ASTM D2099-05(2010)e1
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Dynamic Water Resistance of Shoe Upper Leather by the Maeser Water Penetration Tester
Standard Test Method for Dynamic Water Resistance of Shoe Upper Leather by the Maeser Water Penetration Tester
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
This test method is intended to estimate the water resistance of shoe upper leather. The flex imparted to the leather is similar to the flex given the vamp of the shoe in actual wear.
Note 1—There is an indication that this test method cannot be used interchangeably for specification purposes with Test Method D2098.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the dynamic water resistance of shoe upper leather by the Maeser water penetration tester. It is applicable to all types of shoe upper leather. Certain waterproof processes can cause contamination of the stainless steel balls. When this happens, visual inspection is recommended. This test method does not apply to wet blue.
1.2 Initial water penetration and water absorption can be measured by this test method.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
´1
Designation: D2099 − 05(Reapproved 2010)
Standard Test Method for
Dynamic Water Resistance of Shoe Upper Leather by the
Maeser Water Penetration Tester
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D2099; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
´ NOTE—Updated units statement and corrected SI value in 4.2.1 editorially in April 2010.
1. Scope 3. Significance and Use
1.1 This test method covers the determination of the dy- 3.1 This test method is intended to estimate the water
namic water resistance of shoe upper leather by the Maeser resistance of shoe upper leather. The flex imparted to the
water penetration tester. It is applicable to all types of shoe leather is similar to the flex given the vamp of the shoe in
upper leather. Certain waterproof processes can cause contami- actual wear.
nation of the stainless steel balls. When this happens, visual
NOTE 1—There is an indication that this test method cannot be used
inspection is recommended.This test method does not apply to
interchangeably for specification purposes with Test Method D2098.
wet blue.
4. Apparatus
1.2 Initial water penetration and water absorption can be
4.1 Balance, sensitive to 0.01 g.
measured by this test method.
4.2 Maeser Water Penetration Tester, as shown in Fig. 1,or
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
its equivalent. The essential features of the machine are:
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
4.2.1 Specimen Holder, made of two V-shaped clamps with
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
wedges for holding the specimen. The clamps shall be 2.5 6
and are not considered standard.
0.1 in. (63.5 6 2.5 mm) apart, inside measurement, when their
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
tops are in the same horizontal plane. One clamp shall be in a
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
fixed position. The other clamp shall be pivoted as shown in
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Fig. 1 and attached, through a connecting link, to a motor-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
driven eccentric which turns at 90 6 5 r/min. In one rotation of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
the eccentric, the center of the top of the movable clamp shall
move a distance of 1 6 0.05 in. (25.4 6 1.3 mm) below the
2. Referenced Documents
horizontal and return.
2.1 ASTM Standards:
4.2.2 Water Tank, made of copper, stainless steel, or other
D1610 Practice for Conditioning Leather and Leather Prod-
noncorrosive material. It shall be of such a size that it can be
ucts for Testing
placed around the clamps and of such a depth that, when in
D2098 Test Method for Dynamic Water Resistance of Shoe
position for use, the top is 1.25 to 1.5 in. (31.7 to 38.1 mm)
Upper Leather by the Dow Corning Leather Tester
above the lowest point of the flexed clamp.
4.3 Base for the Water Tank, which is removable from
between the machine frame and the water tank.
This test method is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee D31 on Leather
and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D31.03 on Footwear.
4.4 Two systems can be used to determine the number of
Current edition approved April 1, 2010. Published May 2010. Originally
cycles through which the specimen is flexed. One shall be a
approved in 1962. Last previous edition approved in 2005 as D2099–05. DOI:
10.1520/D2099-05R10E01.
mechanical reset counter connected to the movable clamp. The
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
other system shall be electrical and consist of a high and
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
common electrode. The recommended resistance across the
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
the ASTM website. common electrodes is 50 000 Ω. When the resistance falls
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
´1
D2099 − 05 (2010)
FIG. 1 Maeser Water Penetration Tester
FIG. 1 Maeser Water Penetration Tester (continued)
below this value, the relay will be energized. The high 4.5 Initial water penetration is detected by a current leakage
electrode shown is inside the leather specimen in contact with
from the high electrode through the specimen to the common
the steel balls. The common electrode is in a salt solution
electrode in the conducting solution. This causes a thyatron
which is in continuous contact with the specimen during
tube to fire, opening the relay and stopping the machine.
flexing.
´1
D2099 − 05 (2010)
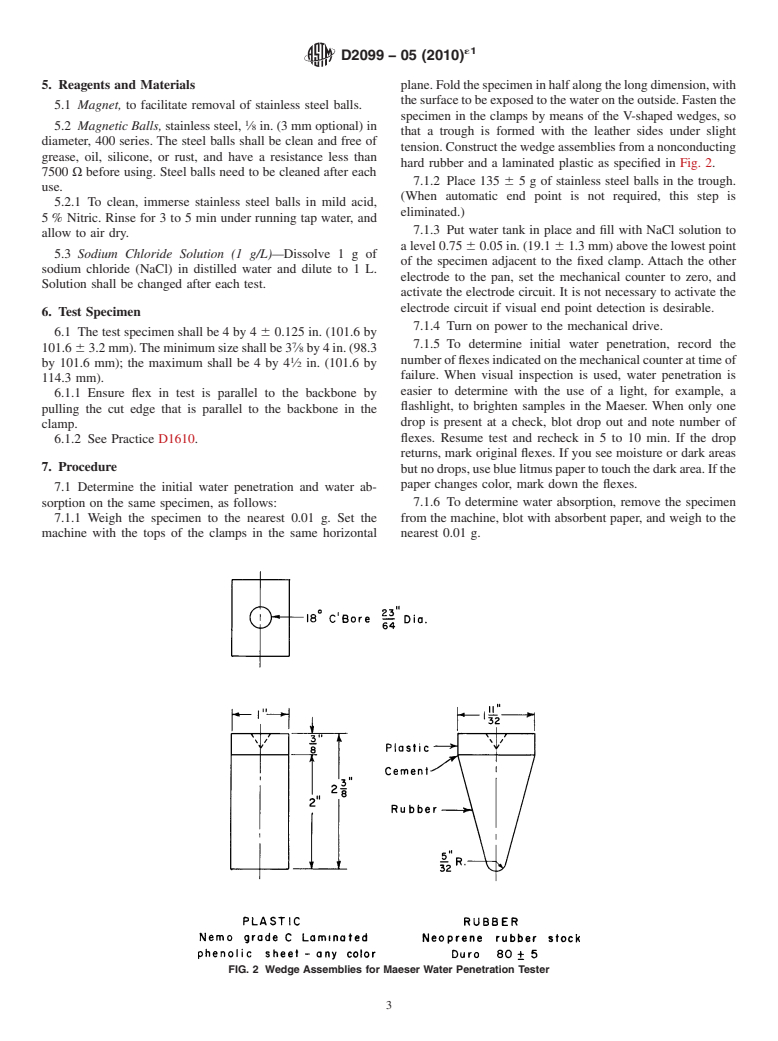
5. Reagents and Materials plane.Foldthespecimeninhalfalongthelongdimension,with
thesurfacetobeexposedtothewaterontheoutside.Fastenthe
5.1 Magnet, to facilitate removal of stainless steel balls.
specimen in the clamps by means of the V-shaped wedges, so
5.2 Magnetic Balls, stainless steel, ⁄8 in. (3 mm optional) in
that a trough is formed with the leather sides under slight
diameter, 400 series. The steel balls shall be clean and free of
tension. Construct the wedge assemblies from a nonconducting
grease, oil, silicone, or rust, and have a resistance less than
hard rubber and a laminated plastic as specified in Fig. 2.
7500Ω before using. Steel balls need to be cleaned after each
7.1.2 Place 135 6 5 g of stainless steel balls in the trough.
use.
(When automatic end point is not required, this step is
5.2.1 To clean, immerse stainless steel balls in mild acid,
eliminated.)
5 % Ni
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.