ASTM D5571-22
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) of Plastic Tight-head Drums Not Exceeding 60 Gal (227 L) in Rated Capacity
Standard Test Method for Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) of Plastic Tight-head Drums Not Exceeding 60 Gal (227 L) in Rated Capacity
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 These procedures provide an indication of the environmental stress-crack resistance of plastic tight-head drums. This test method may be used for determining the applicability of various plastic resins, mold designs, processing techniques, and parameters for plastic tight-head drums.
5.2 Environmental stress cracking is indicative of what results when a container is exposed to chemical agents such as soaps, organics, bleaches, or any surface-active solutions while under conditions of stress.
5.3 Environmental stress cracking is a mechanism of chemical attack that is highly dependent upon the test reagent, resin, container manufacturing or processing history, exposure temperature, applied stress, and other factors. The combination of these factors may result in eventual stress crack failure.
5.4 Both procedures minimize the potential for test variability by providing the user with rigidly defined test conditions. This test method may be used as design qualification and auditing tools for plastic tight-head drums.
5.5 This test method is not meant to provide a quantitative value of measurement (that is, number of days to failure). It is intended only as a pass/fail procedure in accordance with user’s specifications, or as agreed upon between the user and supplier. It is not intended as a predictor or indicator of field performance regarding time to failure.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method provides an indication of the environmental stress crack resistance of plastic tight-head drums as a summation of the effects of container design, resin, manufacturing conditions, field performance, and other factors.
1.2 This test method may be used to evaluate a plastic drum's resistance to failure by cracking when in the presence of chemical and physical stresses.
1.3 Two procedures are provided as follows:
1.3.1 Procedure A—Internal pressure stress crack resistance method to nonyl phenoxypoly (ethyleneoxy) ethanol solution, a stress cracking reagent. The internal pressure is controlled at a constant elevated pressure and temperature.
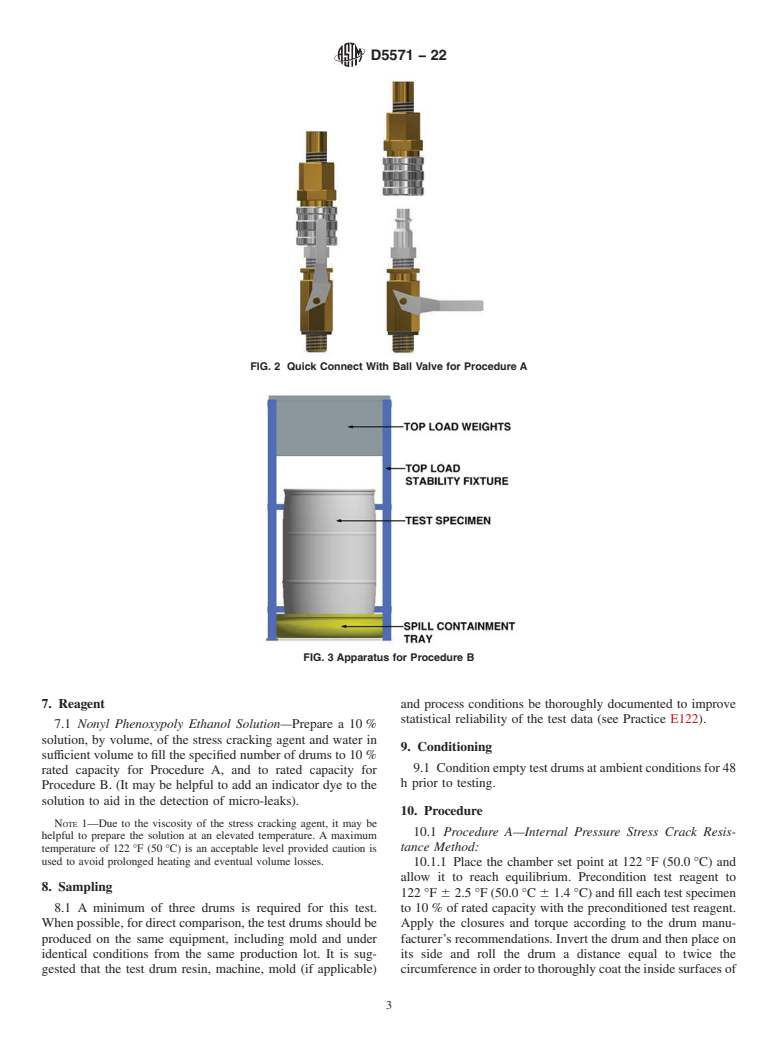
1.3.2 Procedure B—Top-load stress crack resistance method to nonyl phenoxypoly ethanol, a stress cracking reagent. The compressive top-load is controlled at a constant weight while maintaining an elevated temperature.
1.4 Although these procedures are not designed to test the ability of the closure or closure gasket material to retain the test reagent, the inclusion of closure failure as a container failure mode is optional. However, leakage through a closure may affect the internal pressure that could affect the test results.
1.5 This test method does not attempt to address all factors that could lead to stress cracking of plastic drums. The user of this standard may use other test parameters, such as top-loads, chemical reagents, etc., as agreed upon between the user and supplier in the event of a drum qualification or purchase agreement.
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The SI units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific warning statements are given in 6.2.
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5571 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) of Plastic
Tight-head Drums Not Exceeding 60 Gal (227 L) in Rated
1
Capacity
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5571; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
1.1 This test method provides an indication of the environ-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to
mental stress crack resistance of plastic tight-head drums as a
use. Specific warning statements are given in 6.2.
summation of the effects of container design, resin, manufac-
1.8 This international standard was developed in accor-
turing conditions, field performance, and other factors.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.2 This test method may be used to evaluate a plastic
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
drum’s resistance to failure by cracking when in the presence
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
of chemical and physical stresses.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
1.3 Two procedures are provided as follows:
1.3.1 Procedure A—Internal pressure stress crack resistance
2. Referenced Documents
method to nonyl phenoxypoly (ethyleneoxy) ethanol solution,
2
a stress cracking reagent. The internal pressure is controlled at 2.1 ASTM Standards:
D996 Terminology of Packaging and Distribution Environ-
a constant elevated pressure and temperature.
1.3.2 Procedure B—Top-load stress crack resistance method ments
D4577 Test Method for Compression Resistance of a Con-
to nonyl phenoxypoly ethanol, a stress cracking reagent. The
compressive top-load is controlled at a constant weight while tainer Under Constant Load
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate,With
maintaining an elevated temperature.
Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a
1.4 Although these procedures are not designed to test the
Lot or Process
abilityoftheclosureorclosuregasketmaterialtoretainthetest
reagent, the inclusion of closure failure as a container failure
3. Terminology
mode is optional. However, leakage through a closure may
3.1 Definitions—Reference Terminology D996 for defini-
affect the internal pressure that could affect the test results.
tions of terms applicable to this test method.
1.5 This test method does not attempt to address all factors
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
that could lead to stress cracking of plastic drums. The user of
3.2.1 environmental stress crack—a crack that develops
this standard may use other test parameters, such as top-loads,
when a plastic drum is exposed to chemical and physical
chemical reagents, etc., as agreed upon between the user and
stresses.
supplier in the event of a drum qualification or purchase
3.2.2 plastic tight-head drum—Anon-removable head plas-
agreement.
tic drum, maximum capacity not exceeding 60 gal (227 L),
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
with openings for filling and emptying not exceeding 2.76 in.
as the standard. The SI units given in parentheses are for
(70 mm) in diameter.
information only.
3.2.3 stress crack failure—any environmental stress crack
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the
that penetrates through the thickness of the drum resulting in a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
loss or leakage of the test reagent shall be interpreted as a
failure.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D10 on
Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D10.21 on Shipping
2
Containers and Systems - Application of Performance Test Methods. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2022. Published November 2022. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2016 as D5571 – 16. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D5571-22. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: D5571 − 16 D5571 − 22
Standard Test Method for
Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) of Plastic
TightheadTight-head Drums Not Exceeding 60 Gal (227 L) in
1
Rated Capacity
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5571; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Scope*
1.1 This test method provides an indication of the environmental stress crack resistance of plastic tightheadtight-head drums as
a summation of the effects of container design, resin, manufacturing conditions, field performance, and other factors.
1.2 This test method may be used to evaluate a plastic drum’s resistance to failure by cracking when in the presence of chemical
and physical stresses.
1.3 Two procedures are provided as follows:
1.3.1 Procedure A—Internal pressure stress crack resistance method to nonyl phenoxypoly (ethyleneoxy) ethanol solution, a stress
cracking reagent. The internal pressure is controlled at a constant elevated pressure and temperature.
1.3.2 Procedure B—Top-load stress crack resistance method to nonyl phenoxypoly ethanol, a stress cracking reagent. The
compressive top load top-load is controlled at a constant weight while maintaining an elevated temperature.
1.4 Although these procedures are not designed to test the ability of the closure or closure gasket material to retain the test reagent,
the inclusion of closure failure as a container failure mode is optional. However, leakage through a closure may affect the internal
pressure that could affect the test results.
1.5 This test method does not attempt to address all factors that could lead to stress cracking of plastic drums. The user of this
standard may use other test parameters, such as top loads, top-loads, chemical reagents, etc., as agreed upon between the user and
supplier in the event of a drum qualification or purchase agreement.
1.6 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The SI units given in parentheses are for information
only.
1.7 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. use. Specific warning statements are given in 6.2.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D10 on Packaging and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D10.21 on Shipping Containers and
Systems - Application of Performance Test Methods.
Current edition approved June 1, 2016Oct. 1, 2022. Published July 2016November 2022. Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 20102016 as
D5571D5571 – 16.–94 (2010). DOI: 10.1520/D5571-16.10.1520/D5571-22.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D5571 − 22
1.8 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D996 Terminology of Packaging and Distribution Environments
D4577 Test Method for Compression Resistance of a Container Under Constant Load
E122 Practice for Calculating Sample Size to Estimate, With Specified Precision, the Average for a Characteristic of a Lot or
Process
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Reference Terminology D996 for definitions of terms applicable to this test method.
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 environmental stress crack—a crack that develops when a plastic drum is exposed to chemical and physical stresses.
3.2.2 plastic tightheadtight-head drum—A non-removable head plastic drum, maximum capacity not exceeding 60 gal (227 L),
with openings for filling and emptying not exceeding 2.76 in. (70 mm) in diameter.
3.2.3 stress crack failure—any environmental stress crack that penetrates through the thickness of the drum resultin
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.