ASTM C779/C779M-19
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
Standard Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
4.1 The three test methods provide simulated abrasion conditions, which can be used to evaluate the effects on abrasion resistance of concrete, concrete materials, and curing or finishing procedures. They may also be used for quality acceptance of products and surface exposed to wear. They are not intended to provide a quantitative measurement of length of service.
4.2 The equipment used by each of these procedures is portable and thus suitable for either laboratory or field testing. The three procedures determine the relative wear of concrete surfaces as follows:
4.2.1 Procedure A—The revolving-disk machine operates by sliding and scuffing of steel disks in conjunction with abrasive grit.
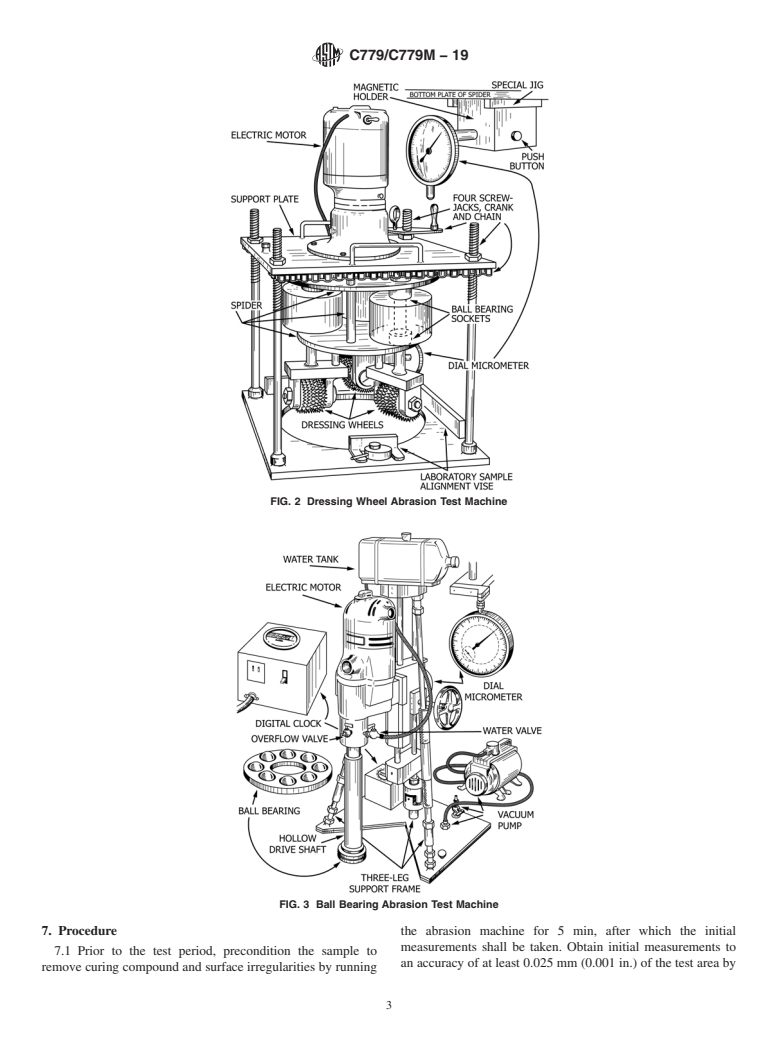
4.2.2 Procedure B—The dressing-wheel machine operates by impact and sliding friction of steel dressing wheels.
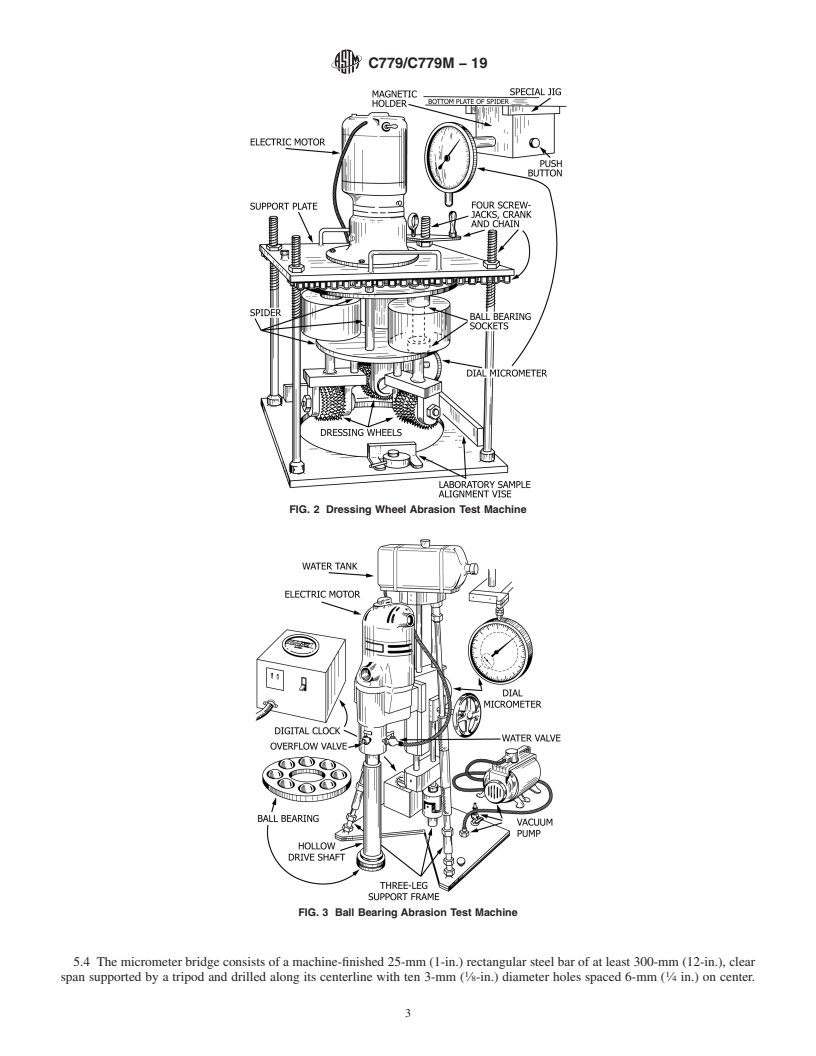
4.2.3 Procedure C—The ball-bearing machine operates by high-contact stresses, impact, and sliding friction from steel balls.
Note 2: Diagrams of three machines meeting these specifications are shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, and Fig. 3.4
FIG. 1 Revolving Disks Abrasion Test Machine
FIG. 2 Dressing Wheel Abrasion Test Machine
FIG. 3 Ball Bearing Abrasion Test Machine
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers three procedures for determining the relative abrasion resistance of horizontal concrete surfaces. The procedures differ in the type and degree of abrasive force they impart, and are intended for use in determining variations in surface properties of concrete affected by mixture proportions, finishing, and surface treatment. They are not intended to provide a quantitative measurement of the length of service that may be expected from a specific surface.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the inch-pound units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall be used independently of each other.
1.3 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes (excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure.2)
Note 1: Other procedures are available for measuring the abrasion resistance of concrete surfaces in addition to the three procedures contained in this test method. Consideration should be given to Test Methods C944/C944M and C418. The test method most closely representing service conditions should be used.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C779/C779M − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C779/C779M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
1.1 This test method covers three procedures for determin-
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
ing the relative abrasion resistance of horizontal concrete
surfaces. The procedures differ in the type and degree of
2. Referenced Documents
abrasive force they impart, and are intended for use in
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
determining variations in surface properties of concrete af-
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Ag-
fected by mixture proportions, finishing, and surface treatment.
gregates
Theyarenotintendedtoprovideaquantitativemeasurementof
C418 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete by
the length of service that may be expected from a specific
Sandblasting
surface.
C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units
for Test Methods for Construction Materials
are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
C944/C944M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Con-
inch-pound units are shown in brackets. The values stated in
crete or Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each
system shall be used independently of each other.
3. Terminology
1.3 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to
that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes
Terminology C125.
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered
4. Significance and Use
as requirements of this standard.
4.1 The three test methods provide simulated abrasion
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
conditions, which can be used to evaluate the effects on
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
abrasion resistance of concrete, concrete materials, and curing
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
or finishing procedures. They may also be used for quality
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
acceptance of products and surface exposed to wear. They are
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
notintendedtoprovideaquantitativemeasurementoflengthof
(Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic
service.
and may cause chemical burns to skin and tissue upon
2
prolonged exposure. )
4.2 The equipment used by each of these procedures is
portable and thus suitable for either laboratory or field testing.
NOTE 1—Other procedures are available for measuring the abrasion
resistance of concrete surfaces in addition to the three procedures The three procedures determine the relative wear of concrete
contained in this test method. Consideration should be given to Test
surfaces as follows:
Methods C944/C944M and C418. The test method most closely repre-
4.2.1 Procedure A—The revolving-disk machine operates
senting service conditions should be used.
by sliding and scuffing of steel disks in conjunction with
1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
abrasive grit.
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
4.2.2 Procedure B—The dressing-wheel machine operates
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
by impact and sliding friction of steel dressing wheels.
4.2.3 Procedure C—The ball-bearing machine operates by
high-contact stresses, impact, and sliding friction from steel
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on
balls.
Concrete and Concrete Aggregatesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee
C09.62 on Abrasion Testing.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2019. Published November 2019. Originally
3
approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 2012 as C779/C779M–12. For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
DOI: 10.1520/C0779_C0779M-19. contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing, Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Annual Book of ASTM Standards,
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C779/C779M − 12 C779/C779M − 19
Standard Test Method for
1
Abrasion Resistance of Horizontal Concrete Surfaces
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C779/C779M; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year
of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.
A superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This test method covers three procedures for determining the relative abrasion resistance of horizontal concrete surfaces.
The procedures differ in the type and degree of abrasive force they impart, and are intended for use in determining variations in
surface properties of concrete affected by mixture proportions, finishing, and surface treatment. They are not intended to provide
a quantitative measurement of the length of service that may be expected from a specific surface.
1.2 The values stated in either SI units or inch-pound units are to be regarded separately as standard. Within the text, the
inch-pound units are shown in brackets. The values stated in each system may not be exact equivalents; therefore, each system shall
be used independently of each other.
1.3 The text of this standard references notes and footnotes that provide explanatory material. These notes and footnotes
(excluding those in tables and figures) shall not be considered as requirements of this standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. (Warning—Fresh hydraulic cementitious mixtures are caustic and may cause
2
chemical burns to skin and tissue upon prolonged exposure. )
NOTE 1—Other procedures are available for measuring the abrasion resistance of concrete surfaces in addition to the three procedures contained in this
test method. Consideration should be given to Test Methods C944C944/C944M and C418. The test method most closely representing service conditions
should be used.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
3
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C125 Terminology Relating to Concrete and Concrete Aggregates
C418 Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete by Sandblasting
C670 Practice for Preparing Precision and Bias Statements for Test Methods for Construction Materials
C944C944/C944M Test Method for Abrasion Resistance of Concrete or Mortar Surfaces by the Rotating-Cutter Method
3. Terminology
3.1 For definitions of terms used in this standard, refer to Terminology C125.
4. Significance and Use
4.1 The three test methods provide simulated abrasion conditions, which can be used to evaluate the effects on abrasion
resistance of concrete, concrete materials, and curing or finishing procedures. They may also be used for quality acceptance of
products and surface exposed to wear. They are not intended to provide a quantitative measurement of length of service.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C09 on Concrete and Concrete Aggregatesand is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C09.62 on
Abrasion Testing.
Current edition approved Dec. 1, 2012Oct. 1, 2019. Published December 2012November 2019. Originally approved in 1974. Last previous edition approved in 20102012
as C779 – 05 (2010).C779/C779M–12. DOI: 10.1520/C0779_C0779M-12.10.1520/C0779_C0779M-19.
2
Section on Safety Precautions, Manual of Aggregate and Concrete Testing,Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.02.
3
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C779/C779M − 19
4.2 The equipment used by each of these procedures i
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.