ASTM D1835-11
(Specification)Standard Specification for Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
Standard Specification for Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
ABSTRACT
This specification covers liquefied petroleum gases consisting of propane, propene (propylene), butane, and mixtures of these materials. The products are intended for use as domestic, commercial and industrial heating, and engine fuels. Care must be taken to in sampling of the liquefied gases for test results to be significant. All four types of liquefied petroleum gases covered by this specification should conform to the specified requirements for vapor pressure, volatile residue, residue matter, relative density, and corrosion.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers those products commonly referred to as liquefied petroleum gases, consisting of propane, propene (propylene), butane, and mixtures of these materials. Four basic types of liquefied petroleum gases are provided to cover the common use applications.
1.2 This specification is applicable to products intended for use as domestic, commercial and industrial heating, and engine fuels.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for information only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D1835 −11
StandardSpecification for
1
Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1835; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* D2163 Test Method for Analysis of Liquefied Petroleum
(LP) Gases and Propene Concentrates by Gas Chromatog-
1.1 This specification covers those products commonly
raphy
referred to as liquefied petroleum gases, consisting of propane,
D2420 Test Method for Hydrogen Sulfide in Liquefied
propene (propylene), butane, and mixtures of these materials.
Petroleum (LP) Gases (Lead Acetate Method)
Four basic types of liquefied petroleum gases are provided to
D2598 Practice for Calculation of Certain Physical Proper-
cover the common use applications.
ties of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases from Composi-
1.2 This specification is applicable to products intended for
tional Analysis
use as domestic, commercial and industrial heating, and engine
D2713 Test Method for Dryness of Propane (Valve Freeze
fuels.
Method)
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as D2784 Test Method for Sulfur in Liquefied Petroleum Gases
(Oxy-Hydrogen Burner or Lamp)
standard. The values given in parentheses are provided for
information only. D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Float-
ing Piston Cylinder
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D6667 Test Method for Determination of Total Volatile
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
Sulfur in Gaseous Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Gases by Ultraviolet Fluorescence
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
D6897 Test Method for Vapor Pressure of Liquefied Petro-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
leum Gases (LPG) (Expansion Method)
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.2 Gas Processors Association Standard:
2
2.1 ASTM Standards: GPA Standard 2140 Liquefied Petroleum Gas Specifications
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP)
and Test Methods
Gases, Manual Method
D1267 Test Method for Gage Vapor Pressure of Liquefied 3. Terminology
Petroleum (LP) Gases (LP-Gas Method)
3.1 Definitions:
D1657 Test Method for Density or Relative Density of Light
3.1.1 commercial butane, n—a hydrocarbon product for use
Hydrocarbons by Pressure Hydrometer
where low volatility is required.
D1837 Test Method for Volatility of Liquefied Petroleum
3.1.2 commercial PB mixtures, n—mixtures of propane and
(LP) Gases
butane for use where intermediate volatility is required.
D1838 TestMethodforCopperStripCorrosionbyLiquefied
3.1.3 commercial propane, n—a hydrocarbon product for
Petroleum (LP) Gases
use where high volatility is required. Commercial propane is
D2158 Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum
suitable for certain low severity internal combustion engine
(LP) Gases
applications.
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on
3.1.4 special-duty propane, n—a product composed chiefly
Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
of propane which exhibits superior antiknock characteristics
D02.H0 on Liquefied Petroleum Gas.
and was specifically developed for use as fuel in spark ignition
Current edition approved May 1, 2011. Published May 2011. Originally
approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D1835–05. DOI: internal combustion engines.
10.1520/D1835–11.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
3
Available from Gas ProcessorsAssociation, 6526 E. 60th St.,Tulsa, OK 74145.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. www.gasprocessors.com
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
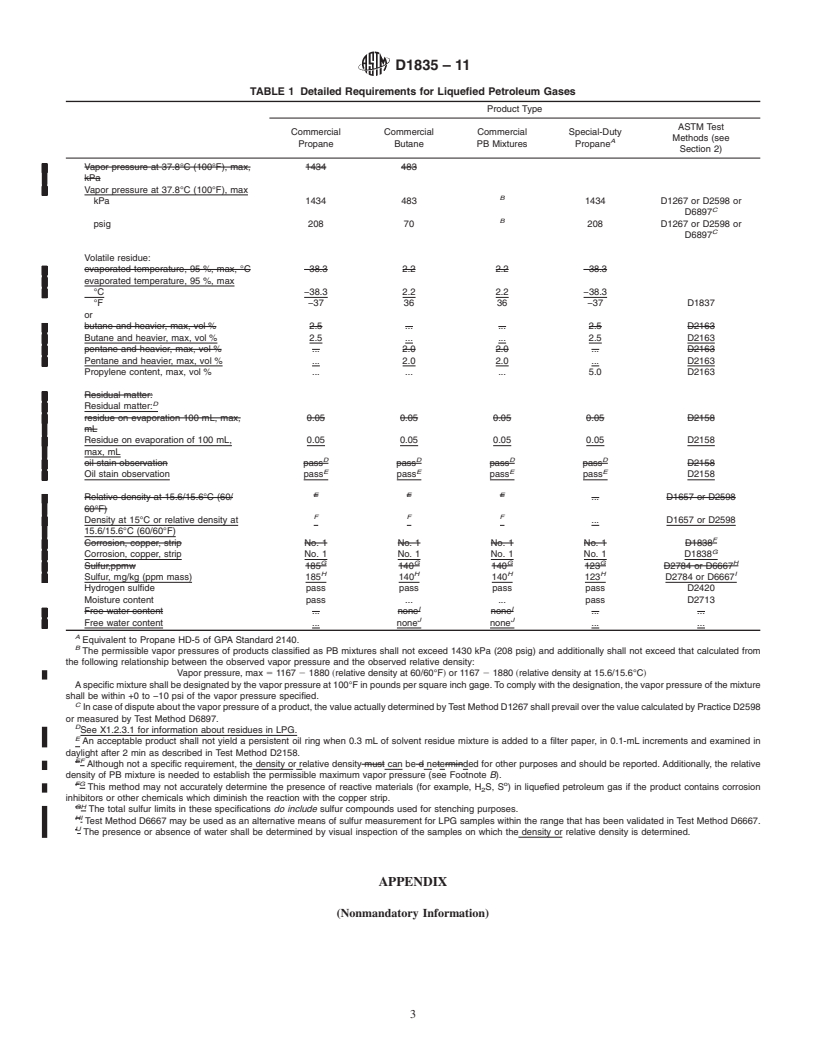
D1835−11
TABLE 1 Detailed Requirements for Liquefied Petroleum Gases
Product Type
ASTM Test
Commercial Commercial Commercial Special-Duty
Methods (see
A
Propane Butane PB Mixtures Propane
Section 2)
Vapor pressure at 37.8°C (100°F), max
B
kPa 1434 483 1434 D1267 or D2598 or
C
D6897
B
psig 208 70 208 D1267 or D2598 or
C
D6897
Volatile residue:
evaporated temperature, 95 %, max
°C −38.3 2.2 2.2 −38.3
°F −37 36 36 −37 D1837
or
Butane and heavier, max, vol % 2.5 . . 2.5 D2163
Pentane and heavier, max, vol % . 2.0 2.0 . D2163
Propylene content, max, vol % . .
...
This document is not anASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of anASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation:D1835–05 Designation: D1835 – 11
Standard Specification for
1
Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D1835; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This specification covers those products commonly referred to as liquefied petroleum gases, consisting of propane, propene
(propylene), butane, and mixtures of these materials. Four basic types of liquefied petroleum gases are provided to cover the
common use applications.
1.2 This specification is applicable to products intended for use as domestic, commercial and industrial heating, and engine
fuels.
1.3 ThevaluesstatedinSIunitsaretoberegardedasthestandard.Thevaluesgiveninparenthesesareprovidedforinformation
only.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory
limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D1265 Practice for Sampling Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases, Manual Method
D1267 Test Method for Gage Vapor Pressure of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases (LP-Gas Method)
D1657 Test Method for Density or Relative Density of Light Hydrocarbons by Pressure Hydrometer
D1837 Test Method for Volatility of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
D1838 Test Method for Copper Strip Corrosion by Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
D2158 Test Method for Residues in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases
D2163 Test Method for Analysis of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases and Propene Concentrates by Gas Chromatography
D2420 Test Method for Hydrogen Sulfide in Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases (Lead Acetate Method)
D2598 Practice for Calculation of Certain Physical Properties of Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases from CompositionalAnalysis
D2713 Test Method for Dryness of Propane (Valve Freeze Method)
D2784 Test Method for Sulfur in Liquefied Petroleum Gases (Oxy-Hydrogen Burner or Lamp)
D3700 Practice for Obtaining LPG Samples Using a Floating Piston Cylinder
D6667 Test Method for Determination of Total Volatile Sulfur in Gaseous Hydrocarbons and Liquefied Petroleum Gases by
Ultraviolet Fluorescence
D6897 Test Method for Vapor Pressure of Liquefied Petroleum Gases (LPG) (Expansion Method)
3
2.2 Other Document:Gas Processors Association Standard:
3
GPA Standard 2140 Liquefied Petroleum Gas Specifications and Test Methods
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 commercial butanecommercial butane, n—a hydrocarbon product for use where low volatility is required.
3.1.2 commercial PB mixturescommercial PB mixtures, n—mixtures of propane and butane for use where intermediate
volatility is required.
3.1.3 commercial propanecommercialpropane, n—ahydrocarbonproductforusewherehighvolatilityisrequired.Commercial
1
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D02 on Petroleum Products and Lubricants and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D02.H0
on Liquefied Petroleum Gas.
Current edition approved Apr. 1, 2005. Published April 2005. Originally approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2003 as D1835–03a.
Current edition approved May 1, 2011. Published May 2011. Originally approved in 1961. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D1835–05. DOI: 10.1520/D1835–11.
2
For referencedASTM standards, visit theASTM website, www.astm.org, or contactASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Gas Processors Assn.,Association, 6526 E. 60th St., Tulsa, OK 74145. www.gasprocessors.com
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
D1835 – 11
propane is suitable for certain low severity internal combustion engine applications.
3.1.4special-duty propane—a high-quality product composed chiefly of propane, which exhibits superior antiknock character-
istics when used as an internal combustion engine fuel.
3.1.4 special-duty propane, n—a product composed chiefly of propane which exhibits superior antiknock c
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.