ASTM F1375-92(1999)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometer (EDX) Analysis of Metallic Surface Condition for Gas Distribution System Components
Standard Test Method for Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometer (EDX) Analysis of Metallic Surface Condition for Gas Distribution System Components
SCOPE
1.1 This test method establishes a procedure for comparing the elemental composition of normal surfaces with any defects found on the surfaces of metal tubing, fittings, valves, or any metal component.
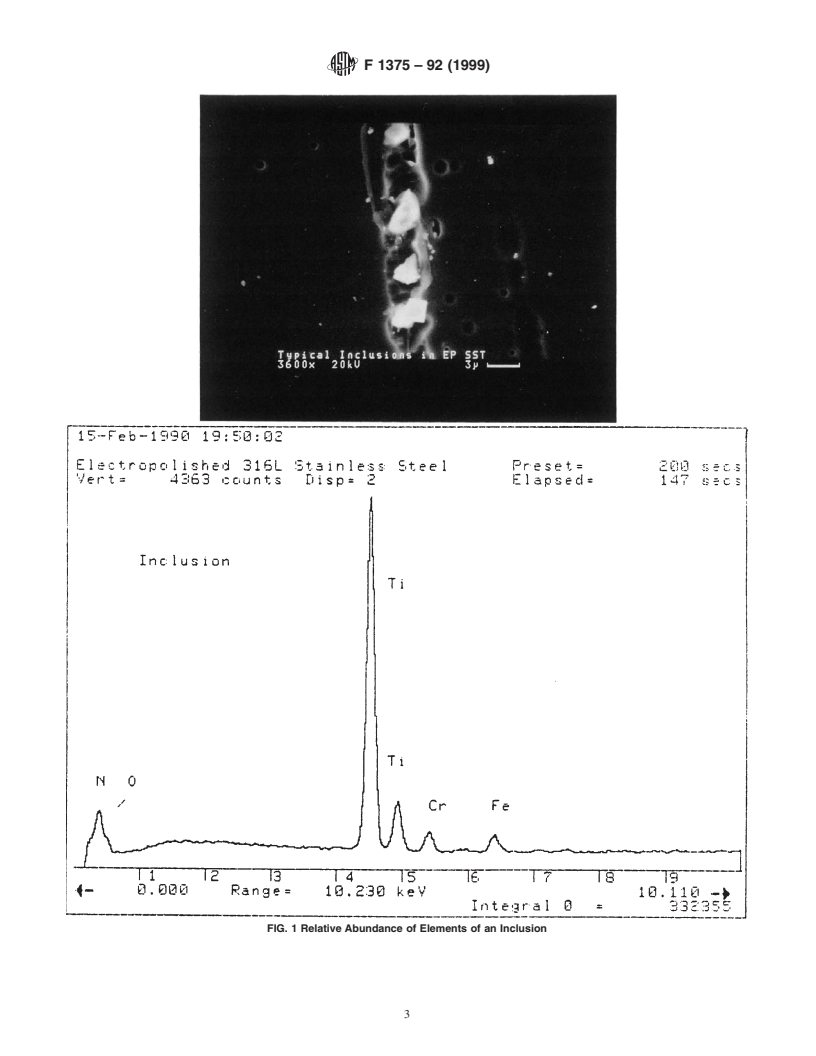
1.2 This test method applies to all steel surfaces of components such as tubing, connectors, regulators, and valves, regardless of size, style, or type.
1.3 Limitations:
1.3.1 This test method is intended for use by scanning electron microscope/energy dispersive x-ray spectrometer (SEM/EDX) operators with skill level typically achieved over a twelve-month period.
1.3.2 SEM used for this study should conform to those limitations outlined in Test Method F1372 and should have a minimum point-to-point resolution of 30 nm.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety problems, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard statements are given in Section 6.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:F 1375–92 (Reapproved 1999)
Standard Test Method for
Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometer (EDX) Analysis of
Metallic Surface Condition for Gas Distribution System
Components
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1375; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
Semiconductor clean rooms are serviced by high-purity gas distribution systems. This test method
presents a procedure that may be applied for the evaluation of one or more components considered for
use in such systems.
1. Scope F 1372 Test Method for Scanning Electron Microscope
(SEM) Analysis of Metallic Surface Condition for Gas
1.1 This test method establishes a procedure for comparing
Distribution System Components
the elemental composition of normal surfaces with any defects
found on the surfaces of metal tubing, fittings, valves, or any
3. Terminology
metal component.
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
1.2 This test method applies to all steel surfaces of compo-
3.1.1 normal surface—an area of the sample that does not
nents such as tubings, connectors, regulators, and valves,
exhibit any visible defect when viewed under the stipulated
regardless of size, style, or type.
SEM magnification. Normal surface is used to provide a
1.3 Limitations:
baseline for comparison with any area exhibiting a defect.
1.3.1 This test method is intended for use by scanning
3.1.2 sample angle—the angle measured normal to the
electron microscope/energy dispersive x-ray spectrometer
incoming electron beam.
(SEM/EDX) operators with skill level typically achieved over
3.1.3 standard conditions—101.3 kPa, 0.0°C (14.73 psia,
a twelve-month period.
32.0°F).
1.3.2 SEM used for this study should conform to those
3.1.4 working distance—the measured distance from the
limitations outlined in Test Method F 1372 and should have a
bottom of the objective lens to the sample.
minimum point-to-point resolution of 30 nm.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
4. Significance and Use
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
4.1 The purpose of this test method is to define a procedure
information only.
for testing components being considered for installation into a
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
high-purity gas distribution system. Application of this test
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
method is expected to yield comparable data among compo-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
nents tested for purposes of qualification for this installation.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use. Specific hazard
5. Apparatus
statements are given in Section 6.
5.1 Materials:
5.1.1 Mounting Stubs, specific to the instrument used are
2. Referenced Documents
required.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1.1.1 Samples shall not be coated with a conductive thin
layer (for example, gold or carbon).
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F01 on 5.1.2 Conductive Paste/Tape, that will provide a conductive
Electronics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F01.10 on Processing
path.Useanymeansoffixingthesampletoastub.Careshould
Environments.
be taken not to contaminate the area of interest.
Current edition approved Feb. 15, 1992. Published April 1992.
5.1.3 Adhesives, used to attach samples to sample stubs are
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
to be vacuum stable.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
5.2 Instrumentation:
the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
F 1375–92 (1999)
5.2.1 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)—Any high 9.4 Move the sample until an area of interest on the
resolution commercially available SEM with photographic sample’s surface comes into focus. The area of interest should
capabilities of a 100 cm image may be used for these be representative of a normal surface, avoiding gross deformi-
analyses. ties.
5.2.2 Instrument Operating Parameters, shall be as follows:
9.5 Orient the sample (with respect to working distance,
accelerating voltage, 20 KeV; final aperture size nominal 200
sample tilt, etc) to maximize X-ray collection efficiency of the
µmorless;andworkingdistanceandsampletilt,asappropriate
EDX detector.
to the EDX detector.
9.6 Adjust accelerating voltage to provide maximum exci-
5.2.2.1 SEM instrument operating parameters shall be such
tation for the element of interest. Typically, this is 20 KeV for
that collection efficiency for the EDX spectrometer is opti-
all elements having an atomic number greater than or equal to
mized.
eleven (the atomic number of sodium) and 10 KeV for those
5.2.3 EDX Spectrometer, capable of full width half maxi-
elements with atomic numbers between boron and sodium.
mum (FWHM) resolution of 170 eV or less (for MnKa), and
9.7 Collect X-ray signals fo
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.