ASTM C186-05
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic Cement
Standard Test Method for Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic Cement
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
The purpose of this test is to determine if the hydraulic cement under test meets the heat of hydration requirement of the applicable hydraulic cement specification.
This test may also be used for research purposes when it is desired to determine the heat of hydration of hydraulic cement at any age.
Note 1—When tests are performed for research purposes, useful additional information can be obtained by determining fineness, chemical and compound compositions.
Determination of the heat of hydration of hydraulic cements provides information that is helpful for calculating temperature rise in mass concrete.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the heat of hydration of a hydraulic cement by measuring the heat of solution of the dry cement and the heat of solution of a separate portion of the cement that has been partially hydrated for 7 and for 28 days, the difference between these values being the heat of hydration for the respective hydrating period.
1.2 The results of this test method may be inaccurate if some of the components of the hydraulic cement are insoluble in the nitric acid/hydrofluoric acid solution.
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.4 Values in SI units shall be obtained by measurement in SI units or by appropriate conversion, using the Rules for Conversion and Rounding given in Standard IEEE/ASTM SI 10, or measurements made in other units.
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability or regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C186 − 05
StandardTest Method for
1
Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic Cement
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C186; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope Testing of Hydraulic Cements
E11 Specification for Woven Wire Test Sieve Cloth and Test
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the heat of
Sieves
hydration of a hydraulic cement by measuring the heat of
IEEE/ASTM SI 10 Standard for Use of the International
solutionofthedrycementandtheheatofsolutionofaseparate
System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System
portion of the cement that has been partially hydrated for 7 and
for 28 days, the difference between these values being the heat
3. Significance and Use
of hydration for the respective hydrating period.
3.1 The purpose of this test is to determine if the hydraulic
1.2 The results of this test method may be inaccurate if
cement under test meets the heat of hydration requirement of
some of the components of the hydraulic cement are insoluble
the applicable hydraulic cement specification.
in the nitric acid/hydrofluoric acid solution.
3.2 This test may also be used for research purposes when it
1.3 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the
is desired to determine the heat of hydration of hydraulic
standard. The values given in parentheses are for information
cement at any age.
only.
NOTE 1—When tests are performed for research purposes, useful
1.4 Values in SI units shall be obtained by measurement in
additional information can be obtained by determining fineness, chemical
SI units or by appropriate conversion, using the Rules for
and compound compositions.
Conversion and Rounding given in Standard IEEE/ASTM SI
3.3 Determination of the heat of hydration of hydraulic
10, or measurements made in other units.
cements provides information that is helpful for calculating
1.5 This standard does not purport to address all of the
temperature rise in mass concrete.
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
4. Apparatus
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
4.1 Calorimetric Apparatus:
bility or regulatory limitations prior to use.
4.1.1 Calorimeter—The calorimeter, such as that illustrated
2. Referenced Documents inFig.1shallconsistofa0.5-L(1-pt),wide-mouthvacuumjar,
2 withcorkstopper,orothersuitablenon-reactivestopperheldin
2.1 ASTM Standards:
a suitably insulated container (See 4.1.2) to keep the vacuum
C109/C109M Test Method for Compressive Strength of
jar in position and to protect the jar from undue temperature
Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube
fluctuations. The vacuum jar shall be coated on the interior
Specimens)
with a material resistant to hydrofluoric acid, such as a baked
C114 Test Methods for Chemical Analysis of Hydraulic
phenolic resin, a baked vinyl chloride acetate resin, or bees-
Cement
wax. The acid-resistant coating shall be intact and free of
C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
cracksatalltimes;itshallbeexaminedfrequentlyandrenewed
for Test Methods for Construction Materials
whenever necessary. As another means of protecting the
C1005 Specification for Reference Masses and Devices for
vacuum jar, a plastic liner of suitable size may be used instead
Determining Mass and Volume for Use in the Physical
of coating the interior of the jar.The contents of the vacuum jar
shall not change more than 0.001 °C/min per degree difference
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee C01 on Cement
from room temperature when filled with 425 g of the acid
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C01.26 on Heat of Hydration.
specified in 6.2, stoppered, and allowed to stand unstirred for
Current edition approved July 1, 2005. Published August 2005. Originally
30 min. The temperature for this check shall approximate the
approved in 1944. Last previous edition approved in 1998 as C186 – 98. DOI:
10.1520/C0186-05.
starting temperatures to be used in making the determination.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
4.1.2 Insulated Container—The container shall have an
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
insulatinglayerofamaterialsuchasnon-reactivefoam,cotton,
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. or fiber-glass, which shall be at least 25 mm (1 in.) in thickness
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 1
...







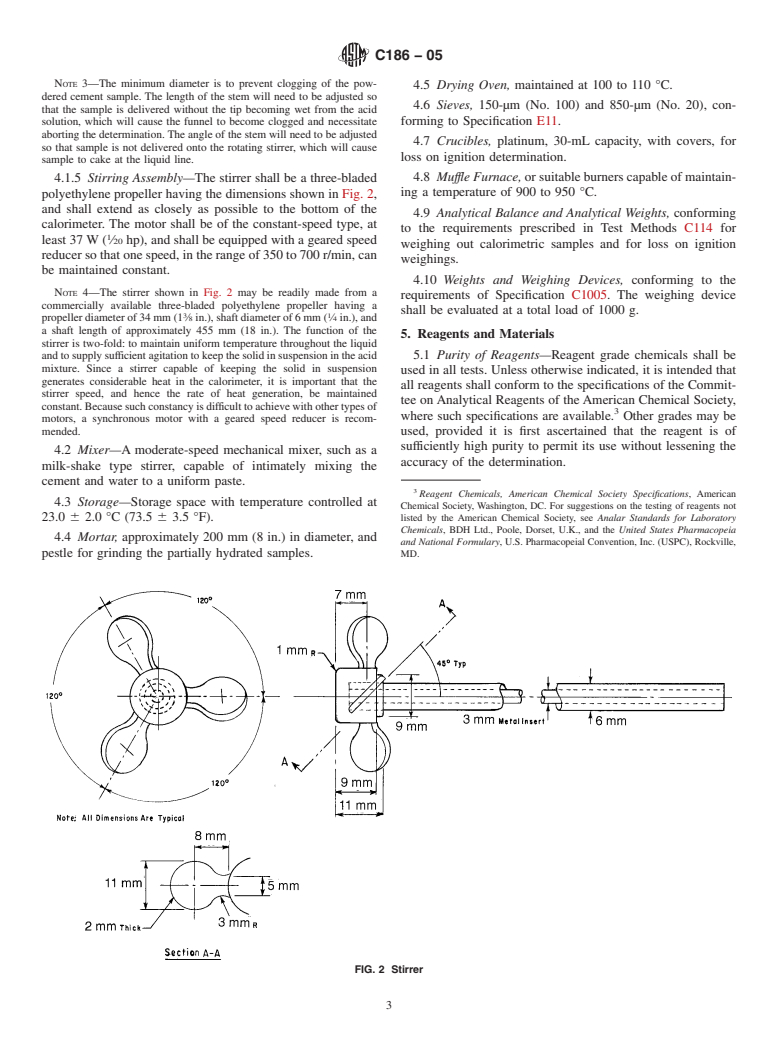
Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.