ASTM C857-95
(Practice)Standard Practice for Minimum Structural Design Loading for Underground Precast Concrete Utility Structures
Standard Practice for Minimum Structural Design Loading for Underground Precast Concrete Utility Structures
SCOPE
1.1 This practice describes the minimum live loads and dead loads to be applied when designing monolithic or sectional precast concrete utility structures. Concrete pipe, box culverts, and material covered in Specification C 478 are excluded from this practice.
Note 1—For additional information see AASHTO Standard Specification for Highway Bridges, Fifteenth Edition.
Note 2—The purchaser is cautioned that he must properly correlate the anticipated loading conditions and the field requirements with the design loads used.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for information only.
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or
withdrawn. Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information.
Designation: C 857 – 95
AMERICAN SOCIETY FOR TESTING AND MATERIALS
100 Barr Harbor Dr., West Conshohocken, PA 19428
Reprinted from the Annual Book of ASTM Standards. Copyright ASTM
Standard Practice for
Minimum Structural Design Loading for Underground
1
Precast Concrete Utility Structures
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C 857; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 4. Design Loads
1.1 This practice describes the minimum live loads and dead 4.1 Roof—The design loads for the roof of any structure at
loads to be applied when designing monolithic or sectional
or below ground level consists of the live loads including
precast concrete utility structures. Concrete pipe, box culverts, impact and dead loads that can develop as a result of earth
and material covered in Specification C 478 are excluded from pressure, hydrostatic pressure, and construction materials such
this practice. as used for roadways and walkways.
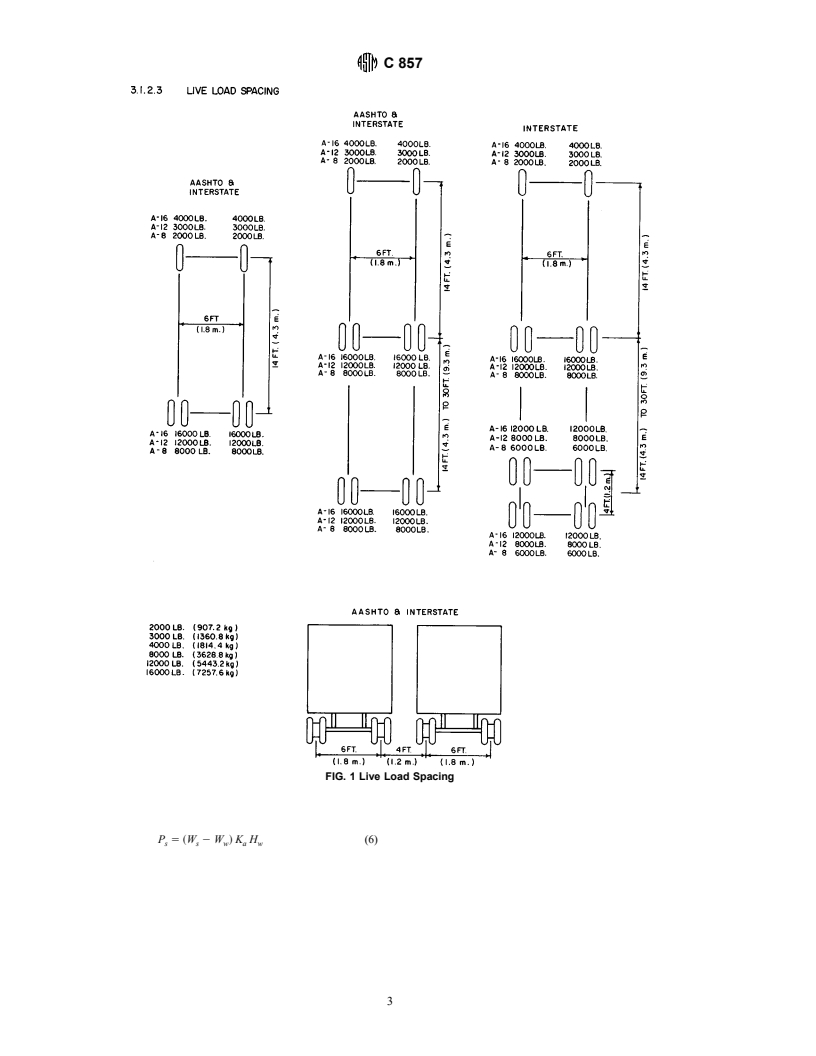
4.1.1 Live Loads—The vehicle and pedestrian load desig-
NOTE 1—For additional information see AASHTO Standard Specifica-
nations are given in Table 1. Live load wheel spacing is shown
tion for Highway Bridges, Fifteenth Edition.
in Fig. 1.
NOTE 2—The purchaser is cautioned that he must properly correlate the
anticipated loading conditions and the field requirements with the design
4.1.2 Impact:
loads used.
4.1.2.1 The live loads A-16, A-12, and A-8 should be
increased as follows to sustain the effect of impact:
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
as the standard. The values given in parentheses are for 4.1.2.2 Live Load Increase:
information only. 0 to 12 in. (0 to 305 mm) below ground level, 30 %
1.3 This standard does not purport to address all of the 13 to 24 in. (330 to 610 mm) below ground level, 20 %
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the 25 to 35 in. (635 to 889 mm) below ground level, 10 %
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro- 36 in. (914 mm) or more below ground level, 0 %
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica- 4.1.3 Dead Loads—Dead loads will consist of the weight of
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
the roof, roadbed, walkways, earth fill, access opening covers,
and any other material that produces a static load.
2. Referenced Documents
4.1.3.1 Recommended unit weights of materials for design
2.1 ASTM Standards:
calculations are as follows:
3 3
C 478 Specification for Precast Reinforced Concrete Man-
Concrete, plain, and reinforced 150 lb/ft (2043 kg/m )
2
3 3
Cast iron 450 lb/ft (7208 kg/m )
hole Sections
3 3
Steel 490 lb/ft (7850 kg/m )
2.2 AASHTO Standard:
3 3
Aluminum 175 lb/ft (2804 kg/m )
3
3 3
Specification for Highway Bridges, Fifteenth Edition
Earth fill (dry) 110 lb/ft (1762 kg/m )
3 3
Macadam 140 lb/ft (2243 kg/m )
3. Terminology
4.1.4 Distribution of Wheel Loads Through Earth Fills:
3.1 Definitions of Terms Specific to This Standard:
4.1.4.1 Wheel loads at ground level should be considered
3.1.1 dead loads—will consist of any other load that can
applied to a wheel load area as indicated in Fig. 2.
affect the design of the structure.
4.1.4.2 Wheel loads should be distributed below ground
3.1.2 live loads—will consist of any moving loads that can
level as a truncated pyramid, as shown in Fig. 3, in which the
affect the design of the structure and their associated impact
top surface is the wheel load area and the distributed load area
and surcharge loads.
is equal to the following:
3.1.3 utility structure—a structure that is used by electric,
DLA 5 ~W 1 1.75 H! ~L 1 1.75 H! (1)
gas, communication, or similar industries.
where:
2 2
DLA 5 distributed load area, ft (m )
1
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C-27 on Precast
W 5 wheel load width, ft (m),
Concrete Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C 27.10on
L 5 wheel load length, ft (m), and
Utility Structures.
Current edition approved Nov. 10, 1995. Published February 1996. Originally
H 5 depth of fill, ft (m).
published as C 857 – 78. Last previous edition C 857 – 87 (1994).
4.1.4.3 When several distributed load areas overlap, the
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.05.
3
total load shall be considered as uniformly distributed over the
Available from American Association of State Highway and Transportation
Officials (AASHTO), 444 N. Capitol St., Washington, DC 20001. area defined by the outside limits of the individual areas as
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C 857
TABLE 1 Vehicle and Pedestrian Load Designations P
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.