ASTM D665-14e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oil in the Presence of Water
Standard Test Method for Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oil in the Presence of Water
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 In many instances, such as in the gears of a steam turbine, water can become mixed with the lubricant, and rusting of ferrous parts can occur. This test indicates how well inhibited mineral oils aid in preventing this type of rusting. This test method is also used for testing hydraulic and circulating oils, including heavier-than-water fluids. It is used for specification of new oils and monitoring of in-service oils.
Note 3: This test method was used as a basis for Test Method D3603. Test Method D3603 is used to test the oil on separate horizontal and vertical test rod surfaces, and can provide a more discriminating evaluation.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the ability of inhibited mineral oils, particularly steam-turbine oils, to aid in preventing the rusting of ferrous parts should water become mixed with the oil. This test method is also used for testing other oils, such as hydraulic oils and circulating oils. Provision is made in the procedure for testing heavier-than-water fluids.
Note 1: For synthetic fluids, such as phosphate ester types, the plastic holder and beaker cover should be made of chemically resistant material suitable for the type of fluid tested.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 7.4 – 7.6.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D665 − 14
Designation: 135/06
Standard Test Method for
Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oil in
1
the Presence of Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D665; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—Subsection 7.3 was corrected editorially in February 2015.
1. Scope* A240/A240M Specification for Chromium and Chromium-
Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the ability of
Vessels and for General Applications
inhibited mineral oils, particularly steam-turbine oils, to aid in
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating
preventing the rusting of ferrous parts should water become
Oils
mixed with the oil. This test method is also used for testing
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
other oils, such as hydraulic oils and circulating oils. Provision
D2422 Classification of Industrial Fluid Lubricants by Vis-
is made in the procedure for testing heavier-than-water fluids.
cosity System
NOTE 1—For synthetic fluids, such as phosphate ester types, the plastic
D3603 Test Method for Rust-Preventing Characteristics of
holder and beaker cover should be made of chemically resistant material
Steam Turbine Oil in the Presence of Water (Horizontal
suitable for the type of fluid tested.
Disk Method)
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
Petroleum Products
standard.
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
2.2 Other Documents:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the Motor Fuels, Section I, Annex A2, Table 32, Reference
3
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- Materials and Blending Accessories
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
Specifications-IP Standard Thermometers, Vol 2, Appendix
4
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. For specific A
warning statements, see 7.4 – 7.6.
Specifications for IP Standard Reference Liquids, Appendix
4
B
2. Referenced Documents
SAE Standard J405 Chemical Composition of SAEWrought
5
2
Stainless Steels
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4
BS 871 Specification for abrasive papers and cloths
A108 Specification for Steel Bar, Carbon and Alloy, Cold-
BS 970 Part 1: Carbon and Carbon Manganese Steels
Finished
4
Including Free Cutting Steels
3. Terminology
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
Subcommittee D02.C0.02 on Corrosion and Water/Air Separability.
3.1.1 rust,n—aspecialcaseofcorrosionthatcanbevisually
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2014. Published November 2014. Originally
observed on the surface of round steel test rods as reddish-
approved in 1942. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D665 – 12. DOI:
10.1520/D0665-14E01.
brown discoloration or small black spots.
This standard has been developed through the cooperative effort betweenASTM
International and the Energy Institute, London. The EI and ASTM International
3
logos imply that the ASTM International and EI standards are technically See 1996 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.04.
4
equivalent, but does not imply that both standards are editorially identical. AnnualBookofIPStandardMethodsforAnalysisandTestingofPetroleumand
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Related Products, Vol 2. Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St.,
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM London, WIG 7AR, U.K.
5
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on 1995 SAE Handbook, Vol 1. Available from Society of Automotive Engineers
the ASTM website. (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D665 − 14
NOTE 5—An inverted petri dish makes a suitable cover, as the sides of
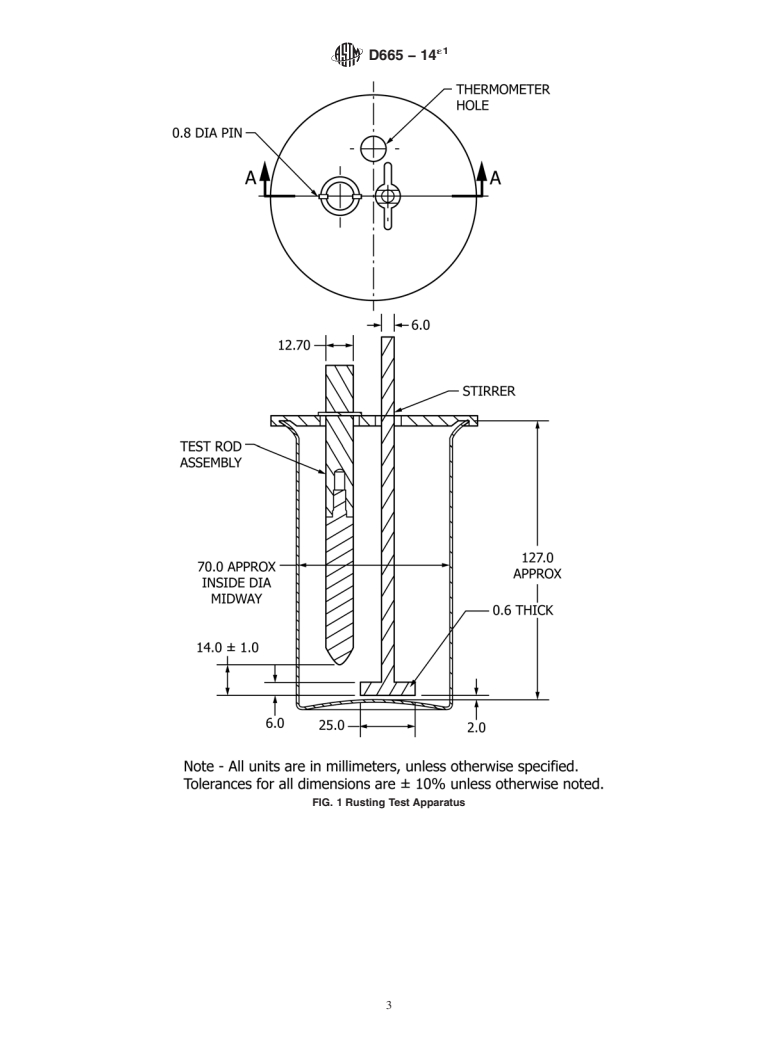
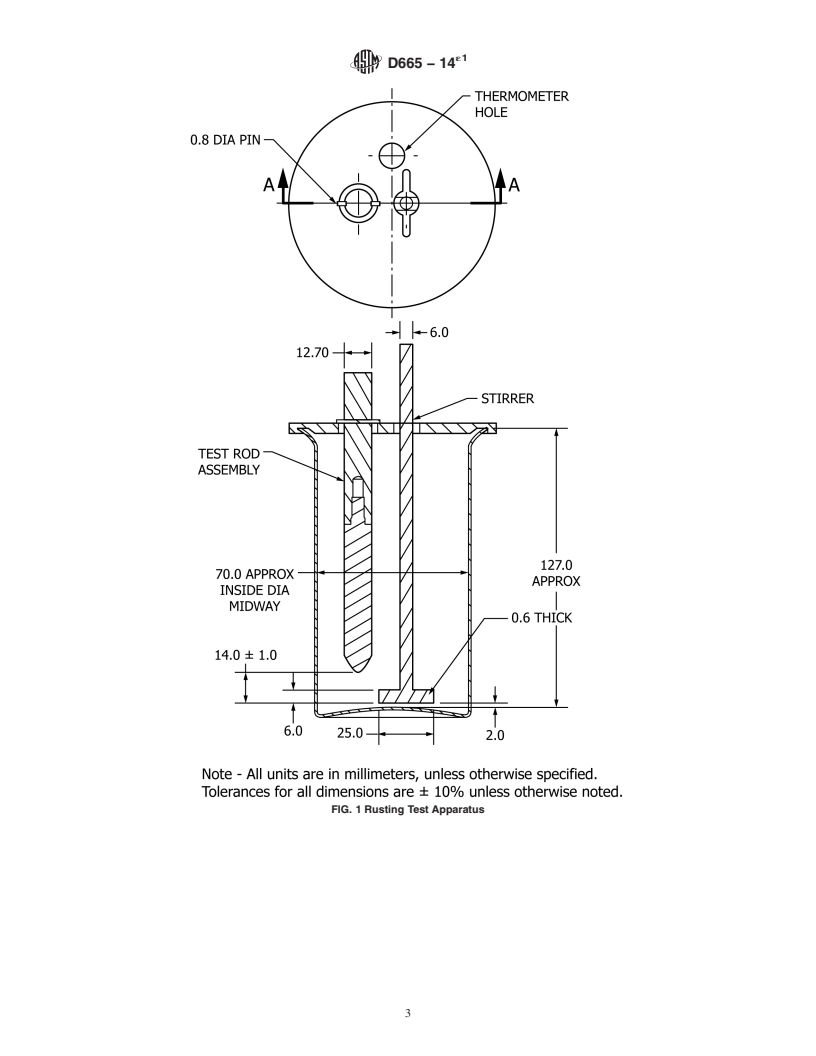
4. Summary of Test Method
the dish aid in keeping it in position. Fig. 2 shows a PMMA resin cover
4.1 Amixture of 300 mLof the oil under test is stirred with
for the be
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
´1
Designation: D665 − 14 D665 − 14
Designation: 135/06
Standard Test Method for
Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oil in
1
the Presence of Water
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D665; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense.
1
ε NOTE—Subsection 7.3 was corrected editorially in February 2015.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers the evaluation of the ability of inhibited mineral oils, particularly steam-turbine oils, to aid in
preventing the rusting of ferrous parts should water become mixed with the oil. This test method is also used for testing other oils,
such as hydraulic oils and circulating oils. Provision is made in the procedure for testing heavier-than-water fluids.
NOTE 1—For synthetic fluids, such as phosphate ester types, the plastic holder and beaker cover should be made of chemically resistant material suitable
for the type of fluid tested.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use. For specific warning statements, see 7.4 – 7.6.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
A108 Specification for Steel Bar, Carbon and Alloy, Cold-Finished
A240/A240M Specification for Chromium and Chromium-Nickel Stainless Steel Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and
for General Applications
D91 Test Method for Precipitation Number of Lubricating Oils
D1193 Specification for Reagent Water
D2422 Classification of Industrial Fluid Lubricants by Viscosity System
D3603 Test Method for Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Steam Turbine Oil in the Presence of Water (Horizontal Disk Method)
D4057 Practice for Manual Sampling of Petroleum and Petroleum Products
E1 Specification for ASTM Liquid-in-Glass Thermometers
2.2 Other Documents:
3
Motor Fuels, Section I, Annex A2, Table 32, Reference Materials and Blending Accessories
4
Specifications-IP Standard Thermometers, Vol 2, Appendix A
4
Specifications for IP Standard Reference Liquids, Appendix B
5
SAE Standard J405 Chemical Composition of SAE Wrought Stainless Steels
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products, Liquid Fuels, and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
D02.C0.02 on Corrosion and Water/Air Separability.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2014. Published November 2014. Originally approved in 1942. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D665 – 12. DOI:
10.1520/D0665-14.10.1520/D0665-14E01.
This standard has been developed through the cooperative effort between ASTM International and the Energy Institute, London. The EI and ASTM International logos
imply that the ASTM International and EI standards are technically equivalent, but does not imply that both standards are editorially identical.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
See 1996 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.04.
4
Annual Book of IP Standard Methods for Analysis and Testing of Petroleum and Related Products, Vol 2. Available from Energy Institute, 61 New Cavendish St., London,
WIG 7AR, U.K.
5
1995 SAE Handbook, Vol 1. Available from Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), 400 Commonwealth Dr., Warrendale, PA 15096-0001.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
´1
D665 − 14
4
BS 871 Specification for abrasive papers and cloths
4
BS 970 Part 1: Carbon and Carbon Manganese Steels Including Free Cutting Steels
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
3.1.1 rust, n—a special case of corrosion that can be visually observed on the surf
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.