ASTM D4266-96
(Test Method)Standard Test Methods for Precoat Capacity of Powdered Ion-Exchange Resins
Standard Test Methods for Precoat Capacity of Powdered Ion-Exchange Resins
SCOPE
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the operating ion-exchange capacity of both powdered cation-exchange resins (hydrogen form) and powdered anion-exchange resins (hydroxide form). These test methods are intended for use in testing new powdered ion-exchange resins when used for the treatment of water. The following two test methods are included: SectionsTest Method A-Operating Capacity, Anion-Exchange Resin, Hydroxide Form7-15 Test Method B-Operating Capacity, Cation-Exchange Resin, Hydrogen Form16-24
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: D 4266 – 96
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Test Methods for
1
Precoat Capacity of Powdered Ion-Exchange Resins
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 4266; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 3.1.1 powdered ion-exchange material,, n—an ion-
exchange resin that has undergone post-manufacturing size
1.1 These test methods cover the determination of the
reduction to less than 300 μm.
operating ion-exchange capacity of both powdered cation-
3.1.2 resin dosage,, n—the weight of mixed resin applied
exchange resins (hydrogen form) and powdered anion-
per unit area of precoatable filter surface. This is expressed as
exchange resins (hydroxide form). These test methods are
dry pounds per square foot.
intended for use in testing new powdered ion-exchange resins
3.1.3 resin floc,, n—that voluminous aggregate formed
when used for the treatment of water. The following two test
when powdered anion-exchange resin and powdered cation-
methods are included:
exchange resin are slurried together in an aqueous suspension.
3.1.4 resin ratio,, n—the ratio of the weights of powdered
Sections
cation-exchange resin to powdered anion-exchange resin used
Test Method A—Operating Capacity, Anion-Exchange 7to15
to prepare a resin slurry. If not otherwise indicated, it is
Resin, Hydroxide Form.
understood to be the ratio of the dry resin weights.
Test Method B—Operating Capacity, Cation-Exchange 16 to 24
3.2 Definitions—For definitions of other terms used in these
Resin, Hydrogen Form.
test methods, refer to Terminology D 1129.
1.2 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
standard. The inch-pound units given in parentheses are for
4. Significance and Use
information only.
4.1 The salt removal capacity of a powdered resin precoat is
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
limited by the capacity of either the anion-exchange resin or
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
the cation-exchange resin contained in it. Applications include
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
condensate polishing in fossil-fueled electric generating plants,
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
as well as condensate polishing, spent fuel pool water treat-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
ment, reactor water treatment, and low-level radioactive liquid
2. Referenced Documents
waste treatment in nuclear-powered electric generating plants.
4.2 By determining the ion-exchange capacity profile of
2.1 ASTM Standards:
either a cation exchange resin or an anion-exchange resin
D 1125 Test Methods for Electrical Conductivity and Re-
2
(capacity expended per unit of time under specific conditions),
sistivity of Water
2
it is possible to estimate runlength and remaining capacity
D 1129 Terminology Relating to Water
2
when treating a liquid of the same makeup. Although they
D 1193 Specification for Reagent Water
cannot accurately predict performance during condenser leaks,
D 2687 Practices for Sampling Particulate Ion-Exchange
3
these test methods are useful for determining operating capaci-
Materials
ties as measured under the test conditions used.
D 4456 Test Methods for Physical and Chemical Properties
3
4.3 These test methods may be used to monitor the perfor-
of Powdered Ion-Exchange Resins
mance of either powdered anion-exchange resin or powdered
E 200 Practice for Preparation, Standardization, and Storage
4
cation-exchange resin. The total capacity of either resin de-
of Standard and Reagent Solutions for Chemical Analysis
pends primarily upon the number density of ion-exchange sites
3. Terminology
within the resin. The operating capacity is a function of the
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
total capacity, degree of conversion to the desired ionic form
when received, and properties of the resin and the system that
affect ion exchange kinetics.
1
These test methods are under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D-19 on
Water and are the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D19.08 on Membranes and
5. Purity of Reagents
Ion-Exchange Materials.
Current edition approved July 10, 1996. Published November 1996. Originally
5.1 Reagent grade chemicals shall be used in all tests.
e1
published as D 4266 – 83. Last previous edition D 4266 – 83 (1990) .
Unless otherwise indicated, i
...







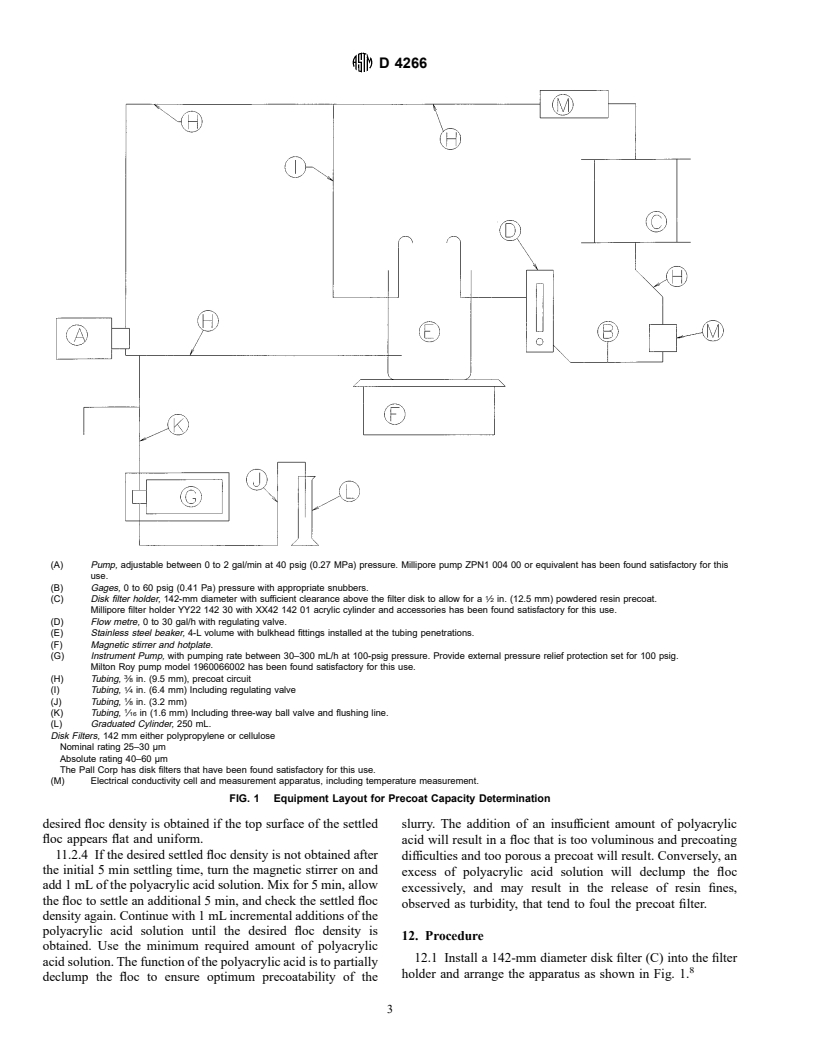
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.