ASTM C1279-13(2019)
(Test Method)Standard Test Method for Non-Destructive Photoelastic Measurement of Edge and Surface Stresses in Annealed, Heat-Strengthened, and Fully Tempered Flat Glass
Standard Test Method for Non-Destructive Photoelastic Measurement of Edge and Surface Stresses in Annealed, Heat-Strengthened, and Fully Tempered Flat Glass
SIGNIFICANCE AND USE
5.1 The strength and performance of heat-strengthened and fully-tempered glass is greatly affected by the surface and edge stress induced during the heat-treating process.
5.2 The edge and surface stress levels are specified in Specification C1048, in the Engineering Standards Manual3 of GANA Tempering Division and in foreign specifications.
5.3 This test method offers a direct and convenient way to non-destructively determine the residual state of stress on the surface and at the edge of annealed and heat-treated glass.
SCOPE
1.1 This test method covers the determination of edge stresses and surface stresses in annealed, heat-strengthened, and fully tempered flat glass products.
1.2 This test method is non-destructive.
1.3 This test method uses transmitted light and is, therefore, applicable to light-transmitting glasses.
1.4 The test method is not applicable to chemically-tempered glass.
1.5 Using the procedure described, surface stresses can be measured only on the “tin” side of float glass.
1.6 Surface-stress measuring instruments are designed for a specific range of surface index of refraction.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: C1279 − 13 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Non-Destructive Photoelastic Measurement of Edge and
Surface Stresses in Annealed, Heat-Strengthened, and Fully
1
Tempered Flat Glass
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1279; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method covers the determination of edge 2.1 ASTM Standards:
stresses and surface stresses in annealed, heat-strengthened, C158Test Methods for Strength of Glass by Flexure (De-
and fully tempered flat glass products. termination of Modulus of Rupture)
C162Terminology of Glass and Glass Products
1.2 This test method is non-destructive.
C770Test Method for Measurement of Glass Stress—
1.3 This test method uses transmitted light and is, therefore,
Optical Coefficient
applicable to light-transmitting glasses.
C1048Specification for Heat-Strengthened and Fully Tem-
pered Flat Glass
1.4 The test method is not applicable to chemically-
E691Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
tempered glass.
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.5 Using the procedure described, surface stresses can be
2.2 Other Documents:
measured only on the “tin” side of float glass.
3
Engineering Standards Manual
4
1.6 Surface-stress measuring instruments are designed for a
“Surface and Edge Stress in Tempered Glass”
specific range of surface index of refraction.
3. Terminology
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.1 analyzer—a polarizing element, typically positioned
standard.
between the specimen being evaluated and the viewer.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2 polarizer—an optical assembly that transmits light
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
vibrating in a single planar direction, typically positioned
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
between a light source and the specimen being evaluated.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
3.1.3 retardation compensator—an optical device, variants
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
of which are used to quantify the optical retardation produced
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
in transparent birefringent materials: typically positioned be-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
tween the specimen being evaluated and the analyzer.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.2 For definition of terms used in this test method, refer to
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Terminology C162.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C14 on Glass Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
and Glass Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C14.08 on Flat the ASTM website.
3
Glass. Available from GlassAssociation of NorthAmerica (GANA), 800 SWJackson
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2019. Published August 2019 Originally Street, Ste 1500, Topeka, Kansas 66612–1200. http://www.glasswebsite.com
4
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as C1279–13. DOI: Redner, A. S. and Voloshin, A. S., Proceedings of the Ninth International
10.1520/C1279-13R19. Conference on Experimental Mechanics, Denmark, 1990.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1279 − 13 (2019)
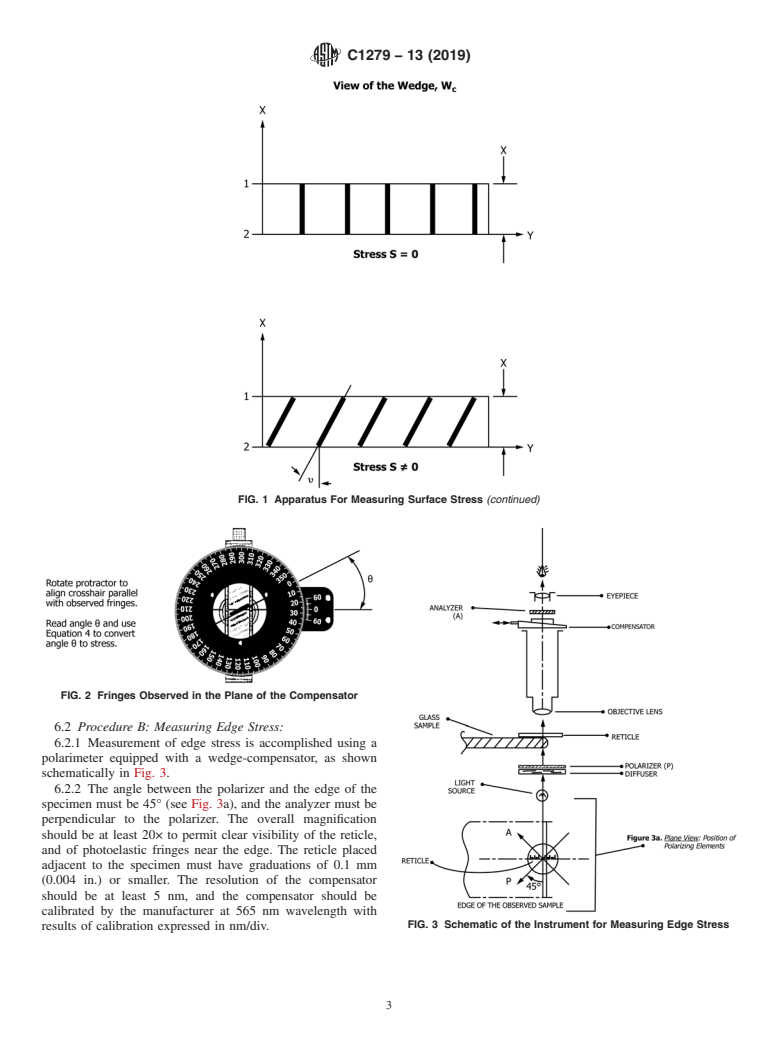
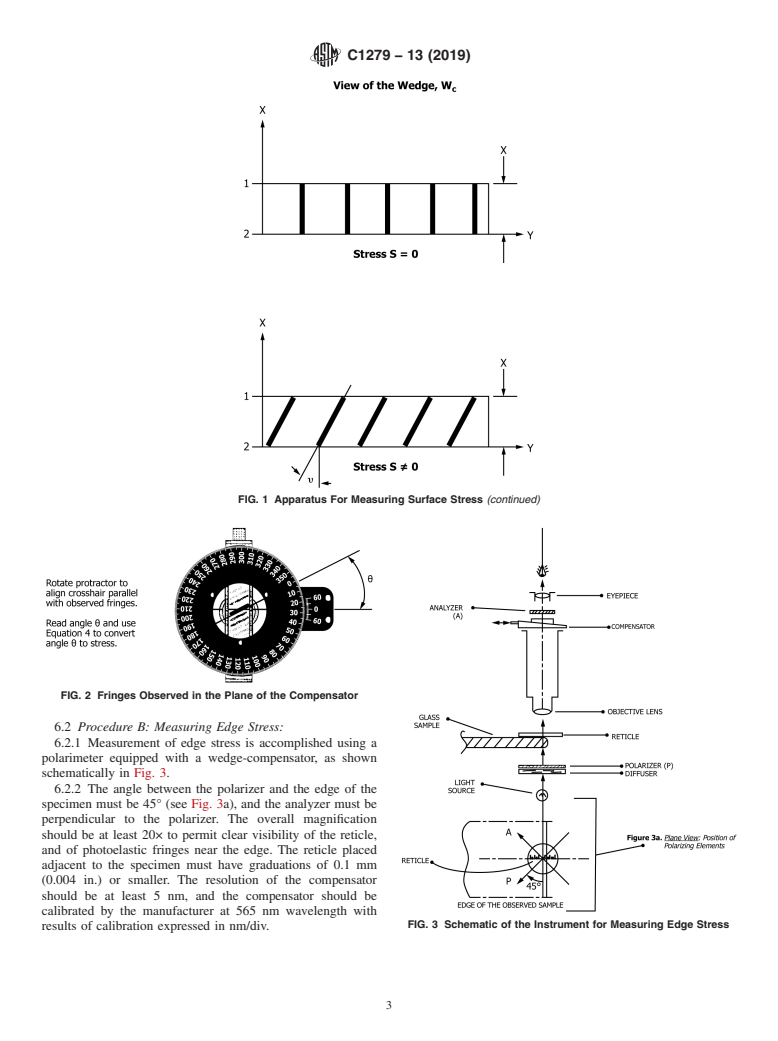
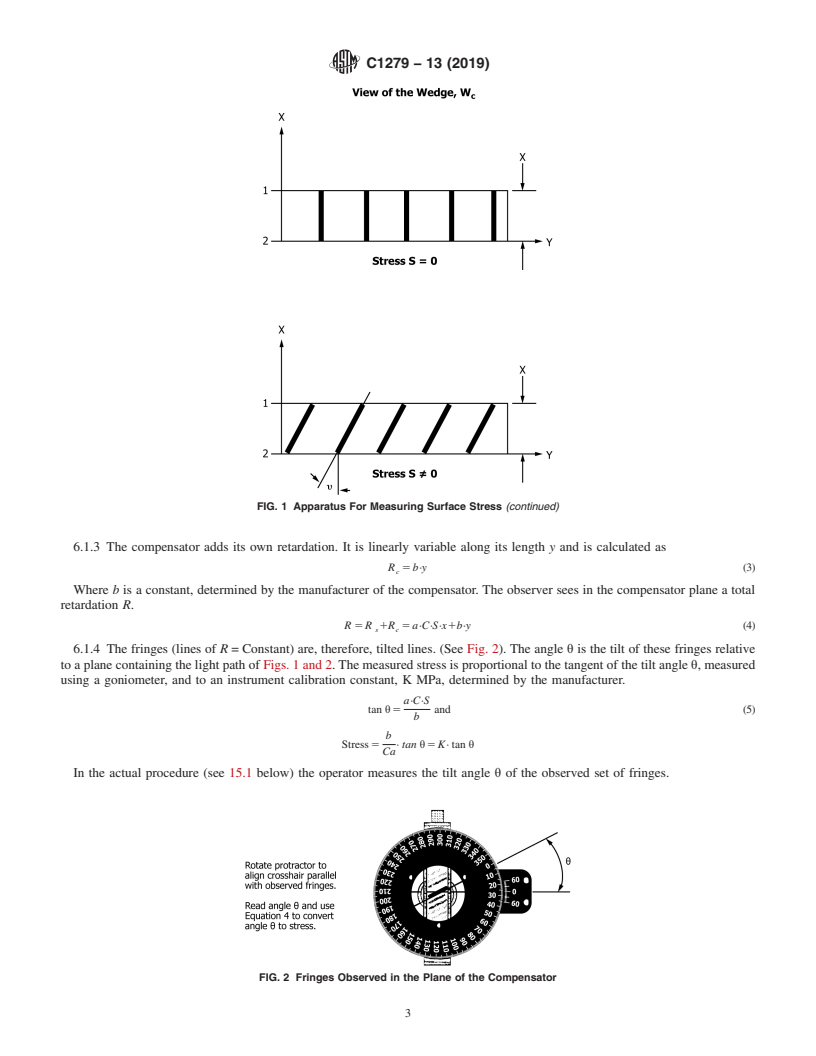
4. Summary of Test Methods compensator, W , generates a visible set of fringes or lines of
c
constant retardation R where
4.1 Two test methods are described in this standard:
4.1.1 Procedure A—describes a test method for measuring R 5 R 1R (1)
s c
surface stress using light propagating nearly parallel to the
Sincethespecimen-inducedretardationisproportionaltothe
surface.
surface stress, S, and the path, t, we have:
4.1.2 Procedure B—describes a test method for measuring
R 5 C·S·t 5 C·S·ax (2)
edge-stressusinglightpropagatinginthedirectionperpendicu-
s
lar to the
...
NOTICE: This standard has either been superseded and replaced by a new version or withdrawn.
Contact ASTM International (www.astm.org) for the latest information
Designation: C1279 − 13 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Non-Destructive Photoelastic Measurement of Edge and
Surface Stresses in Annealed, Heat-Strengthened, and Fully
1
Tempered Flat Glass
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1279; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope 2. Referenced Documents
2
1.1 This test method covers the determination of edge 2.1 ASTM Standards:
stresses and surface stresses in annealed, heat-strengthened, C158 Test Methods for Strength of Glass by Flexure (De-
and fully tempered flat glass products. termination of Modulus of Rupture)
C162 Terminology of Glass and Glass Products
1.2 This test method is non-destructive.
C770 Test Method for Measurement of Glass Stress—
1.3 This test method uses transmitted light and is, therefore,
Optical Coefficient
applicable to light-transmitting glasses.
C1048 Specification for Heat-Strengthened and Fully Tem-
pered Flat Glass
1.4 The test method is not applicable to chemically-
tempered glass. E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to
Determine the Precision of a Test Method
1.5 Using the procedure described, surface stresses can be
2.2 Other Documents:
measured only on the “tin” side of float glass.
3
Engineering Standards Manual
4
1.6 Surface-stress measuring instruments are designed for a
“Surface and Edge Stress in Tempered Glass”
specific range of surface index of refraction.
3. Terminology
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as
3.1 Definitions:
standard. No other units of measurement are included in this
3.1.1 analyzer—a polarizing element, typically positioned
standard.
between the specimen being evaluated and the viewer.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the
3.1.2 polarizer—an optical assembly that transmits light
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
vibrating in a single planar direction, typically positioned
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
between a light source and the specimen being evaluated.
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter-
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. 3.1.3 retardation compensator—an optical device, variants
1.9 This international standard was developed in accor-
of which are used to quantify the optical retardation produced
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard- in transparent birefringent materials: typically positioned be-
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the tween the specimen being evaluated and the analyzer.
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
3.2 For definition of terms used in this test method, refer to
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
Terminology C162.
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C14 on Glass Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
and Glass Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C14.08 on Flat the ASTM website.
3
Glass. Available from Glass Association of North America (GANA), 800 SW Jackson
Current edition approved Aug. 1, 2019. Published August 2019 Originally Street, Ste 1500, Topeka, Kansas 66612–1200. http://www.glasswebsite.com
4
approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 2013 as C1279 – 13. DOI: Redner, A. S. and Voloshin, A. S., Proceedings of the Ninth International
10.1520/C1279-13R19. Conference on Experimental Mechanics, Denmark, 1990.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1279 − 13 (2019)
4. Summary of Test Methods compensator, W , generates a visible set of fringes or lines of
c
constant retardation R where
4.1 Two test methods are described in this standard:
R 5 R 1R (1)
4.1.1 Procedure A—describes a test method for measuring
s c
surface stress using light propagating nearly parallel to the
Since the specimen-induced retardation is proportional to the
surface.
surface stress, S, and the path, t, we have:
4.1.2 Procedure B—describes a test method for measuring
R 5 C·S·t 5 C·S·ax (2)
edge-stress using light propagating in the direction perpendicu-
s
lar to the surface.
where:
4.2 In both methods, the fundamental photoelastic concept
R = is the relative retardation,
is used. As a re
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: C1279 − 13 C1279 − 13 (Reapproved 2019)
Standard Test Method for
Non-Destructive Photoelastic Measurement of Edge and
Surface Stresses in Annealed, Heat-Strengthened, and Fully
1
Tempered Flat Glass
This standard is issued under the fixed designation C1279; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope
1.1 This test method covers the determination of edge stresses and surface stresses in annealed, heat-strengthened, and fully
tempered flat glass products.
1.2 This test method is non-destructive.
1.3 This test method uses transmitted light and is, therefore, applicable to light-transmitting glasses.
1.4 The test method is not applicable to chemically-tempered glass.
1.5 Using the procedure described, surface stresses can be measured only on the “tin” side of float glass.
1.6 Surface-stress measuring instruments are designed for a specific range of surface index of refraction.
1.7 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as standard. No other units of measurement are included in this standard.
1.8 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety safety, health, and healthenvironmental practices and determine the
applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
1.9 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
C158 Test Methods for Strength of Glass by Flexure (Determination of Modulus of Rupture)
C162 Terminology of Glass and Glass Products
C770 Test Method for Measurement of Glass Stress—Optical Coefficient
C1048 Specification for Heat-Strengthened and Fully Tempered Flat Glass
E691 Practice for Conducting an Interlaboratory Study to Determine the Precision of a Test Method
2.2 Other Documents:
3
Engineering Standards Manual
4
“Surface and Edge Stress in Tempered Glass”
3. Terminology
3.1 Definitions:
3.1.1 analyzer—a polarizing element, typically positioned between the specimen being evaluated and the viewer.
3.1.2 polarizer—an optical assembly that transmits light vibrating in a single planar direction, typically positioned between a
light source and the specimen being evaluated.
1
This test method is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee C14 on Glass and Glass Products and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee C14.08 on Flat Glass.
Current edition approved Oct. 1, 2013Aug. 1, 2019. Published October 2013August 2019 Originally approved in 1994. Last previous edition approved in 20092013 as
C1279C1279 – 13.-09. DOI: 10.1520/C1279-13.10.1520/C1279-13R19.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
3
Available from Glass Association of North America (GANA), 800 SW Jackson Street, Ste 1500, Topeka, Kansas 66612–1200. http://www.glasswebsite.com
4
Redner, A. S. and Voloshin, A. S., Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Experimental Mechanics, Denmark, 1990.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
C1279 − 13 (2019)
3.1.3 retardation compensator—an optical device, variants of which are used to quantify the optical retardation produced in
transparent birefringent materials: typically positioned between the specimen being evaluated and the analyzer.
3.2 For definition of terms used in this test method, refer to Terminology C162.
4. Summary of Test Methods
4.1 Two test methods are described in this standard:
4.1.1 Procedure A—describes a test method for measuring surface stress using light propagating nearly parallel to the surface.
4.1.2 Procedure B—describes a test method for measuring edge-stress using light propagating in the direction perpendicular to
the surface.
4.2 In both methods, the fun
...









Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.