ASTM D4066-01a(2008)
(Classification)Standard Classification System for Nylon Injection and Extrusion Materials (PA) (Withdrawn 2012)
Standard Classification System for Nylon Injection and Extrusion Materials (PA) (Withdrawn 2012)
ABSTRACT
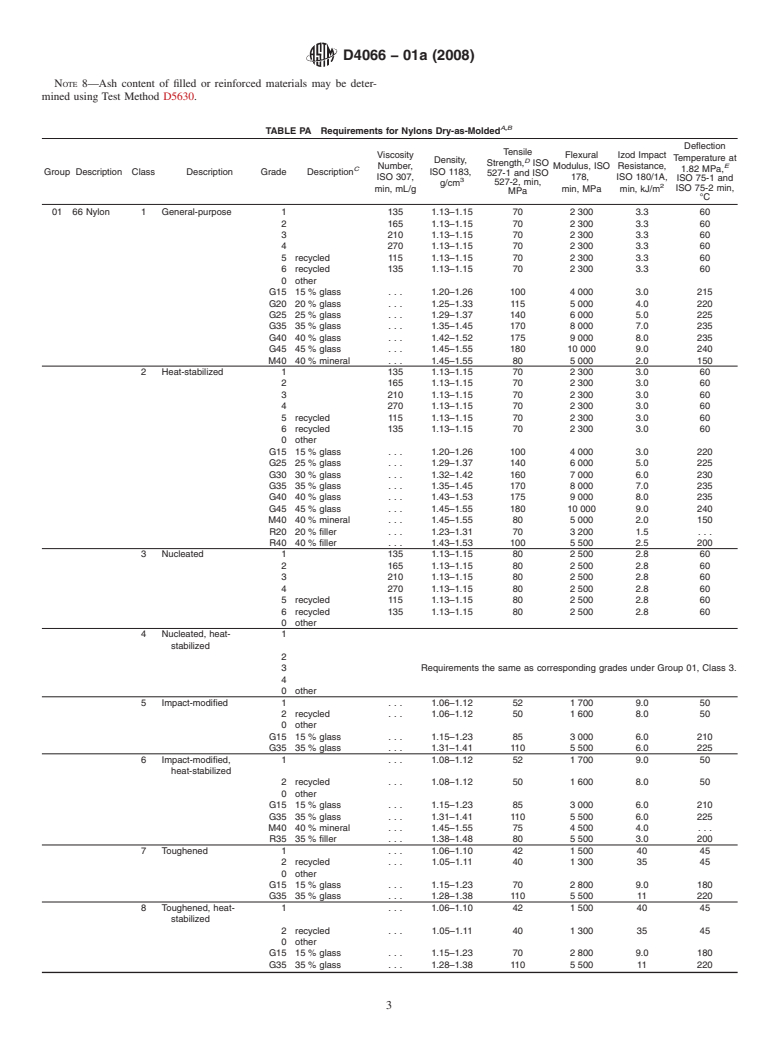
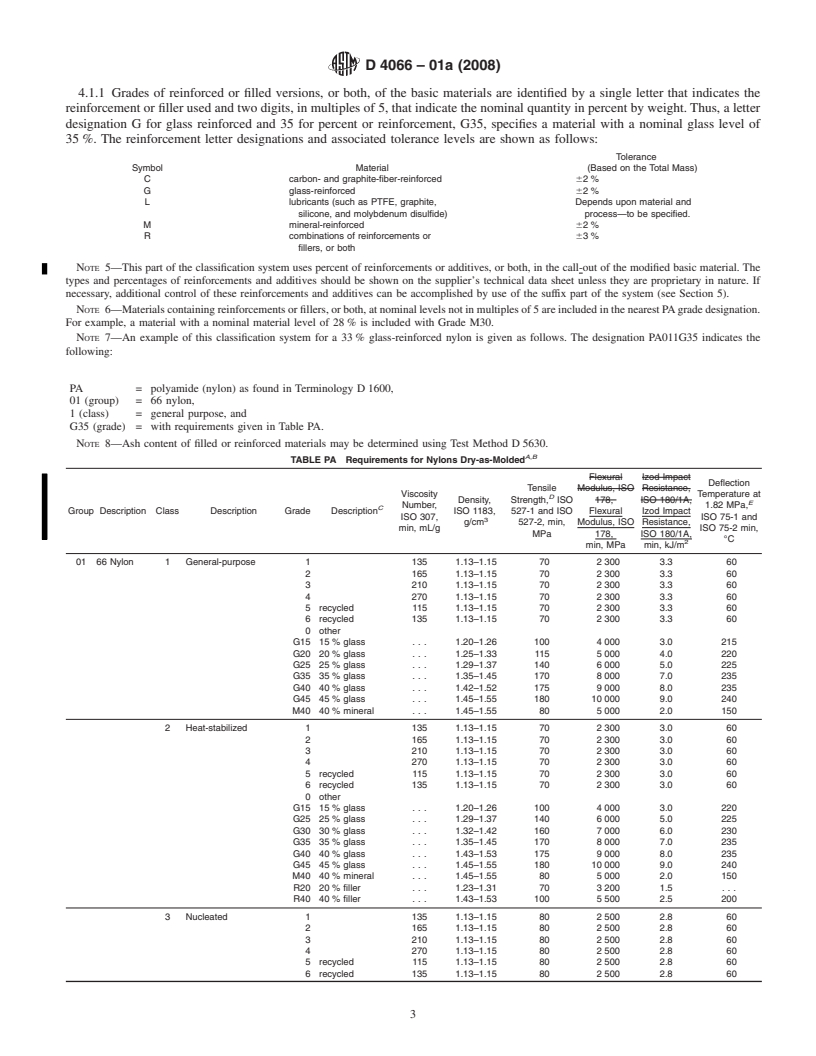
This classification system covers nylon injection and extrusion materials. Nylon materials are classified into groups according to their composition. Groups are further classified into classes and grades. Grades are identified by a single letter that indicates the reinforcement or filler used and two digits, in multiples of 5, which indicate the nominal quantity in weight percent. Specific requirements for variations of nylon materials shall be shown by a six-character designator. Suffixes shall be used for those properties not covered by basic requirements. Specific suffix requirements shall always take precedence over basic requirements. Tensile strength, flexural strength, Izod impact resistance, deflection temperature, and density shall be done on test pieces based on injection molded ISO 3167 type multipurpose test specimens. Conditioning, preparation, testing, inspection, packaging, and marking shall be in conformance to the requirements in this standard classification system.
SCOPE
1.1 This classification system covers nylon materials suitable for injection molding and extrusion. Some of these compositions are also suitable for compression molding and application from solution.
1.2 The properties included in this classification system are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specialized applications. These may be specified by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.3 This classification system and subsequent line call-out (specification) are intended to provide a means of calling out plastic materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material selection should be made by those having expertise in the plastic field after careful consideration of the design and the performance required of the part, the environment to which it will be exposed, the fabrication process to be employed, the costs involved, and the inherent properties of the material other than those covered by this classification system.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this classification system. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Note 1—This classification system is similar to ISO 1874-1/-2 1993, although the technical content is significantly different.
Note 2—This classification system is being revised to include international 4-mm specimens and test procedures as the standard for compliance. The 3.2-mm specimens; test methods; and Tables PA, A, and B are included in Appendix X3 as a reference for those wishing to use them. It is recommended that the material manufacturer be consulted on all call-outs against this classification system.
WITHDRAWN RATIONALE
This classification system covers nylon materials suitable for injection molding and extrusion. Some of these compositions are also suitable for compression molding and application from solution.
Formerly under the jurisdiction of Committee D20 on Plastics, this standard was withdrawn in November 2012 in accordance with section 10.6.3.1 of the Regulations Governing ASTM Technical Committees, which requires that standards shall be updated by the end of the eighth year since the last approval date. It is replaced by Classification System D6779.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D4066 −01a(Reapproved 2008)
Standard Classification System for
1
Nylon Injection and Extrusion Materials (PA)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D4066; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
is recommended that the material manufacturer be consulted on all
1. Scope*
call-outs against this classification system.
1.1 This classification system covers nylon materials suit-
able for injection molding and extrusion. Some of these
2. Referenced Documents
compositions are also suitable for compression molding and
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
application from solution.
D149Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and
1.2 The properties included in this classification system are
DielectricStrengthofSolidElectricalInsulatingMaterials
thoserequiredtoidentifythecompositionscovered.Theremay
at Commercial Power Frequencies
be other requirements necessary to identify particular charac-
D150Test Methods forAC Loss Characteristics and Permit-
teristics important to specialized applications. These may be
tivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulation
specified by using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
D256Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum
1.3 This classification system and subsequent line call-out
Impact Resistance of Plastics
(specification) are intended to provide a means of calling out
D257Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
plastic materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts.
Insulating Materials
It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material
D618Practice for Conditioning Plastics for Testing
selection should be made by those having expertise in the
D638Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
plastic field after careful consideration of the design and the
D648Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics
performance required of the part, the environment to which it
Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position
will be exposed, the fabrication process to be employed, the
D789Test Methods for Determination of Solution Viscosi-
costsinvolved,andtheinherentpropertiesofthematerialother
ties of Polyamide (PA)
than those covered by this classification system.
D790Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced
and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materi-
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
als
standard.
D792Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Rela-
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the
tive Density) of Plastics by Displacement
test methods portion, Section 11, of this classification system.
D883Terminology Relating to Plastics
This standard does not purport to address all of the safety
D1600TerminologyforAbbreviatedTermsRelatingtoPlas-
concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
tics
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and
D3418Test Method for Transition Temperatures and En-
health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
thalpies of Fusion and Crystallization of Polymers by
limitations prior to use.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
NOTE 1—This classification system is similar to ISO 1874-1/-2 1993,
D3641Practice for Injection Molding Test Specimens of
although the technical content is significantly different.
Thermoplastic Molding and Extrusion Materials
NOTE 2—This classification system is being revised to include interna-
D3892Practice for Packaging/Packing of Plastics
tional 4-mm specimens and test procedures as the standard for compli-
D4000Classification System for Specifying Plastic Materi-
ance. The 3.2-mm specimens; test methods; and Tables PA,A, and B are
included in Appendix X3 as a reference for those wishing to use them. It
als
D5630Test Method for Ash Content in Plastics
1
ThisclassificationsystemisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD20on
Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
2
Materials. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Current edition approved Sept. 15, 2008. Published September 2008. Originally contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
approved in 1982. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D4066-01a. DOI: Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
10.1520/D4066-01AR08. the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
An American National Standard Designation: D 4066 – 01a (Reapproved 2008)
Designation:D4066–01
Standard Classification System for
1
Nylon Injection and Extrusion Materials (PA)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4066; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope*
1.1 This classification system covers nylon materials suitable for injection molding and extrusion. Some of these compositions
are also suitable for compression molding and application from solution.
1.2 The properties included in this classification system are those required to identify the compositions covered. There may be
other requirements necessary to identify particular characteristics important to specialized applications.These may be specified by
using the suffixes as given in Section 5.
1.3 This classification system and subsequent line call-out (specification) are intended to provide a means of calling out plastic
materials used in the fabrication of end items or parts. It is not intended for the selection of materials. Material selection should
be made by those having expertise in the plastic field after careful consideration of the design and the performance required of the
part, the environment to which it will be exposed, the fabrication process to be employed, the costs involved, and the inherent
properties of the material other than those covered by this classification system.
1.4 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard.
1.5 The following precautionary caveat pertains only to the test methods portion, Section 11, of this classification system. This
standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user
of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
to use.
NOTE 1—This classification system is similar to ISO 1874-1/-2 1993, although the technical content is significantly different.
NOTE 2—This classification system is being revised to include international 4-mm specimens and test procedures as the standard for compliance. The
3.2-mm specimens; test methods; and Tables PA,A, and B are included inAppendix X3 as a reference for those wishing to use them. It is recommended
that the material manufacturer be consulted on all call-outs against this classification system.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 149 Test Method for Dielectric Breakdown Voltage and Dielectric Strength of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials at
Commercial Power Frequencies
D 150 Test Methods for A-CAC Loss Characteristics and Permittivity (Dielectric Constant) of Solid Electrical Insulating
2
Materials Insulation
D 256 Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics
D 257 Test Methods for D-CDC Resistance or Conductance of Insulating Materials
D 618 Practice for Conditioning Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials for Testing
D 638 Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics
D 648 Test Method for Deflection Temperature of Plastics Under Flexural Load in the Edgewise Position
D 789 Test Methods for Determination of Relative Viscosity, Melting Point, and Moisture Content Solution Viscosities of
Polyamide (PA)
D 790 Test Methods for Flexural Properties of Unreinforced and Reinforced Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials
D 792 Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement
D 883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
3
D 1600Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to Plastics
1
This classification system is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D20 on Plastics and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D20.15 on Thermoplastic
Materials (Section D20.15.09). .
CurrenteditionapprovedMarch10,2001.Sept.15,2008.PublishedJune2001.September2008.OriginallypublishedasD4066–82.approvedin1982.Lastpreviousedition
D4066–00a.approved in 2001 as D 4066 - 01a.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
, Vol 10.01.volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A
...








Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.