ASTM D5103-07(2018)
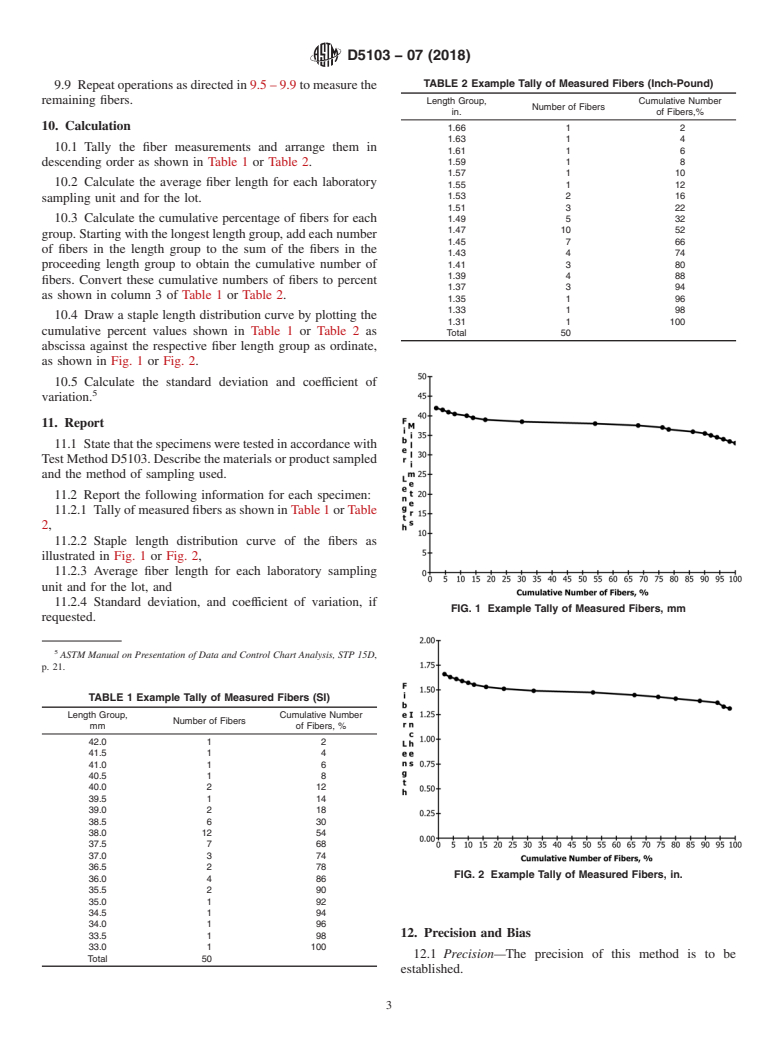
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Length and Length Distribution of Manufactured Staple Fibers (Single-Fiber Test)
Standard Test Method for Length and Length Distribution of Manufactured Staple Fibers (Single-Fiber Test)
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 This test method is used for research, development, quality control, product specifications, and may be used for acceptance testing of commercial shipments of textile fibers. However, caution is advised since information on between-laboratory precision is lacking. Comparative tests as directed in 5.1.1 may be advisable.
5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance between reported test results for two laboratories (or more), comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical assistance. As a minimum, test samples that are as homogenous as possible, drawn from the material from which the disparate test results were obtained, and randomly assigned in equal numbers to each laboratory for testing. The test results from the two laboratories should be compared using a statistical test for upaired data, at a probability level chosen prior to the testing series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and corrected, or future test results for that material must be adjusted in consideration of the known bias.
5.2 This test method provides objective measurements for determining the average fiber length and length distribution in a sample of fiber.
5.3 The staple length diagram of a fiber sample can be used to determine the relative number of fibers above and below a specified length. If a fiber is too long, it will not process well in spinning, and if there is a preponderance of short fibers, the yarn might have lower than normal breaking strength.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of average staple length and staple length distribution of both manufactured and natural fibers by manually measuring single fiber lengths. This test method is also used to measure the length of fibers removed from a staple yarn, but such a measurement may not represent the fiber's staple length, as manufactured.
1.2 Because this test method requires measuring the length of only 50 fibers, it is not suitable for use in determining the number of long fibers that occur infrequently in a sample.
Note 1: For determination for overlength fibers, refer to Test Method D3513.
Note 2: For methods covering the determination of the average length and length distribution of natural fibers, refer to the following methods: for cotton, Test Method D1440, and Test Method D1447, for wool, Test Method D519, Test Method D1234, and Test Method D1575.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: D5103 − 07 (Reapproved 2018)
Standard Test Method for
Length and Length Distribution of Manufactured Staple
Fibers (Single-Fiber Test)
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D5103; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope D1440Test Method for Length and Length Distribution of
Cotton Fibers (Array Method)
1.1 This test method covers the determination of average
D1447Test Method for Length and Length Uniformity of
staple length and staple length distribution of both manufac-
Cotton Fibers by Photoelectric Measurement
tured and natural fibers by manually measuring single fiber
D1575Test Method for Fiber Length of Wool in Scoured
lengths. This test method is also used to measure the length of
Wool and in Card Sliver
fibers removed from a staple yarn, but such a measurement
D1776Practice for Conditioning and Testing Textiles
may not represent the fiber’s staple length, as manufactured.
D2258Practice for Sampling Yarn for Testing
1.2 Because this test method requires measuring the length
D3333Practice for Sampling Manufactured Staple Fibers,
of only 50 fibers, it is not suitable for use in determining the
Sliver, or Tow for Testing
number of long fibers that occur infrequently in a sample.
D3513Test Method for Overlength Fiber Content of Manu-
factured Staple Fiber
NOTE 1—For determination for overlength fibers, refer to Test Method
D3513.
D4849Terminology Related to Yarns and Fibers
NOTE2—Formethodscoveringthedeterminationoftheaveragelength
and length distribution of natural fibers, refer to the following methods:
3. Terminology
for cotton, Test Method D1440, and Test Method D1447, for wool, Test
3.1 For all terminology relating to D13.58, Yarns and
Method D519, Test Method D1234, and Test Method D1575.
Fibers, refer to Terminology D4849.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.1 The following terms are relevant to this standard:
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
length distribution, velveteen.
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
3.2 For all other terminology related to textiles, see Termi-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
nology D123.
1.4 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- 4. Summary of Test Method
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
4.1 Eachfibertobetestedisgrippedatthetipswithforceps,
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
fully extended without stretching, and measured. The average
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
fiber length of the measured fibers is calculated and the length
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
distribution curve is plotted.
2. Referenced Documents
5. Significance and Use
2.1 ASTM Standards:
5.1 This test method is used for research, development,
D123Terminology Relating to Textiles
quality control, product specifications, and may be used for
D519Test Method for Length of Fiber in Wool Top
acceptance testing of commercial shipments of textile fibers.
D1234Test Method of Sampling and Testing Staple Length
However, caution is advised since information on between-
of Grease Wool
laboratoryprecisionislacking.Comparativetestsasdirectedin
5.1.1 may be advisable.
ThistestmethodisunderthejurisdictionofASTMCommitteeD13onTextiles
5.1.1 If there are differences of practical significance be-
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D13.58 on Yarns and Fibers
tween reported test results for two laboratories (or more),
Current edition approved July 1, 2018. Published August 2012. Originally
comparative tests should be performed to determine if there is
approved in 1990. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as D5103–07(2012).
DOI: 10.1520/D5103-07R18.
a statistical bias between them, using competent statistical
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
assistance.Asaminimum,testsamplesthatareashomogenous
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
as possible, drawn from the material from which the disparate
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. test results were obtained, and randomly assigned in equal
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D5103 − 07 (2018)
numberstoeachlaboratoryfortesting.Thetestresultsfromthe shipping container in the lot sample. If differing numbers of
two laboratories should be compared using a statistical test for laboratory sampling units are to be taken from shipping
upaired data, at a probability level chosen prior to the testing containers in the lot sample, determine at random which
series. If a bias is found, either its cause must be found and shippingcontainersaretohaveeachnumberoflaboratoryunits
corrected, or future test results for that material must be drawn.
adjusted in consideration of the known bias. 7.2.1 For Staple Fiber—Take 50-g samples from laboratory
units.
5.2 This test method provides objective measurements for
7.2.2 For Sliver (or Top) or Tow—Take 1 m from the
determining the average fiber length and length distribution in
leading end which has a clean, uniform appearance.
a sample of fiber.
7.2.3 For Yarns—Prepare at least a 50-m skein from each
5.3 The staple length diagram of a fiber sample can be used
package.
to determine the relative number of fibers above and below a
7.3 Test Specimens—From each laboratory sampling unit,
specified length. If a fiber is too long, it will not process well
take ten specimens at random. If the standard deviation
in spinning, and if there is a preponderance of short fibers, the
determined for the ten specimens is more than a value agreed
yarn might have lower than normal breaking strength.
upon between the purchaser and supplier, continue testing in
groups of ten specimens from the same laboratory sampling
6. Apparatus
unit until the standard deviation for all specimens tested is not
6.1 Test Board, covered with suitable material, for example,
more than the agreed to value or, by agreement, stop testing
velveteen, of contrasting color to that of the fiber and at least
after a specified number.
10 mm ( ⁄2 in.) longer than the longest fiber to be measured.
7.3.1 Carefully remove twist before taking specimens from
6.2 Precision Scale, graduated with 1.0-mm (0.02-in.) divi-
yarn. Using tweezers and grasping the specimens at the ends,
sions.
gently remove the required number of specimens from the
laboratory sampling units for testing. In some cases, if speci-
6.3 Illuminated Magnifier, with a 3×–10× lens equipped
mens are not to be tested immediately, place them on an
with illumi
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.