ASTM F1248-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Determination of Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) of Polyethylene Pipe
Standard Test Method for Determination of Environmental Stress Crack Resistance (ESCR) of Polyethylene Pipe
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of a polyethylene pipe specimen's resistance to stress cracking when subjected to compression to deformation in the presence of a surface active agent at elevated temperature.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
Designation: F 1248 – 96 An American National Standard
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Method for
Determination of Environmental Stress Crack Resistance
1
(ESCR) of Polyethylene Pipe
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F 1248; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Summary of Test Method
1.1 This test method covers the determination of a polyeth- 4.1 A ring specimen of the polyethylene pipe, having a
ylene pipe specimen’s resistance to stress cracking when controlled imperfection at one location, is exposed at an
subjected to compression to deformation in the presence of a elevated temperature to the action of a surface active agent
surface active agent at elevated temperature. while compressed to deformation between parallel plates. The
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded elapsed time in hours to observation of a stress crack failure in
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for the specimen is recorded.
information only.
5. Significance and Use
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 5.1 This test method may be used to determine the environ-
mental stress crack resistance properties of a polyethylene pipe
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- specimen while under high stress in the presence of the surface
active agent, and at an elevated temperature.
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents 6. Apparatus
6.1 Specimen Holder—The test specimen holder shall con-
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 1600 Terminology for Abbreviated Terms Relating to sist of two parallel plates having a width at least 1.2 times the
2
nominal outside diameter of the pipe. Fig. 1 shows suggested
Plastics
1
D 1693 Test Method for Environmental Stress Cracking of dimensions for a holder for 1 ⁄4-in. pipe. Construction shall be
2
of corrosion-resistant metal such as Type 304 or 316 stainless
Ethylene Plastics
3
F 412 Terminology Relating to Plastic Piping Systems steel. The plates shall have a series of appropriately spaced
holes through which bolts or threaded rod can be inserted to
3. Terminology
effect compression of the test specimen by the use of nuts. It is
3.1 Definitions—Definitions of terms are in accordance with required that spacers having a thickness equal to the distance
Terminology F 412 and abbreviations are in accordance with required for compression be used to minimize the time to effect
Terminology D 1600, unless otherwise indicated. compression of the test specimen to ensure consistent and
3.2 Descriptions of Terms Specific to This Standard: uniform compression and to prevent overcompression. The
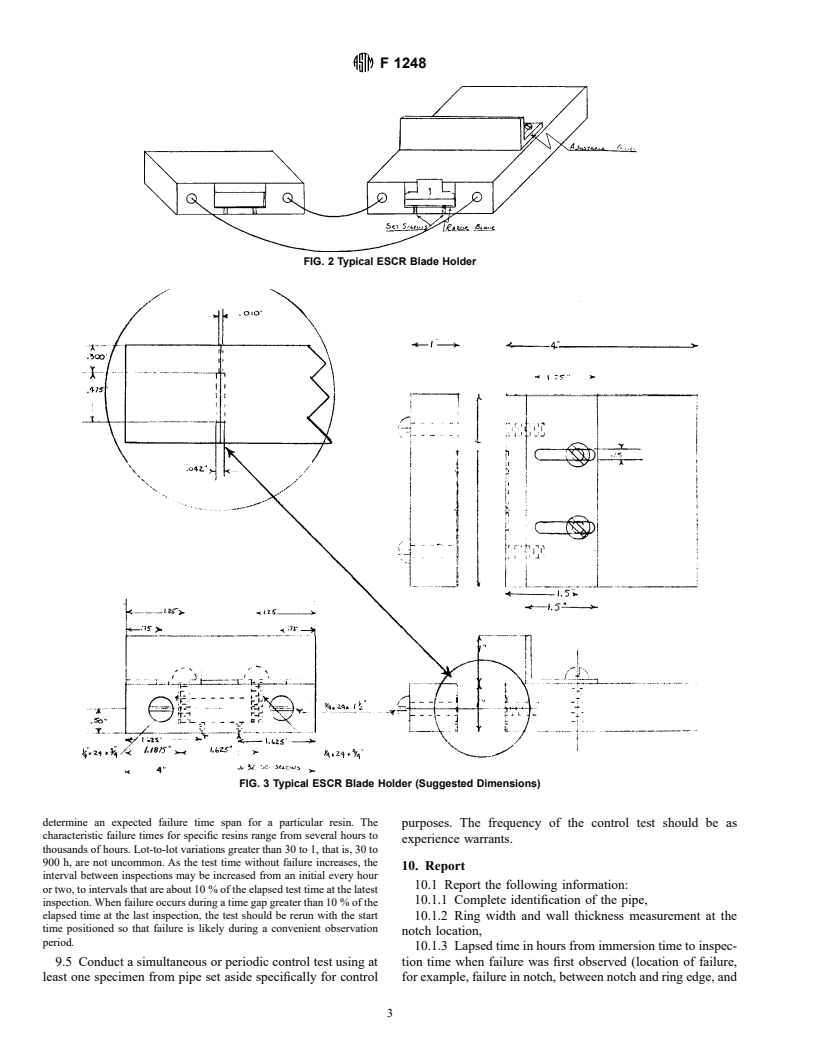
3.2.1 environmental stress crack resistance (ESCR)—a plates shall remain parallel throughout the testing period.
number in units of hours to failure indicating the resistance of 6.2 Notching Jig—The blade used shall be a single-edge
4
PE pipe to cracking at stresses below the short-term mechani- stainless blade (Table 1). The blade shall be replaced after it
cal stress values of the pipe while immersed in a surface active has been used to produce 20 notches. Additionally, the blade
liquid at elevated temperature. shall be inspected before each use employing a 43 magnifying
3.2.2 failure—a crack in the surface of the pipe specimen, glass, and shall be replaced whenever there is question of its
visible to an observer with normal eyesight. Extension of the having become dull or damaged. The required blade holder
controlled notch is not a failure. Appearance of more than one design and dimensions are shown in Fig. 2 and Fig. 3.
crack in a specimen shall be classified as a single failure. 6.3 Constant-Temperature Bath—A covered container filled
with the test reagent and maintained at 122 6 3.6°F (50 6
2°C). Add distilled water as necessary to maintain the specified
concentration of the test reagent in the bath. The bath and other
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F-17 on Plastic
components shall be constructed of materials that are not
Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.40 on Test
Methods.
Current edition approved March 10, 1996. Published May 1996. Originally
4
published as F 1248 – 89. Last previous edition F 1248 – 89. A blade made by the American Safety Razor Co., Industrial Products Division,
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 08.01. Razor Blade Lane, Verona, VA 24482, or equivalent, has been found satisfactory for
3
Annual Book
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.