ASTM D709-01(2007)
(Specification)Standard Specification for Laminated Thermosetting Materials
Standard Specification for Laminated Thermosetting Materials
ABSTRACT
This specification establishes the manufacture, property requirements, and testing of several grades of laminated thermosetting materials consisting of two or more plies or layers of reinforcing material such as cellulose paper, cotton fabric, glass fabric, and synthetic fiber fabrics, bonded by a thermosetting synthetic resin. These materials are available in the form of sheets, rolled and molded tubes, and molded rods.
SCOPE
1.1 This specification covers laminated thermosetting materials consisting of two or more plies or layers of reinforcing material bonded by a thermosetting synthetic resin. Examples of such reinforcement are cellulose paper, cotton fabric, glass fabric, and synthetic fiber fabrics. These materials are available in the form of sheets, rolled and molded tubes, and molded rods.
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as the standard. Note 1
This specification resembles IEC 60893-3 in title only. The content is significantly different.
The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the test methods described in this specification. This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
General Information
Relations
Standards Content (Sample)
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation:D709 −01(Reapproved 2007) An American National Standard
Standard Specification for
Laminated Thermosetting Materials
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D709; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
This standard has been approved for use by agencies of the Department of Defense.
1. Scope D495 Test Method for High-Voltage, Low-Current, DryArc
Resistance of Solid Electrical Insulation
1.1 This specification covers laminated thermosetting mate-
D621 Specification for Jute Rove and Plied Yarn for Elec-
rials consisting of two or more plies or layers of reinforcing
trical and Packing Purposes (Withdrawn 2000)
material bonded by a thermosetting synthetic resin. Examples
D668 TestMethodsofMeasuringDimensionsofRigidRods
of such reinforcement are cellulose paper, cotton fabric, glass
and Tubes Used for Electrical Insulation
fabric,andsyntheticfiberfabrics.Thesematerialsareavailable
D883 Terminology Relating to Plastics
in the form of sheets, rolled and molded tubes, and molded
D1180 Method of Test for Warpage of Sheet Plastics (With-
rods.
drawn 1988)
1.2 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded
D1711 Terminology Relating to Electrical Insulation
as the standard.
D2303 Test Methods for Liquid-Contaminant, Inclined-
Plane Tracking and Erosion of Insulating Materials
NOTE 1—This specification resembles IEC 60893-3 in title only. The
content is significantly different.
D2304 Test Method for Thermal Endurance of Rigid Elec-
trical Insulating Materials
1.3 The following safety hazards caveat pertains only to the
D3636 Practice for Sampling and Judging Quality of Solid
test methods described in this specification. This standard does
Electrical Insulating Materials
not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any,
D6054 Practice for Conditioning Electrical Insulating Mate-
associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this
rials for Testing
standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices
2.2 IEEE Standards:
and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior
1 General Principles forTemperature Limits in the Rating of
to use.
Electric Equipment
2. Referenced Documents
98 Guide for the Preparation of Test Procedures for the
Thermal Evaluation and Establishment of Temperature
2.1 ASTM Standards:
Indices of Solid Electrical Insulating Materials
D229 Test Methods for Rigid Sheet and Plate Materials
99 Guide for the Preparation of Test Procedures for the
Used for Electrical Insulation
Thermal Evaluation of Insulation Systems for Electric
D257 Test Methods for DC Resistance or Conductance of
Equipment
Insulating Materials
101 Guide for the Statistical Analysis of Thermal Life Test
D348 Test Methods for Rigid Tubes Used for Electrical
Data
Insulation
2.3 NEMA Standards:
D349 Test Methods for Laminated Round Rods Used for
LI 1-1971 Industrial Laminated Thermosetting Products
Electrical Insulation
LI 5-1969 Temperature Indices of Industrial Thermosetting
Laminates
This specification is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D09 on
LI 3-1961 High-Temperature Properties of Industrial Ther-
Electrical and Electronic Insulating Materials and is the direct responsibility of
mosetting Laminates
Subcommittee D09.07 on Flexible and Rigid Insulating Materials.
Current edition approved May 1, 2007. Published June 2007. Originally
approved in 1943. Last previous edition approved in 2001 as D709 – 01. DOI: The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
10.1520/D0709-01R07. www.astm.org.
2 4
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or Available from Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Inc. (IEEE),
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM 445 Hoes Ln., P.O. Box 1331, Piscataway, NJ 08854-1331, http://www.ieee.org.
Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on Available from National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), 1300
the ASTM website. N. 17th St., Suite 1752, Rosslyn, VA 22209, http://www.nema.org.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
D709−01 (2007)
NOTE 4—Molded rods are composed of laminations of impregnated
2.4 Military Specifications:
sheet material molded in cylindrical molds under heat and pressure, and
MIL-P-997 Plastic Material, Laminated, Thermosetting,
then ground to size. Molded rods are of two classes made by winding the
Electric Insulation, Sheets, Glass Cloth, Silicone Resin
impregnated sheet convolutely before molding or by forming strips in the
MIL-P-15035 Plastic Sheet, Laminated, Thermosetting,
molding operation.
Cotton-Fabric-Base, Phenolic-Resin
Machined rods, manufactured from certain grades of sheet material, are
not covered by this specification. In rods machined from sheets, the
MIL-P-15037 Plastic Sheet, Laminated, Thermosetting,
laminations are parallel chords of a circular cross-section. In general, the
Glass-Cloth, Melamine-Resin
properties of these rods conform to those of the grade of sheet stock from
MIL-P-15047 Plastic Material, Laminated Thermosetting
which they are cut. This type of rod may be low in flexural strength when
Sheets, Nylon Fabric Base, Phenolic-Resin
stress is applied perpendicular to the lamination.
MIL-P-18177 Plastic Sheet, Laminated, Thermosetting, NOTE 5—Molded shapes are composed of impregnated sheet materials
cut into various sizes and shapes to fit the contours of a mold, and molded
Glass Fibre Base, Epoxy-Resin
under heat and pressure. In special cases some macerated material is used
MIL-P-22324 Plastic Sheet, Thermosetting, Paper-Base,
in combination with impregnated sheet materials, depending upon the
Epoxy-Resin
design of the piece. The requirements of this specification, particularly
with regard to mechanical properties, cannot be considered as applying to
2.5 Federal Specifications:
molded shapes, except for rectangular and square tubes, since such
L-P-513 Plastic Sheet and Insulation Sheet, Electrical
properties will depend to a considerable extent upon the design of the
(Laminated, Thermosetting, Paper-Base, Phenolic-Resin)
piece.
L-P-509 Plastic Sheet, Rod and Tube, Laminated Thermo-
setting
6. General Requirements
2.6 IEC Standard:
6.1 Materials and Workmanship—Laminated material shall
Publication 60893-3 Specification for Industrial Laminated
be uniform in quality. It shall be free of blisters, wrinkles, or
Sheets Based on Thermosetting Resins for Electrical
cracks and shall be reasonably free of other small defects such
Purposes
as scratches, heat marks, etc., as defined inTerminology D883.
Tubes of any grade having wall thickness greater than ⁄2 in.
3. Terminology
(13 mm) and molded paper-base rods (Grades XX and XXX)
3.1 Definitions—For definitions of terms used in this
having diameters greater than 1 in. (25 mm) may show checks
specification, refer to Terminologies D883 or D1711.
or cracks between the laminations on machined or sawed
edges.
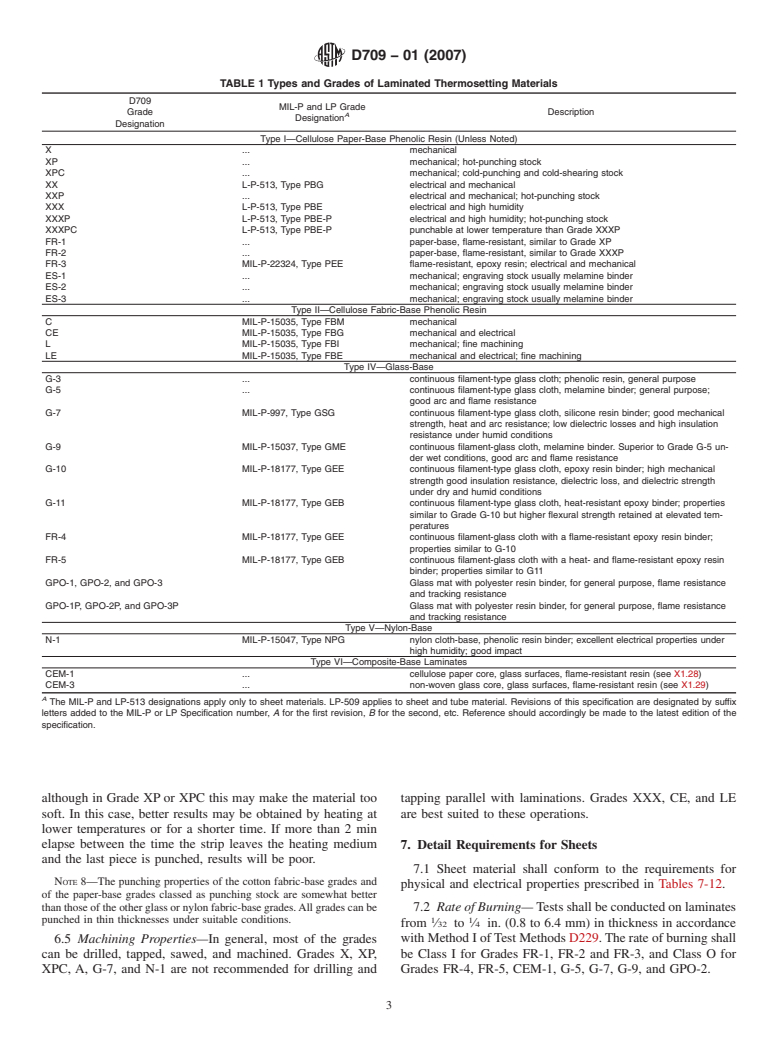
4. Types and Grades
6.2 Finish and Color— Requirements for finish (Note 6)
4.1 Laminated materials covered by this specification are
and color (Note 7) shall be as specified by the purchaser in the
classifiedinaccordancewiththetypesofreinforcementusedin
contract or order.
their manufacture, and the electrical, mechanical, and heat-
NOTE 6—The various forms and grades of laminated thermosetting
resisting characteristics of the finished products (Note 2).
material are available in the finishes shown in Table 3.
NOTE 2—Further descriptive information regarding these various types
NOTE 7—The various types and grades of laminated thermosetting
and grades of laminated thermosetting materials is given in Table 1 and
material are available in the colors shown in Table 4. Where MIL-P
Appendix X1-Appendix X3. Appendix X3 also includes tables covering
specifications are involved, natural color only shall be supplied.
engineering information on other properties of the various grades of
6.3 Warp or Twist— The warp or twist shall not exceed the
laminated thermosetting products that are not included in these specifica-
values prescribed in Table 5.
tion requirements.
6.4 Punching Properties—The grades of material differ in
5. Forms
their suitability for punching, but thin pieces of any of the
5.1 Laminated thermosetting materials are available in four
grades may be punched in simple shapes, provided good
forms:sheets,tubes(Note3),rods(Note4),andmoldedshapes
punching practice is used, including sharp, close-clearance
(Note 5), as indicated in Table 2. This specification covers the
dies, proper stripper plates, and proper heating conditions.
material in three forms: sheets, tubes of two classes (rolled and
When using good punching practice as outlined below, the
molded),andmoldedrods.Theclassesoftubesdesiredshallbe
various grades shall punch satisfactorily in thickness up to and
specified by the purchaser in the contract or order. In cases
including the maximum limits as prescribed in Table 6. Where
where the purchaser desires a particular class of molded rod he
punching properties better than those listed in Table 6 are
should so specify.
required for particular parts, this shall be subject to agreement
between the purchaser and the manufacturer. In good punching
NOTE 3—Tubes are made of laminations of fibrous sheet impregnated
practice the edges of the piece shall be no closer to the edge of
material, rolled upon mandrels under tension or between heated pressure
rolls, or both.They are of two classes, rolled and molded. Rolled tubes are
thestripthantwicethethicknessofthesheet,theholesshallbe
oven-bakedafterrollingonthemandrels.Moldedtubesarecuredinmolds
no smaller in diameter than the thickness of the sheet nor have
under heat and pressure.
square corners, and the distance between the holes or between
the holes and the edge of the piece shall be no less than the
thickness of the sheet. For thicker materials, depending upon
AvailablefromStandardizationDocumentsOrderDesk,Bldg.4SectionD,700
the grade, heating the material to a temperature of 120 to 140
Robbins Ave., Philadelphia, PA 19111-5094 Attn: NPODS.
°C (approximately 15 min for material ⁄8 in. (3 mm) in
Available fromAmerican National Standards Institute (ANSI), 25 W. 43rd St.,
4th Floor, New York, NY 10036, http://www.ansi.org. thickness) is generally necessary for best punching results,
D709−01 (2007)
TABLE 1 Types and Grades of Laminated Thermosetting Materials
D709
MIL-P and LP Grade
Grade Description
A
Designation
Designation
Type I—Cellulose Paper-Base Phenolic Resin (Unless Noted)
X . mechanical
XP . mechanical; hot-punching stock
XPC . mechanical; cold-punching and cold-shearing stock
XX L-P-513, Type PBG electrical and mechanical
XXP . electrical and mechanical; hot-punching stock
XXX L-P-513, Type PBE electrical and high humidity
XXXP L-P-513, Type PBE-P electrical and high humidity; hot-punching stock
XXXPC L-P-513, Type PBE-P punchable at lower temperature than Grade XXXP
FR-1 . paper-base, flame-resistant, similar to Grade XP
FR-2 . paper-base, flame-resistant, similar to Grade XXXP
FR-3 MIL-P-22324, Type PEE flame-resistant, epoxy resin; electrical and mechanical
ES-1 . mechanical; engraving stock usually melamine binder
ES-2 . mechanical; engraving stock usually melamine binder
ES-3 . mechanical; engraving stock usually melamine binder
Type II—Cellulose Fabric-Base Phenolic Resin
C MIL-P-15035, Type FBM mechanical
CE MIL-P-15035, Type FBG mechanical and electrical
L MIL-P-15035, Type FBI mechanical; fine machining
LE MIL-P-15035, Type FBE mechanical and electrical; fine machining
Type IV—Glass-Base
G-3 . continuous filament-type glass cloth; phenolic resin, general purpose
G-5 . continuous filament-type glass cloth, melamine binder; general purpose;
good arc and flame resistance
G-7 MIL-P-997, Type GSG continuous filament-type glass cloth, silicone resin binder; good mechanical
strength, heat and arc resistance; low dielectric losses and high insulation
resistance under humid conditions
G-9 MIL-P-15037, Type GME continuous filament-glass cloth, melamine binder. Superior to Grade G-5 un-
der wet conditions, good arc and flame resistance
G-10 MIL-P-18177, Type GEE continuous filament-type glass cloth, epoxy resin binder; high mechanical
strength good insulation resistance, dielectric loss, and dielectric strength
under dry and humid conditions
G-11 MIL-P-18177, Type GEB continuous filament-type glass cloth, heat-resistant epoxy binder; properties
similar to Grade G-10 but higher flexural strength retained at elevated tem-
peratures
FR-4 MIL-P-18177, Type GEE continuous filament-glass cloth with a flame-resistant epoxy resin binder;
properties similar to G-10
FR-5 MIL-P-18177, Type GEB continuous filament-glass cloth with a heat- and flame-resistant epoxy resin
binder; properties similar to G11
GPO-1, GPO-2, and GPO-3 Glass mat with polyester resin binder, for general purpose, flame resistance
and tracking resistance
GPO-1P, GPO-2P, and GPO-3P Glass mat with polyester resin binder, for general purpose, flame resistance
and tracking resistance
Type V—Nylon-Base
N-1 MIL-P-15047, Type NPG nylon cloth-base, phenolic resin binder; excellent electrical properties under
high humidity; good impact
Type VI—Composite-Base Laminates
CEM-1 . cellulose paper core, glass surfaces, flame-resistant resin (see X1.28)
CEM-3 . non-woven glass core, glass surfaces, flame-resistant resin (see X1.29)
A
The MIL-P and LP-513 designations apply only to sheet materials. LP-509 applies to sheet and tube material. Revisions of this specification are designated by suffix
letters added to the MIL-P or LP Specification number, A for the first revision, B for the second, etc. Reference should accordingly be made to the latest edition of the
specification.
although in Grade XP or XPC this may make the material too tapping parallel with laminations. Grades XXX, CE, and LE
soft. In this case, better results may be obtained by heating at
are best suited to these operations.
lower temperatures or for a shorter time. If more than 2 min
elapse between the time the strip leaves the heating medium
7. Detail Requirements for Sheets
and the last piece is punched, results will be poor.
7.1 Sheet material shall conform to the requirements for
NOTE 8—The punching properties of the cotton fabric-base grades and
physical and electrical properties prescribed in Tables 7-12.
of the
...







Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.