ASTM F1790/F1790M-15(2021)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Measuring Cut Resistance of Materials Used in Protective Clothing with CPP Test Equipment
Standard Test Method for Measuring Cut Resistance of Materials Used in Protective Clothing with CPP Test Equipment
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method assesses the cut resistance of a material when exposed to a cutting edge under specified loads. Data obtained from this test method can be used to compare the cut resistance of different materials.
5.2 This test method only addresses that range of cutting hazards that are related to a cutting action by a smooth, sharp edge across the surface of the material. It is not representative of any other cutting hazard to which the material may be subjected such as serrated edges, saw blades, or motorized cutting tools. Nor is it representative of puncture, tear, or other modes of fabric failure.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the cut resistance of a material when mounted on a mandrel and subjected to a cutting edge under a specified load using the Cut Protection Performance (CPP) Tester.
1.1.1 This procedure is not valid for high-porosity materials which allow cutting edge contact with the mounting surface prior to cutting.
1.1.2 Test apparatus may have limitations in testing materials with a thickness greater than 3 mm or having a high frictional coefficient such as elastomers.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of the other. Combining values from the two systems may result in nonconformance with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F1790/F1790M − 15 (Reapproved 2021)
Standard Test Method for
Measuring Cut Resistance of Materials Used in Protective
Clothing with CPP Test Equipment
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF1790/F1790M;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyear
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Cut resistance is an important property for protective clothing and equipment, and several standard
testing devices have been adopted across different industries to measure this property. A common
practiceincutresistancetestingistosubjectamaterialspecimentoatransverselymovingbladeunder
an applied load and measure the distance of blade travel required to cut through the specimen. This
test method calculates the load required to cut through different specimens at 25.4 mm [1 in.] blade
travel. This calculated load, defined as the calculated cutting load, can be used to compare the cut
resistance of materials.
The original F1790–97 test method defined a commercially available apparatus known as the Cut
Protection Performance Tester (CPP). In an attempt to harmonize F1790/F1790M with ISO 13997
(another international testing standard for measuring cut resistance) and improve the test method, the
scope of the test method was changed in F1790–05 to allow the use of other cut testing equipment,
specificallytheTomodynamometer(TDM-100)andamodificationtotheCPParmcalledtheModified
CPP (mCPP). The revision addressed issues related to measurement of high frictional coefficient
materials like elastomers, specimen mounting, calculated cutting load determination, and other
procedures to harmonize with ISO 13997:1999. After further round-robin evaluation by the
subcommittee, it was demonstrated that the revisions to the test method result in a bias between the
original F1790–97 test method and the revised F1790–05 test method when using the CPP. F1790–05
wasnotwidelyadoptedinNorthAmericabecauseofthisbiasandlargeamountofdataandexperience
accumulatedwithF1790–97.F1790–97continuestobethetestmethodpredominatelypracticedwhen
using the CPP device. To reduce confusion for end-users of F1790/F1790M and to allow for
differences between testing devices, the subcommittee has decided to limit the scope of F1790/
F1790M to include only the CPP device and created a separate test method for use of the TDM-100
(Test Method F2992/F2992M).
1. Scope 1.1.2 Test apparatus may have limitations in testing materi-
als with a thickness greater than 3 mm or having a high
1.1 This test method covers the measurement of the cut
frictional coefficient such as elastomers.
resistance of a material when mounted on a mandrel and
subjected to a cutting edge under a specified load using the Cut 1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
Protection Performance (CPP) Tester. are to be regarded separately as standard. The values stated in
1.1.1 This procedure is not valid for high-porosity materials each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
which allow cutting edge contact with the mounting surface system shall be used independently of the other. Combining
prior to cutting. values from the two systems may result in nonconformance
with the standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeF23onPersonal
Protective Clothing and Equipment and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
F23.20 on Physical.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Current edition approved March 1, 2021. Published March 2021. Originally
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
approved in 1997. Last previous edition approved in 2015 as F1790/F1790M – 15.
DOI: 10.1520/F1790_F1790M-15R21. mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
F1790/F1790M − 15 (2021)
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor- isolating the external environment from contamination by the
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- wearer of the clothing.
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the 3.1.6.1 Discussion—Inthistestmethod,thepotentialhazard
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom- is cutting.
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1.7 calculated cutting load, n—in cut resistance testing,
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
the load required to cause a cutting edge to produce a
cut-through when it traverses the reference distance across the
2. Referenced Documents
material being tested.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.1.7.1 Discussion—The calculated cutting load is deter-
D123 Terminology Relating to Textiles
mined by performing a series of tests at three or more loads as
D1000 Test Methods for Pressure-Sensitive Adhesive-
described in Section 11. A material with a higher calculated
Coated Tapes Used for Electrical and Electronic Applica-
cutting load is considered to be more cut resistant.
tions
3.1.8 reference distance, n—in cut resistance testing, a
D1776/D1776M Practice for Conditioning and Testing Tex-
standardized distance for a blade to travel across a material to
tiles
produce a cut-through.
F1494 Terminology Relating to Protective Clothing
3.1.8.1 Discussion—For this test method, the reference
F2992/F2992M Test Method for Measuring Cut Resistance
distance is 25.4 mm [1.0 in.].
of Materials Used in Protective Clothing with Tomodyna-
3.2 Additional Terminology—Terms relevant to textiles are
mometer (TDM-100) Test Equipment
defined in Terminology D123. Terms relevant to protective
2.2 ISO Standards:
clothing are defined in Terminology F1494.
ISO 13997 Protective Clothing—Mechanical Properties—
Determination of Resistance to Cutting by Sharp Objects
4. Summary of Test Method
3. Terminology
4.1 Acutting edge under a specified load is moved one time
3.1 Definitions: across a specimen mounted on a mandrel.
3.1.1 cut resistance, n—in blade cut testing, the property
4.2 The cut-through distance from initial contact to cut-
that hinders cut-through when a material or a combination of
through is determined, for each load.
materials is exposed to a sharp-edged device.
4.2.1 Aseriesoftests,ataminimumofthreedifferentloads,
3.1.2 cut-through, n—in blade cut resistance tests, the pen-
must be performed to establish a range of cut distance at these
etration of the cutting edge entirely through material, as
different loads.
indicated by electrical contact of the cutting edge and the
4.3 The test method uses data from multiple loads to
conductive strip or substrate.
determine the calculated cutting load for the material.
3.1.2.1 Discussion—For this test, penetration of the cutting
edge entirely through the material includes the specimen and
5. Significance and Use
mounting tape.
5.1 Thistestmethodassessesthecutresistanceofamaterial
3.1.3 cut-through distance, n—in cut resistance testing, the
when exposed to a cutting edge under specified loads. Data
distance of required travel by the cutting edge to cut through
obtained from this test method can be used to compare the cut
the specimen.
resistance of different materials.
3.1.3.1 Discussion—For this test, distance of required travel
5.2 This test method only addresses that range of cutting
by the cutting edge to cut through the specimen includes the
hazards that are related to a cutting action by a smooth, sharp
specimen and mounting tape.
edge across the surface of the material. It is not representative
3.1.4 cutting edge, n—in cut resistance tests, a sharp-edged
of any other cutting hazard to which the material may be
device used to initiate cut-through of a planar structure.
subjected such as serrated edges, saw blades, or motorized
3.1.5 no cut, n—in cut resistance testing, a trial for which
cutting tools. Nor is it representative of puncture, tear, or other
the load used is insufficient to cause a cut-through in the
modes of fabric failure.
maximum allowable blade travel of the apparatus.
3.1.5.1 Discussion—For this test method, the maximum
6. Apparatus
allowable blade travel is 50.8 mm [2.0 in.].
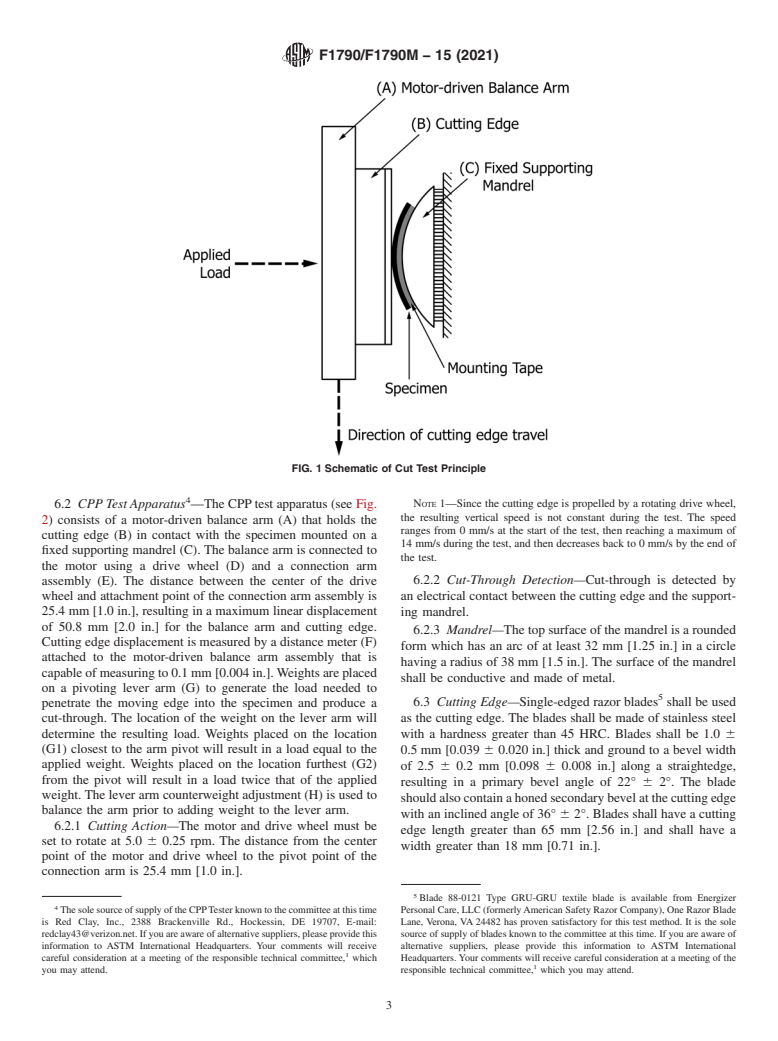
6.1 Test Principle—The principle of the cut test is to
3.1.6 protective clothing, n—an item of clothing that is
measure the distance traveled by a cutting edge as it is
specifically designed and constructed for the intended purpose
maintained under a load during the test. The cut test apparatus
of isolating all or part of the body from a potential hazard; or,
consists of the following primary components (see Fig. 1): (A)
a motor-driven balance arm to hold the cutting edge and to
which the load is applied; (B) a cutting edge; and (C) a fixed
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
supporting mandrel on which the specimen is to be mounted.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
The apparatus should propel the cutting edge across the
the ASTM website.
specimen until sufficient work is applied to cause the specimen
Available from International Organization for Standardization (ISO), 1, ch. de
la Voie-Creuse, CP 56, CH-1211 Geneva 20, Switzerland, http://www.iso.org. to cut through.
F1790/F1790M − 15 (2021)
FIG. 1 Schematic of Cut Test Principle
NOTE 1—Since the cutting edge is propelled by a rotating drive wheel,
6.2 CPP Test Apparatus —The CPPtest apparatus (see Fig.
the resulting vertical speed is not constant during the test. The speed
2) consists of a motor-driven balance arm (A) that holds the
ranges from 0 mm/s at the start of the test, then reaching a maximum of
cutting edge (B) in contact with the specimen mounted on a
14 mm/s during the test, and then decreases back to 0 mm/s by the end of
fixed supporting mandrel (C). The balance arm is connected to
the test.
the motor using a drive wheel (D) and a connection arm
6.2.2 Cut-Through Detection—Cut-through is detected by
assembly (E). The distance between the center of the drive
wheel and attachment point of the connection arm assembly is an electrical contact between the cutting edge and the support-
25.4 mm [1.0 in.], resulting in a maximum linear displacement ing mandrel.
of 50.8 mm [2.0 in.] for the balance arm and cutting edge.
6.2.3 Mandrel—The top surface of the mandrel is a rounded
Cutting edge displacement is measured by a distance meter (F)
form which has an arc of at least 32 mm [1.25 in.] in a circle
attached to the motor-driven balance arm assembly that is
having a radius of 38 mm [1.5 in.]. The surface of the mandrel
capableofmeasuringto0.1mm[0.004in.].Weightsareplaced
shall be conductive and made of metal.
on a pivoting lever arm (G) to generate the load needed to
penetrate the moving edge into the specimen and produce a 6.3 Cutting Edge—Single-edged razor blades shall be used
cut-through. The location of the weight on the lever arm will as the cutting edge. The blades shall be made of stainless steel
determine the resulting load. Weights placed on the location
with a hardness greater than 45 HRC. Blades shall be 1.0 6
(G1) closest to the arm pivot will result in a load equal to the
0.5 mm [0.039 6 0.020 in.] thick and ground to a bevel width
applied weight. Weights placed on the location furthest (G2)
of 2.5 6 0.2 mm [0.098 6 0.008 in.] along a straightedge,
from the pivot will result in a load twice that of the applied
resulting in a primary bevel angle of 22° 6 2°. The blade
weight. The lever arm counterweight adjustment (H) is used to
shouldalsocontainahonedsecondarybevelatthecuttingedge
balance the arm prior to adding weight to the lever arm.
with an inclined angle of 36° 6 2°. Blades shall have a cutting
6.2.1 Cutting Action—The motor and drive wheel must be
edge length greater than 65 mm [2.56 in.] and shall have a
set to rotate at 5.0 6 0.25 rpm. The distance from the center
width greater than 18 mm [0.71 in.].
point of the motor and drive wheel to the pivot point of the
connection arm is 25.4 mm [1.0 in.].
Blade 88-0121 Type GRU-GRU textile blade is available from Energizer
ThesolesourceofsupplyoftheCPPTesterknowntothecommitteeatthistime Personal Care, LLC (formerlyAmerican Safety Razor Company), One Razor Blade
is Red Clay, Inc., 2388 Brackenville Rd., Hockessin, DE 19707, E-mail: Lane, Verona, VA 24482 has proven satisfactory for this test method. It is the sole
redclay43@verizon.net.Ifyouareawareofalternativesuppliers,pleaseprovidethis source of supply of blades known to the committee at this time. If you are aware of
information to ASTM International Headquarters. Your comments will receive alternative suppliers, please provide this information to ASTM International
careful consideration at a meeting of the responsible technical committee, which Headquarters.Your comments will receive careful consideration at a meeting of the
you may attend. responsible technical committee, which you may attend.
F1790/F1790M − 15 (2021)
FIG. 2 Schematic of the CPP Tester (Side View)
6.4 Mounting Tape—Double-sided tape shall be used to 8. Sampling and Test Specimens
secure the test specimen to the apparatus.The tape should have
8.1 LotSample—Asalotsampleforacceptancetesting,take
a cloth carrier and rubber-based adhesive on both sides with a
at random the number of shipping units directed in an
total thickness of 0.38 6 0.25 mm, weight of 473 6 33g/m ,
applicable material specification.
and a minimum tensile strength of 90 N/cm (see Test Methods
8.2 Laboratory Sample—As a laboratory sample for accep-
D1000 for details on test methods for adhesive tape).
tance testing, take at random from each shipping unit in the lot
sample, the number of packages or pieces directed in an
7. Hazards
applicable material specification, or other agreement between
7.1 Thecuttestequipmentcanposeapotentialhazardtothe
the purchaser and the supplier.
technician if proper safety precautions are not followed. The
8.3 Protective Clothing Sample—Asample of actual protec-
cut test apparatus is to be used only by authorized personnel
tive clothing article.
that have been properly trained.
8.4 Test Specimens:
7.2 Store used blades in a sealed container.
8.4.1 Take test specime
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.