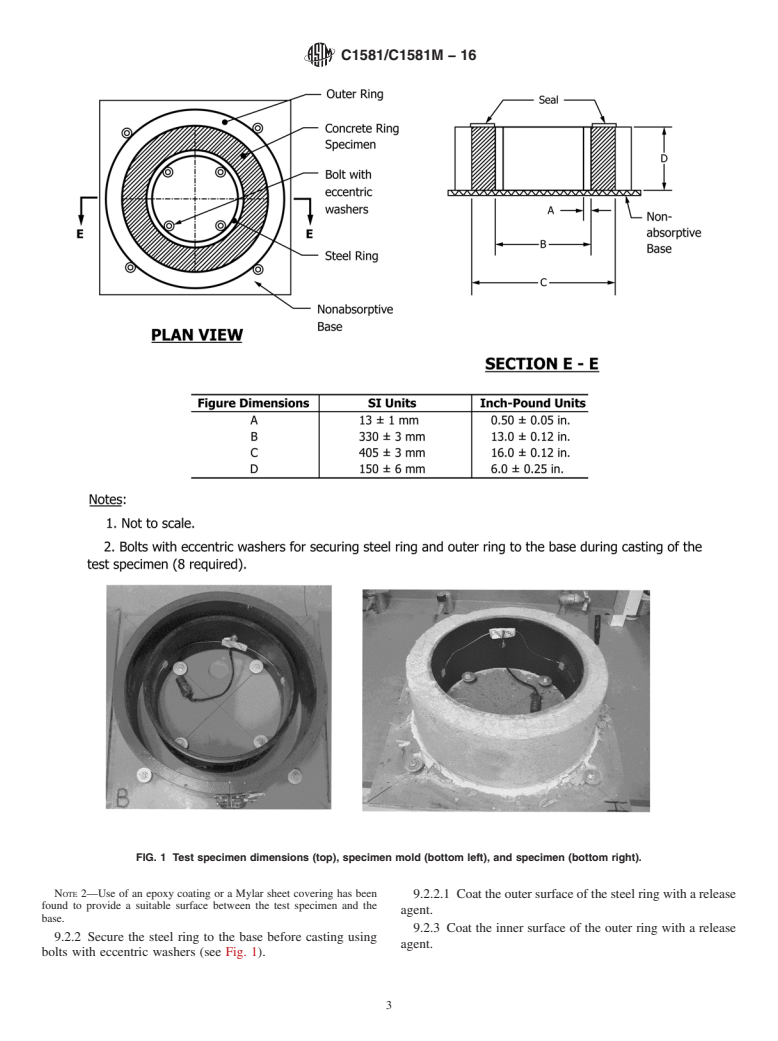
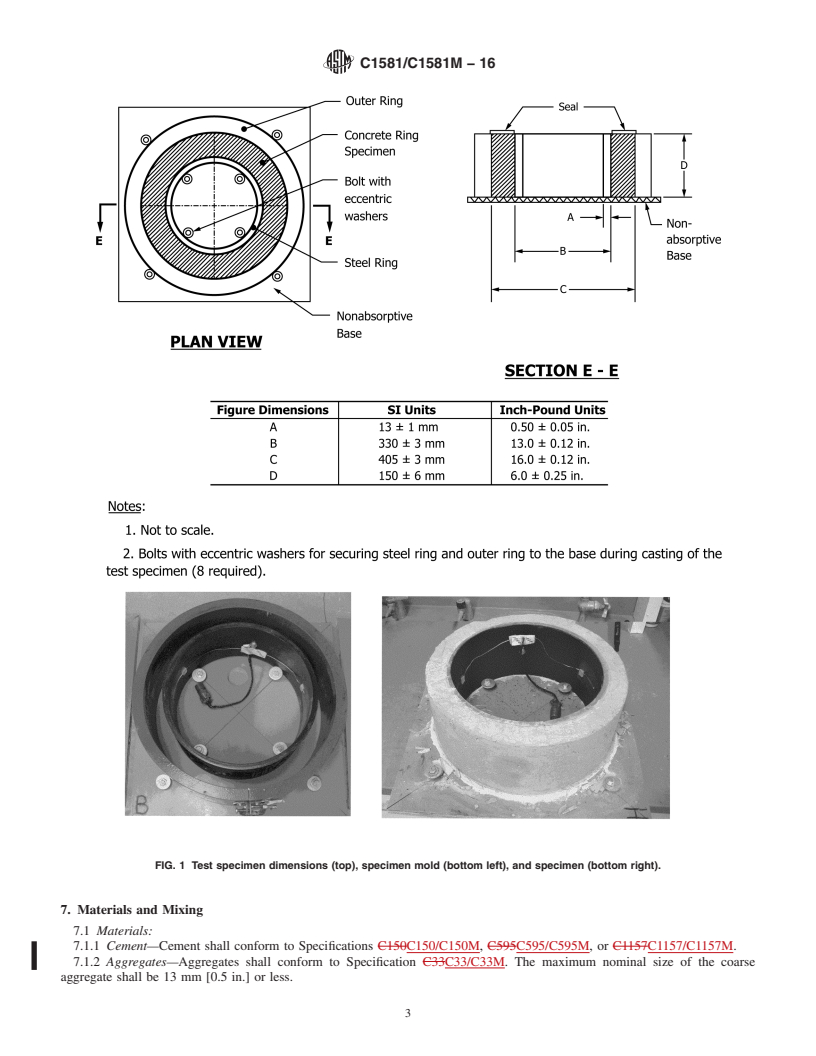
5.2 This test method is applicable to mixtures with aggregates of 13-mm [0.5-in.] maximum nominal size or less.
5.3 This test method is useful for determining the relative likelihood of early-age cracking of different cementitious mixtures and for aiding in the selection of cement-based materials that are less likely to crack under retrained shrinkage. Actual cracking tendency in service depends on many variables including type of structure, degree of restraint, rate of property development, construction and curing methods, and environmental conditions.
5.4 This test method can be used to determine the relative effects of material variations on induced tensile stresses and cracking potential. These variations can include, but are not limited to, aggregate source, aggregate gradation, cement type, cement content, water content, supplementary cementing materials, or chemical admixtures.
5.5 For materials that have not cracked during the test, the rate of tensile stress development at the time the test is terminated provides a basis for comparison of the materials.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of the age at cracking and induced tensile stress characteristics of mortar or concrete specimens under restrained shrinkage. The procedure can be used to determine the effects of variations in the proportions and material properties of mortar or concrete on cracking due to both drying shrinkage and deformations caused by autogenous shrinkage and heat of hydration.
1.2 This test method is not intended for expansive materials.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.2)
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1581/C1581M − 16
Standard Test Method for
Determining Age at Cracking and Induced Tensile Stress
Characteristics of Mortar and Concrete under Restrained
1
Shrinkage
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1581/C1581M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* C138/C138MTestMethodforDensity(UnitWeight),Yield,
and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Concrete
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of
C143/C143MTest Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement
the age at cracking and induced tensile stress characteristics of
Concrete
mortar or concrete specimens under restrained shrinkage. The
C150/C150MSpecification for Portland Cement
procedure can be used to determine the effects of variations in
C171Specification for Sheet Materials for Curing Concrete
the proportions and material properties of mortar or concrete
C192/C192MPracticeforMakingandCuringConcreteTest
on cracking due to both drying shrinkage and deformations
Specimens in the Laboratory
caused by autogenous shrinkage and heat of hydration.
C387/C387MSpecification for Packaged, Dry, Combined
1.2 Thistestmethodisnotintendedforexpansivematerials.
Materials for Concrete and High Strength Mortar
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units C595/C595MSpecification for Blended Hydraulic Cements
C1157/C1157MPerformance Specification for Hydraulic
are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each Cement
C1437Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar
system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
values from the two systems may result in non-conformance F441/F441MSpecificationforChlorinatedPoly(VinylChlo-
ride) (CPVC) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40 and 80
with the standard.
4
2.2 ASME Standards:
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
B46.1Surface Texture (Surface Roughness, Waviness and
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Lay)
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and to determine the
3. Terminology
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1 Definitions:
(Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer
and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon
2
to Terminology C125.
prolonged exposure. )
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2. Referenced Documents
3.2.1 age at cracking, n—the age of each test specimen,
3
measured from the time of casting, when a sudden decrease in
2.1 ASTM Standards:
strain occurs.
C33/C33MSpecification for Concrete Aggregates
C125Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag- 3.2.2 net strain, n—the value corresponding to the differ-
gregates ence between the strain in the steel ring at each recorded time
and the initial strain.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
4. Summary of Test Method
Concrete and ConcreteAggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
C09.68 on Volume Change. 4.1 A sample of freshly mixed mortar or concrete is com-
Current edition approved July 1, 2016. Published August 2016. Originally
pacted in a circular mold around an instrumented steel ring.
approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as C1581–09a. DOI:
The compressive strain developed in the steel ring caused by
10.1520/C1581_C1581M-16.
2
shrinkageofthemortarorconcretespecimenismeasuredfrom
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing ,
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on International Headquarters, Three Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
the ASTM website. www.asme.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1581/C1581M − 16
5
the time of casting (1-6). Cracking of the test specimen is 6.4 Base—Epoxy-coated plywood or other non-absorptive
indicated by a sudden decrease in the steel ring strain.The age and non-reactive surface.
atcrackingandtherateoftensilestressdevelopmentinthetest
6.5 Outer ring—Use one of th
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1581/C1581M − 09a C1581/C1581M − 16
Standard Test Method for
Determining Age at Cracking and Induced Tensile Stress
Characteristics of Mortar and Concrete under Restrained
1
Shrinkage
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1581/C1581M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the laboratory determination of the age at cracking and induced tensile stress characteristics of
mortar or concrete specimens under restrained shrinkage. The procedure can be used to determine the effects of variations in the
proportions and material properties of mortar or concrete on cracking due to both drying shrinkage and deformations caused by
autogenous shrinkage and heat of hydration.
1.2 This test method is not intended for expansive materials.
1.3 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each
system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
two systems may result in non-conformance with the standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and
2
tissue upon prolonged exposure. )
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C33C33/C33M Specification for Concrete Aggregates
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates
C138/C138M Test Method for Density (Unit Weight), Yield, and Air Content (Gravimetric) of Concrete
C143/C143M Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete
C150C150/C150M Specification for Portland Cement
C171 Specification for Sheet Materials for Curing Concrete
C192/C192M Practice for Making and Curing Concrete Test Specimens in the Laboratory
C387C387/C387M Specification for Packaged, Dry, Combined Materials for Mortar and ConcreteConcrete and High Strength
Mortar
C595C595/C595M Specification for Blended Hydraulic Cements
C1157C1157/C1157M Performance Specification for Hydraulic Cement
C1437 Test Method for Flow of Hydraulic Cement Mortar
F441/F441M Specification for Chlorinated Poly(Vinyl Chloride) (CPVC) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40 and 80
4
2.2 ASME Standards:
B 46.1 Surface Texture (Surface Roughness, Waviness and Lay)
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on Concrete and Concrete Aggregates and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.68 on
Volume Change.
Current edition approved July 1, 2009July 1, 2016. Published August 2009August 2016. Originally approved in 2004. Last previous edition approved in 2009 as
C1581 – 09.C1581 – 09a. DOI: 10.1520/C1581_C1581M-09A.10.1520/C1581_C1581M-16.
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing , Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
4
Available from American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), ASME International Headquarters, Three Park Ave., New York, NY 10016-5990, http://
www.asme.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1581/C1581M − 16
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 For definitions of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology C125.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 age at cracking, n—the age of each test specimen, measured from the time of casting, when a sudden decrease in strain
occurs.
3.2.2 net strain, n—the value corresponding to the difference between the strain in the steel ring at each recorded time and the
initial strain.
4. Summary of Test Method
4.1 A sample of freshly mixed mortar or concrete is compacted in a circular mold around an in
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.