ASTM C1208/C1208M-00
(Specification)Standard Specification for Vitrified Clay Pipe and Joints for Use in Microtunneling, Sliplining, Pipe Bursting, and Tunnels
Standard Specification for Vitrified Clay Pipe and Joints for Use in Microtunneling, Sliplining, Pipe Bursting, and Tunnels
SCOPE
1.1 This specification establishes the criteria for the manufacture, quality assurance testing, inspection, installation, field acceptance testing, and product marking of vitrified clay pipe to be used in microtunneling, sliplining, pipe bursting, in casings, and in tunnels for the conveyance of sewage, industrial wastes, and storm water.
1.1.1 Sections 3 through 7 and 9 of this specification contain manufacturing, quality assurance testing, inspection, and product marking criteria which are applicable to vitrified clay pipe prior to installation.
1.1.2 Section 8 of this specification contains criteria for the installation and field acceptance testing of vitrified clay pipe.
1.2 This specification also covers materials and test requirements for jointing of the pipe.
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the specification.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or discontinued.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C 1208/C 1208M – 00
Standard Specification for
Vitrified Clay Pipe and Joints for Use in Microtunneling,
Sliplining, Pipe Bursting, and Tunnels
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 1208/C 1208M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the
year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last
reapproval. A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope tration Testing of Vitrified Clay Pipe Lines
D 395 Test Methods for Rubber Property—Compression
1.1 This specification establishes the criteria for the manu-
Set
facture, quality assurance testing, inspection, installation, field
D 412 Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermo-
acceptance testing, and product marking of vitrified clay pipe
plastic Rubbers and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension
to be used in microtunneling, sliplining, pipe bursting, in
D 471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liq-
casings, and in tunnels for the conveyance of sewage, industrial
uids
wastes, and storm water.
D 518 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface
1.1.1 Sections 4-7 and 9 of this specification contain manu-
Cracking
facturing, quality assurance testing, inspection, and product
D 543 Test Method for Resistance of Plastics to Chemical
marking criteria which are applicable to vitrified clay pipe prior
Reagents
to installation.
D 573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
1.1.2 Section 8 of this specification contains criteria for the
Oven
installation and field acceptance testing of vitrified clay pipe.
D 1149 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface
1.2 This specification also covers materials and test require-
Ozone Cracking in a Chamber
ments for jointing of the pipe.
D 2240 Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer
1.3 The values stated in either inch-pound units or SI units
Hardness
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
SI units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each
3. Terminology
system are not exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall
3.1 Definitions— Terminology C 896 can be used for clari-
be used independently of the other. Combining values from the
fication of terminology in this specification.
two systems may result in nonconformance with the specifi-
cation.
PIPE
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
4. Materials and Manufacture
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4.1 Vitrified clay pipe shall be manufactured from fire clay,
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
shale, surface clay, or a combination of these materials that,
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
when formed into pipe and fired to suitable temperatures,
yields a product that conforms to this specification.
2. Referenced Documents
4.2 Test Requirements for Pipe:
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2.1 Test Samples:
C 67 Test Methods of Sampling and Testing Brick and
4.2.1.1 When requested, test samples representative of the
Structural Clay Tile
pipe to be used shall be selected by the purchaser or his
C 301 Test Methods for Vitrified Clay Pipe
representative from the supplier’s stock.
C 828 Test Method for Low-Pressure Air Test of Vitrified
4.2.1.2 The number of samples to be tested shall not exceed
Clay Pipe Lines
0.5 % of the number of pipe of each size furnished, except that
C 896 Terminology Relating to Clay Products
no less than three samples shall be tested.
C 1091 Test Method for Hydrostatic Infiltration and Exfil-
4.2.1.3 If any of the test samples fail to meet the require-
ments of 4.2.2-4.2.5, the manufacturer will be allowed to retest
two additional samples representative of the original material
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C04 on
Vitrified Clay Pipe and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C04.20 on for each one that failed. The pipe will be acceptable if all retest
Methods of Test and Specifications.
Current edition approved Aug. 10, 2000. Published September 2000. Originally
published as C 1208 – 91 and C 1208M – 91. Last previous edition C 1208/
C 1208M – 99a. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 09.01.
2 4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.05. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01.
Copyright © ASTM, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
C 1208/C 1208M
TABLE 1 Three Edge Bearing Strength TABLE 3 Hydrostatic Pressure Test Time
Nominal Diameter, in. Bearing Strength, lb/linear ft Barrel Thickness, in. Test Time, min
4 2000 Up to and including 1 7
6 2000 Over 1 including 1.5 9
8 2200 Over 1.5 including 2 12
10 2400 Over 2 including 2.5 15
12 2600 Over 2.5 including 3 18
15 2900 Over 3 21
18 3300
21 3850
24 4400
TABLE 4 Hydrostatic Pressure Test Time [SI]
27 4700
30 5000
Barrel Thickness, mm Test Time, min
36 6000
Up to and including 25 7
42 7000
Over 25 including 38 9
Over 38 including 50 12
Over 50 including 64 15
TABLE 2 Three Edge Bearing Strength [SI] Over 64 including 76 18
Over 76 21
Nominal Diameter, mm Bearing Strength, kN/m
100 29
150 29
4.2.3.7 The bearing surface of the test samples shall be
200 32
ground to planes, parallel within 0.002 in. (0.05 mm). The use
250 35
300 38 of capping material is not permitted.
400 42
4.2.3.8 Apply the load up to 3500 psi [25 MPa].The
500 52
remaining required load is applied at the uniform rate in not
600 64
700 69 less than 1 min nor more than 2 min.
800 77
4.2.3.9 Calculate and report the compressive strength as
900 88
follows:
1000 96
1100 105
Compressive Strength, C 5 W/A (1)
where:
samples meet the test requirements. If any of the re-test pipe
C = compressive strength of the specimen, lbf/in. [kgf/
2 2 2
fail, the lot shall be rejected.
cm ] to the nearest 100 lbf/in. [0.07 kgf/mm ],
4.2.1.4 If, subsequent to an initial test failure, the accuracy
W = recorded load, lbf [kgf/mm ], indicated by the testing
of the testing equipment is questioned, at the request of the
machine, and
manufacturer, the equipment shall be recalibrated and a retest A = average of the gross areas of the upper and lower
2 2
made or a retest made using other equipment of known bearing surfaces of the specimen, in. [mm ]tothe
2 2
accuracy. nearest 0.04 in. [25 mm ].
4.2.2 Bearing Strength— Pipe shall meet the bearing 4.2.4 Hydrostatic Pressure Test or Absorption Test:
strength requirements of Tables 1 and 2. 4.2.4.1 The manufacturer shall, at his option, apply either a
4.2.3 Compressive Strength Test: hydrostatic pressure test or an absorption test to all of the test
4.2.3.1 This test is used to determine the compressive specimens.
strength of pipe material. This test shall be performed only 4.2.4.2 Hydrostatic Pressure Test—When the pipe is sub-
when specified. jected to an internal hydrostatic pressure of 10 psi [70 kPa] for
4.2.3.2 Pipe material shall have a minimum compressive the elapsed time indicated in Tables 3 and 4, there shall be no
strength of 7000 psi [50 MPa]. leakage. Moisture appearing on the surface shall not be
4.2.3.3 The testing machine shall be of a type having considered leakage. However, moisture which starts to run on
sufficient capacity and capable of providing the rates of loading the pipe shall be construed as leakage, regardless of quantity.
prescribed. The bearing area from which the force will be At the option of the manufacturer, water within approximately
applied shall be spherically seated. 5°F [3°C] of the ambient air temperature may be introduced
4.2.3.4 The specimen shall be a cylinder cut from the pipe into the pipe for control of condensation.
so that the length of the specimen is along the longitudinal axis 4.2.4.3 Absorption Test—The absorption of vitrified clay
of the pipe. The cylinder shall have a minimum diameter of 1 pipe shall not exceed 8 % when tested in accordance with Test
in. (25 mm) for pipe wall thickness through 2 1/2 in. (65 mm) Methods C 301.
and 2 in. (50 mm) for greater wall thicknesses and a diameter 4.2.5 Acid Resistance:
to length ratio of 1:2. The tolerance of the diameter and length 4.2.5.1 This test is used to determine the resistance of pipe
shall be + – 5%. Measurements shall be made to the nearest to the action of acids specified in Test Methods C 301. The test
0.001 in. (0.025 mm). shall be performed only when specified.
4.2.3.5 The test load on the specimen shall be centered 4.2.5.2 The pipe of each size and shipment shall be accept-
axially on the ends of the cylinder. able if the acid-soluble matter, from specimens representing
4.2.3.6 The bearing surfaces of the specimen shall be such pipe, does not exceed 0.25 %.
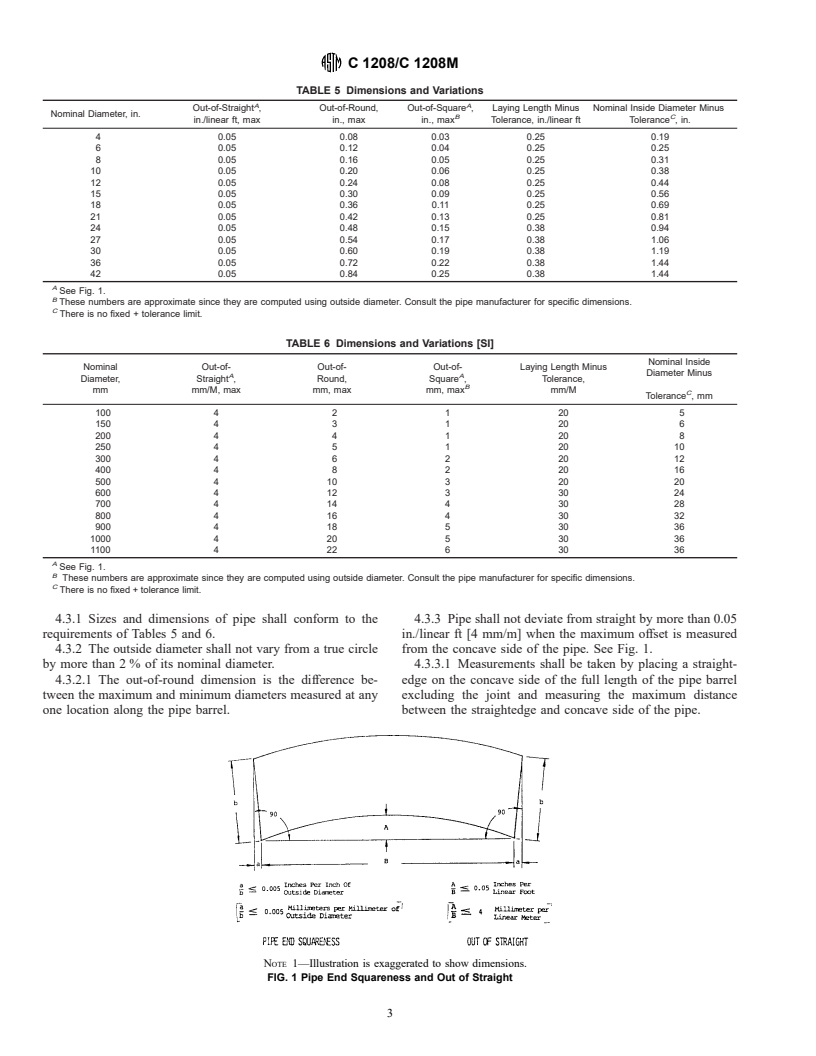
parallel planes and perpendicular to the vertical axis. 4.3 Sizes and Dimensions:
C 1208/C 1208M
TABLE 5 Dimensions and Variations
A A
Out-of-Straight , Out-of-Round, Out-of-Square , Laying Length Minus Nominal Inside Diameter Minus
Nominal Diameter, in.
B C
in./linear ft, max in., max in., max Tolerance, in./linear ft Tolerance , in.
4 0.05 0.08 0.03 0.25 0.19
6 0.05 0.12 0.04 0.25 0.25
8 0.05 0.16 0.05 0.25 0.31
10 0.05 0.20 0.06 0.25 0.38
12 0.05 0.24 0.08 0.25 0.44
15 0.05 0.30 0.09 0.25 0.56
18 0.05 0.36 0.11 0.25 0.69
21 0.05 0.42 0.13 0.25 0.81
24 0.05 0.48 0.15 0.38 0.94
27 0.05 0.54 0.17 0.38 1.06
30 0.05 0.60 0.19 0.38 1.19
36 0.05 0.72 0.22 0.38 1.44
42 0.05 0.84 0.25 0.38 1.44
A
See Fig. 1.
B
These numbers are approximate since they are computed using outside diameter. Consult the pipe manufacturer for specific dimensions.
C
There is no fixed + tolerance limit.
TABLE 6 Dimensions and Variations [SI]
Nominal Inside
Nominal Out-of- Out-of- Out-of- Laying
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.