ASTM F2412-11
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Foot Protection
Standard Test Methods for Foot Protection
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
These test methods contain requirements to evaluate the performance of footwear for the following:
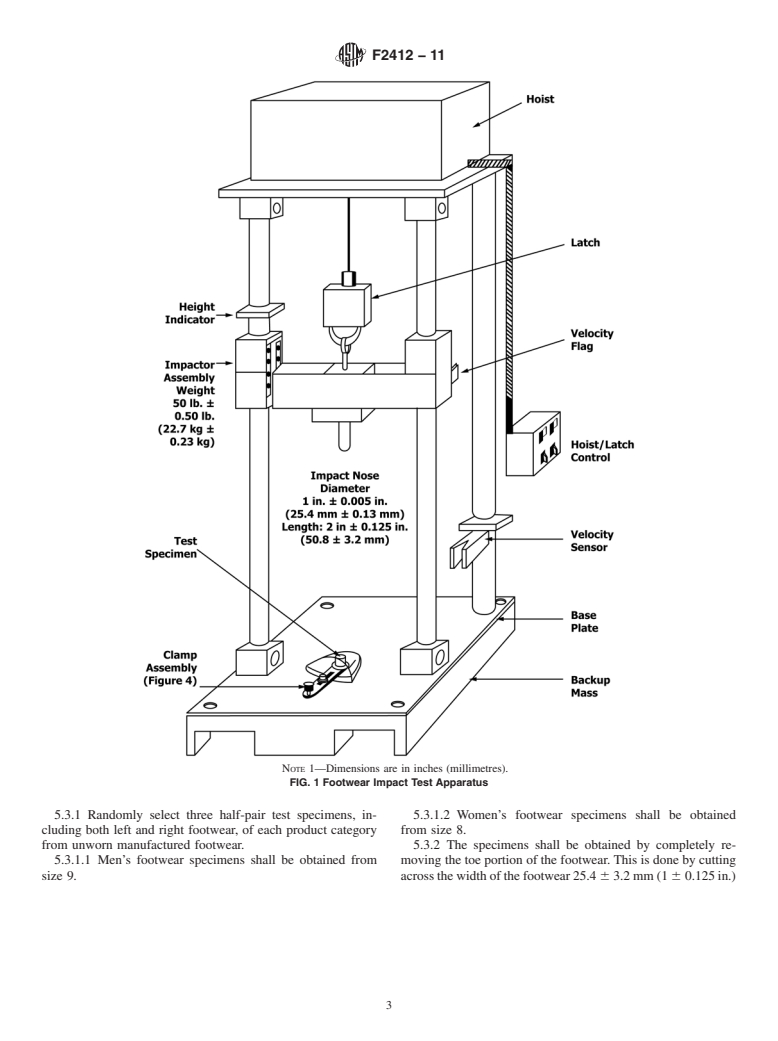
Impact resistance for the toe area of footwear (I/75),
Compression resistance for the toe area of footwear (C/75),
Metatarsal protection that reduces the chance of injury to the metatarsal bones at the top of the foot (Mt/75),
Conductive properties which reduce hazards that may result from static electricity buildup, and reduce the possibility of ignition of explosives and volatile chemicals (Cd),
Electric Hazard by stepping on live wire (EH),
Static dissipative (SD) properties to reduce hazards due to excessively low footwear electrical resistance that may exist where SD footwear is required, and
Puncture resistance footwear devices (PR).
Any changes to the original components of safety toe footwear such as replacing or adding after market footbeds/inserts could cause non compliance to any or all parts of this standard rendering the ASTM label invalid. Protective toe footwear specimens or samples shall be retested for any of the following changes.
Change in material used to make protective toe cap, change in protective cap manufacturer, change in the design of the toe cap.
Change in construction method used to make footwear or change in factory in which footwear is produced.
Change in the upper or insole material thickness greater than 25 %, change to the soling system or a change in the hardness of the outsole.
Change in shape of last used in the manufacturing of footwear.
Change in material or supplier of protective insole.
Change in material or supplier of met guard.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods measure the resistance of footwear to a variety of hazards that can potentially result in injury.
1.2 These test methods may be used to test for compliance to minimum performance requirements in established safety standards.
1.2.1 By agreement between the purchaser and the supplier, or as required by established safety standards, these test methods can be used to determine any one, or all of the following: (1) impact resistance (I), (2) compression resistance (C), (3) metatarsal impact resistance (Mt), (4) resistance to electrical conductivity (Cd), (5) resistance to electric hazard (EH), (6) static dissipative performance (SD), and (7) puncture resistance (PR).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: F2412 − 11
Standard Test Methods for
1
Foot Protection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2412; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
For more than sixty years, the predecessor to these test methods, ANSI Z41, established the
performance criteria for a wide range of footwear to protect from the hazards that affect the personal
safetyofworkers.ThevalueofthesestandardswasrecognizedearlyinthehistoryoftheOccupational
Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and incorporated as a reference standard in the Code of
Federal Regulation (CFR) Section 1910.
ThesetestmethodscontainstestprotocolsdevelopedinconjunctionwithANSIZ41aswellasother
ASTM standards that are used to evaluate the performance of footwear when exposed to a variety of
hazards: (1) impact resistance (I) for the toe area of footwear; (2) compression resistance (C) for the
toe area of footwear; (3) metatarsal impact protection (Mt) that reduces the chance of injury to the
metatarsal bones at the top of the foot; (4) conductive properties (Cd) that reduce hazards that may
result from static electricity buildup and reduce the possibility of ignition of explosives and volatile
chemicals; (5) electric hazard resistant (EH) non-conductive; (6) static dissipative (SD) properties to
reducehazardsduetoexcessivelylowfootwearelectricalresistancethatmayexistwhereSDfootwear
is required; and (7) puncture resistance (PR) of foot devices.
1. Scope responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
1.1 These test methods measure the resistance of footwear
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
to a variety of hazards that can potentially result in injury.
1.2 These test methods may be used to test for compliance
2. Referenced Documents
to minimum performance requirements in established safety
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
standards.
B117 Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus
1.2.1 By agreement between the purchaser and the supplier,
3
2.2 CSA Standard:
or as required by established safety standards, these test
CAN/CSA Z195 Protective Footwear
methods can be used to determine any one, or all of the
following: (1) impact resistance (I), (2) compression resistance
3. Terminology
(C), (3) metatarsal impact resistance (Mt), (4) resistance to
electrical conductivity (Cd), (5) resistance to electric hazard
3.1 Definitions:
(EH), (6) static dissipative performance (SD), and (7) puncture
3.1.1 insert/footbed/sockliner (all removable), n—footbed
resistance (PR).
normally made of a foam product with leather or fabric cover
shapedtocovertheentireinsolewhichcanbeinsertedbetween
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information the foot and insole board.
only.
3.1.2 insole, n—foundation of the shoe; the inner sole of the
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the shoe which is next to the foot, under the sock liner or insert,
onto which the upper is lasted.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
1 2
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F13 on For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
Pedestrian/Walkway Safety and Footwearand are the direct responsibility of contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Subcommittee F13.30 on Footwear. Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Current edition approved July 1, 2011. Published August 2011. Originally the ASTM website.
3
approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as F2412 – 05. DOI: Available from Canadian Standards Association (CSA), 178 Rexdale Blvd.,
10.1520/F2412-11. Toronto, ON Canada M9W1R3.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2412 − 11
3.1.3 last, n—solid hinged form, in the general shape of a standard rendering the ASTM label invalid. Protective toe
foot, around which footwear is constructed. footwear specimens or samples shall be retested for any of the
following changes.
3.1.4 lasting, v—building of footwear around a specific foot
4.2.1 Change in material used to make protective toe cap,
form.
change in protective cap manufacturer, change in the design of
3.1.5 lining, n—term used to describe all components that
the toe cap.
can be used to construct the interior of the upper portion of the
4.2.2 Changeinc
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:F2412–05 Designation:F2412–11
Standard Test Methods for
1
Foot Protection
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F2412; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
INTRODUCTION
For more than sixty years, the predecessor to these test methods, ANSI Z41, established the
performance criteria for a wide range of footwear to protect from the hazards that affect the personal
safetyofworkers.ThevalueofthesestandardswasrecognizedearlyinthehistoryoftheOccupational
Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and incorporated as a reference standard in the Code of
Federal Regulation (CFR) Section 1910.
ThesetestmethodscontainstestprotocolsdevelopedinconjunctionwithANSIZ41aswellasother
ASTM standards that are used to evaluate the performance of footwear when exposed to a variety of
hazards: (1) impact resistance (I) for the toe area of footwear; (2) compression resistance (C) for the
toe area of footwear; (3) metatarsal impact protection (Mt) that reduces the chance of injury to the
metatarsal bones at the top of the foot; (4) conductive properties (Cd) that reducesreduce hazards that
may result from static electricity buildup and reduce the possibility of ignition of explosives and
volatile chemicals; (5) electric shock resistant non-conductive; electric hazard resistant (EH)
non-conductive; (6) static dissipative (SD) properties to reduce hazards due to excessively low
footwear electrical resistance that may exist where SD footwear is required; and (7) puncture
resistance of foot bottoms; (8) chain saw cut resistance hazards; and (9) dielectric hazard. puncture
resistance (PR) of foot devices.
1. Scope
1.1 These test methods measure the resistance of footwear to a variety of hazards that can potentially result in injury.
1.2 These test methods may be used to test for compliance to minimum performance requirements in established safety
standards.
1.2.1 By agreement between the purchaser and the supplier, or as required by established safety standards, these test methods
can be used to determine any one, or all of the following: (1) impact resistance, impact resistance (I), (2) compression resistance,
compression resistance (C), (3) metatarsal impact resistance, metatarsal impact resistance (Mt), (4) resistance to electrical
conductivity, resistance to electrical conductivity (Cd), (5) resistance to electric shock, resistance to electric hazard (EH), (6) static
dissipative performance, static dissipative performance (SD), and (7) puncture resistance of outsoles, (8) chain saw cut resistance,
and (9) dielectric insulation.
1.3ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareforinformationonly.puncture
resistance (PR).
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
B117 Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F13 on Pedestrian/Walkway Safety and Footwear and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
F13.30 on Footwear.
Current edition approved March 1, 2005. Published March 2005. DOI: 10.1520/F2412-05.
Current edition approved July 1, 2011. Published August 2011. Originally approved in 2005. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as F2412 – 05. DOI:
10.1520/F2412-11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F2412–11
F1116Test Method for Determining Dielectric Strength of Dielectric Footwear
F1458Test Method for Measurement of Cut Resistance to Chain Saw of Foot Protective Devices Practice for Operating Salt
Spray (Fog) Apparatus
3
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.