ASTM F477-14
(Specification)Standard Specification for Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for Joining Plastic Pipe
Standard Specification for Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for Joining Plastic Pipe
ABSTRACT
This specification covers elastomeric seals (gaskets) used to seal the joints of plastic pipe used for gravity, low-pressure, and high-pressure applications. This refers to push-on joints which require no internal or external pressure to effect the initial seal. Tensile strength, elongation, hardness, compression set, accelerated aging, water immersion, ozone resistance, and force decay shall be tested to meet the requirements prescribed.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers elastomeric seals (gaskets) used to seal the joints of plastic pipe used for gravity, low-pressure, and high-pressure applications. This refers to push-on joints which require no internal or external pressure to effect the initial seal.
1.2 Requirements are given for natural or synthetic rubber gaskets, or a combination of both.
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 7, of this specification: This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F477 −14 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
1
Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for Joining Plastic Pipe
ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationF477;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginal
adoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D412TestMethodsforVulcanizedRubberandThermoplas-
tic Elastomers—Tension
1.1 This specification covers elastomeric seals (gaskets)
D471Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
used to seal the joints of plastic pipe used for gravity,
D518 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface
low-pressure, and high-pressure applications. This refers to
3
Cracking (Withdrawn 2007)
push-onjointswhichrequirenointernalorexternalpressureto
D573Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air
effect the initial seal.
Oven
1.2 Requirements are given for natural or synthetic rubber
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
gaskets, or a combination of both.
D1149TestMethodsforRubberDeterioration—Crackingin
an Ozone Controlled Environment
1.3 Thetextofthisspecificationreferencesnotes,footnotes,
and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These D1229Test Method for Rubber Property—Compression Set
at Low Temperatures
notesandfootnotes(excludingthoseintablesandfigures)shall
not be considered as requirements of the specification. D1349Practice for Rubber—Standard Conditions for Test-
ing
1.4 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
D1414Test Methods for Rubber O-Rings
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
D1415Test Method for Rubber Property—International
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
Hardness
and are not considered standard.
D1566Terminology Relating to Rubber
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
D2240TestMethodforRubberProperty—DurometerHard-
test method portion, Section 7, of this specification: This
ness
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns,
F913Specification for Thermoplastic Elastomeric Seals
if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
(Gaskets) for Joining Plastic Pipe
of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and
2.2 NSF Standards:
environmental practices and determine the applicability of
Standard No. 14for Plastic Piping Components and Related
regulatory limitations prior to use. 4
Materials
1.6 This international standard was developed in accor-
Standard No. 61for Drinking Water Systems Components-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- 4
Health Effects
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
3. Terminology
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
3.1 Definitions—Terms relating to rubber or elastomer shall
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
beasdefinedinTerminologyD1566.Termsrelatingtoplastics
shall be as defined in Terminology D883.
2. Referenced Documents
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
3.2.1 sealing portion of the gasket—any part of the elasto-
D395Test Methods for Rubber Property—Compression Set
meric material that is in deformation which provides seals
between the bell and spigot of adjoining sections of pipe.
4. Composition and Manufacture
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.20 on Joining.
4.1 All gaskets shall be extruded or molded in such a
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2014. Published December 2014. Originally
mannerthatanycrosssectionwillbedense,homogeneous,and
published as approved in 1976. Last previous edition approved in 2010 as
F477–10. DOI: 10.1520/F0477-14.
2 3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM www.astm.org.
4
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from NSF International, P.O. Box 130140, 789 N. Dixboro Rd.,Ann
the ASTM website. Arbor, MI 48113-0140, http://www.nsf.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F477−14
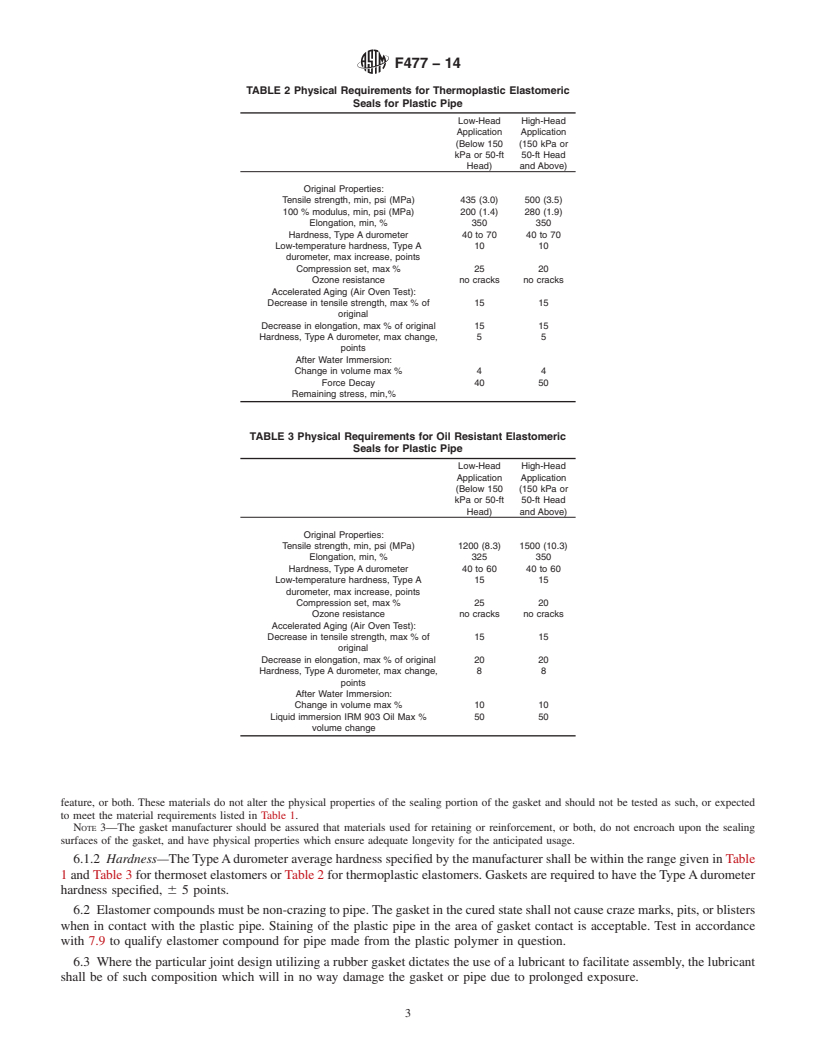
TABLE 1 Physical Requirements for Elastomeric Seals for
free of porosity, blisters, pitting, or other defects that make
Plastic Pipe
them unfit for the use intended. The gasket shall be fabricated
Low-Head High-Head
from a high-grad
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F477 − 10 F477 − 14 An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
1
Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for Joining Plastic Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F477; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original
adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript
epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers elastomeric seals (gaskets) used to seal the joints of plastic pipe used for gravity, low-pressure, and
high-pressure applications. This refers to push-on joints which require no internal or external pressure to effect the initial seal.
1.2 Requirements are given for natural or synthetic rubber gaskets, or a combination of both.
1.3 The text of this specification references notes, footnotes, and appendixes which provide explanatory material. These notes
and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of the specification.
1.4 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test method portion, Section 7, of this specification:This standard
does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations
prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D395 Test Methods for Rubber Property—Compression Set
D412 Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers—Tension
D471 Test Method for Rubber Property—Effect of Liquids
3
D518 Test Method for Rubber Deterioration—Surface Cracking (Withdrawn 2007)
D573 Test Method for Rubber—Deterioration in an Air Oven
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
D1149 Test Methods for Rubber Deterioration—Cracking in an Ozone Controlled Environment
D1229 Test Method for Rubber Property—Compression Set at Low Temperatures
D1349 Practice for Rubber—Standard Conditions for Testing
D1414 Test Methods for Rubber O-Rings
D1415 Test Method for Rubber Property—International Hardness
D1566 Terminology Relating to Rubber
D2240 Test Method for Rubber Property—Durometer Hardness
F913 Specification for Thermoplastic Elastomeric Seals (Gaskets) for Joining Plastic Pipe
2.2 NSF Standards:
4
Standard No. 14 for Plastic Piping Components and Related Materials
4
Standard No. 61 for Drinking Water Systems Components-Health Effects
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions—Terms relating to rubber or elastomer shall be as defined in Terminology D1566. Terms relating to plastics shall
be as defined in Terminology D883.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.20 on Joining.
Current edition approved March 15, 2010Sept. 15, 2014. Published May 2010December 2014. Originally published as approved in 1976. Last previous edition approved
in 20082010 as F477 – 08.F477 – 10. DOI: 10.1520/F0477-10.10.1520/F0477-14.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on www.astm.org.
4
Available from NSF International, P.O. Box 130140, 789 N. Dixboro Rd., Ann Arbor, MI 48113-0140, http://www.nsf.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F477 − 14
3.2 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.2.1 sealing portion of the gasket—any part of the elastomeric material that is in deformation which provides seals between
the bell and spigot of adjoining sections of pipe.
4. Composition and Manufacture
4.1 All gaskets shall be extruded or molded in such a manner that any cross section will be dense, homogeneous, and free of
poro
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.