ASTM C1181-00(2012)
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Compressive Creep of Chemical-Resistant Polymer Machinery Grouts
Standard Test Methods for Compressive Creep of Chemical-Resistant Polymer Machinery Grouts
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 These test methods provide a means of measuring the total compressive deflection of chemical-resistant, machinery-grout materials under a sustained load at the test temperature. Test stress and temperature can be selected to simulate anticipated use conditions. For the purposes of these tests, creep is considered to be the compressive deflection in inches per inch, which occurs after the initial loading of the specimen at laboratory temperature. The results do not necessarily correlate for different specimen thicknesses. No correlation has been established to actual-use conditions.
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover a quantitative, comparative test for compressive creep of chemical-resistant grouting materials under a sustained load at a test temperature. Constant load is maintained using a bolt and spring washers. Measurements are made at laboratory temperature after exposure periods at the selected test temperature.
1.2 Test Method A outlines the molding techniques for an unbonded test specimen. Test Method B covers the molding techniques for a bonded test specimen.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1181 − 00 (Reapproved 2012)
Standard Test Methods for
Compressive Creep of Chemical-Resistant Polymer
Machinery Grouts
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1181; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope grout materials under a sustained load at the test temperature.
Test stress and temperature can be selected to simulate antici-
1.1 These test methods cover a quantitative, comparative
pated use conditions. For the purposes of these tests, creep is
test for compressive creep of chemical-resistant grouting
considered to be the compressive deflection in inches per inch,
materials under a sustained load at a test temperature. Constant
which occurs after the initial loading of the specimen at
load is maintained using a bolt and spring washers. Measure-
laboratory temperature. The results do not necessarily corre-
ments are made at laboratory temperature after exposure
late for different specimen thicknesses. No correlation has been
periods at the selected test temperature.
established to actual-use conditions.
1.2 Test Method A outlines the molding techniques for an
unbonded test specimen. Test Method B covers the molding
5. Apparatus
techniques for a bonded test specimen.
5.1 Steel Loading Plates—Steel plates, as described, are
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
used for loading the grout during the test. They may, also, be
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
part of the mold used to cast the grout specimen.
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
5.1.1 Two steel plates are required for each test specimen.
and are not considered standard.
The plates shall be 4 ⁄4 to 5 in. (11 to 13 cm) square by 1 in. (25
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
mm) thick. A1 ⁄8-in. (30-mm) diameter hole shall be drilled in
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
the center of the plates. The edges of the plates and holes shall
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
be deburred.
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
5.1.2 One of the steel plates shall have four ⁄4-in. (6-mm)
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
measuring holes (one in each corner) with the center ⁄2 in. (13
mm) in from each edge.
2. Referenced Documents
5.2 BoltAssembly—A1-in.(24-mm)diameterby7.5in.(19
2.1 ASTM Standards:
cm) long, high-strength steel bolt, and nut, flat washers, and
C904 Terminology Relating to Chemical-Resistant Nonme-
spring washers are used to maintain the test load.
tallic Materials
5.3 Belleville Spring Washers—Four washers are required
3. Terminology
for each test. These shall be high carbon steel with dimensions
1 1
of 1 ⁄8 by 2 ⁄4 in. (5.7 by 6.0 cm) outside diameter by 0.159-in.
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in these test
(4.0-mm) thickness, with 0.039-in. (1.0-mm) dish. These
methods, see Terminology C904.
washers will have an approximate spring rate of 153 000 lb/in.
4. Significance and Use (27 300 kg/cm) and a rated load of 5793 lb (2630 kg) when
flattened.
4.1 These test methods provide a means of measuring the
total compressive deflection of chemical-resistant, machinery- 5.4 Grout Mold, suitable to cast the 4-in. (10-cm) diameter
by 2 6 0.1 in. (5 cm) thick grout specimen with a 1 ⁄8-in.
diameter center hole as shown in Fig. 1. The faces must be
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
parallel to within 0.030 in. (0.75 mm) over the 4-in. diameter
ConcreteandConcreteAggregatesandarethedirectresponsibilityofSubcommittee
C09.41 on Hydraulic Cement Grouts.
specimen contact area (see 5.3). The mold may utilize the steel
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2012. Published September 2012. Originally
loading plates.
approved in 1991. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as C1181 – 00 (2005).
5.4.1 For the bonded method, the plates are used as mold
DOI: 10.1520/C1181-00R12.
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or end plates.
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
5.5 Compression Machine or Apparatus , capable of apply-
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. ing the test load to within 62.0 %.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
C1181 − 00 (2012)
8.1.2 Test Method A— Using an indicating caliper, measure
the thickness of the specimen in four places around the
circumference to the nearest 0.001 in. Record the average of
the measurements as the specimen thickness. The variation in
the four measurements shall not exceed 0.060 in. (1.5 mm).
8.1.3 Test Method B— Using an indicating caliper, measure
the distance between the two plates at four places around the
circumference to the nearest 0.001 in. Record the average of
the measurements as the specimen thickness. The variation in
the four measurements shall not exceed 0.060 in. (1.5 mm).
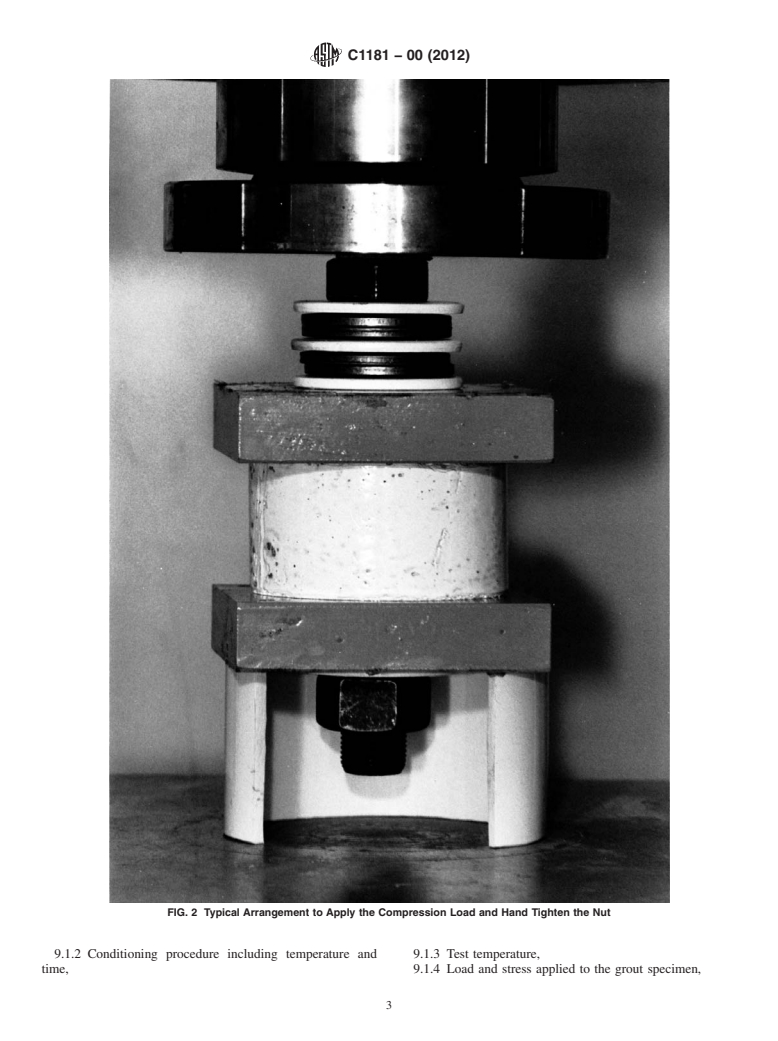
8.2 Assemble the testing apparatus as follows:
8.2.1 Pass the bolt through the assembly consisting of a flat
washer, two nested spring washers, a second flat washer, two
FIG. 1 Test Specimen
more nested spring washers, a third flat washer, the bottom
plate, the grout specimen, the top plate, a fourth flat washer,
and a nut.
5.6 Depth Micrometer, readable to 0.0001 in. (2.5 µ) with
adjustable shaft length capable of reading approximately 3-in.
8.3 Calculate the load required to produce the test stress on
(7.6-cm) depth.
the specimen using the following formula:
5.7 Indicating Caliper, readable to 0.001 in. (25 µ).
πD
L 5 S 2 A (1)
S
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.